Treatment Modes And Modalities
Treatment modes and modalities are technologies or other support systems that the SLP can use in conjunction with, or during implementation of, various treatments. For example, the SLP can use video-based instruction in peer-mediated interventions to address social skills and other target behaviors.
A number of treatment modes and modalities are described below. When selecting a mode or modality, the SLP considers the intervention goal and the individual’s developmental stage. For example, a mode or modality that is appropriate for an individual who is at the emerging language stage may not be appropriate for an individual who is at the prelinguistic stage. The list below is not exhaustive, and inclusion does not imply an endorsement from ASHA.
An AAC system is an integrated group of componentsâincluding symbols, selection techniques, and strategiesâused to enhance communication. AAC uses a variety of techniques and toolsâincluding picture communication systems, line drawings, photographs, video clips, speech-generating devices , tangible objects, manual signs, gestures, and finger spellingâto help the individual express thoughts, ideas, wants, needs, and feelings. AAC can be used to supplement existing expressive verbal communication or with individuals who are unsuccessful at learning expressive verbal communication.
Activity Schedule and Visual Supports
Computer-Based Instruction
Video-Based Instruction
Early Signs And Symptoms
Diagnostic features of ASD are present in very young children. Most families and caregivers report observing symptoms within the first 2 years of life and typically express concern by the time the child reaches 18 months of age.
Studies of children with ASD found the following:
- Parents of children with ASD reported first noticing abnormalities in their children’s developmentâparticularly in language development and social relatednessâat about 14 months of age on average .
- Infants at risk forâand later diagnosed withâASD showed a decline in eye fixation within the first 2â6 months of age. This pattern was not observed in typically developing infants .
- Children with autism used fewer joint attention gestures and behaviors as infants and toddlers than did age-matched peers who were typically developing .
- Children with autism showed subtle differences in sensoryâmotor and social behavior at 9 to 12 months of age when compared with typically developing peers .
- Children with autism showed lower rates of canonical babbling and fewer speech-like vocalizations across the 6- to 24-month age range than did typically developing peers .
- Infants at risk forâand later diagnosed withâASD used significantly more distress vocalizations than did children who were typically developing and children who were developmentally delayed this may reflect the difficulties that children with ASD have with emotional regulation .
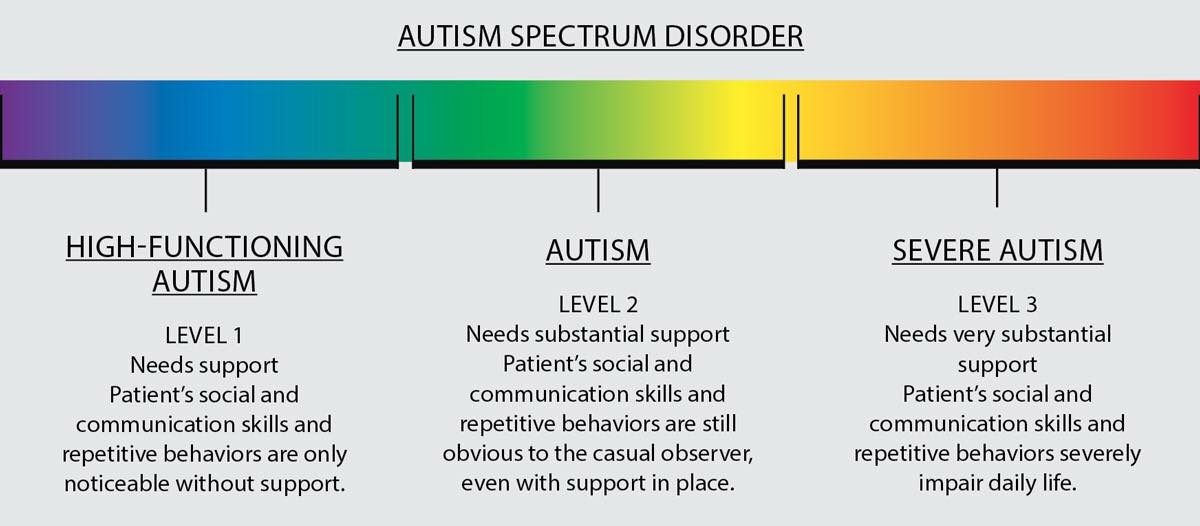
Autism Spectrum Disorder Level : Requiring Support
According to the DSM-5, individuals on level 1 autism require support. They can live by themselves and maintain a high quality of life with little support. Usually, this support is taken in the form of behavioral therapy or other types of therapy, depends on the individuals need. Both of these approaches can help improve social skills and communication skills. Also, behavioral therapy can help develop positive behaviors of individuals that might not come naturally.
Theory of Mind is one of the most effective ways in order to treat level 1 autism. Both ToM and adaptive skill-based treatments target executive function, emotional regulation, cognitive flexibility, social communication skills and reduction in anxiety. These aspects are very important in the field of level 1 treatment.
Individuals with level 1 autism have noticeable impairments, communication problems and problems in socializing. They can have a conversation, however, it might be difficult to maintain a back-and-forth conversation. Some of them at this level might find it hard to reach out and make new friends.
At this level, individuals may show decreased interest in social interactions or activities. They might have difficulties initiating social interactions and communications, such as talking to a person. They are able to engage with a person but they may struggle to maintain a give-and-take of a typical conversation. Some of them who attempt to make friends are seen as odd and typically unsuccessful.
Don’t Miss: The Good Doctor Autism Consultant
How Has Diagnosis Of Autism Changed
Over the years, there have been various diagnosis for autism, now known as autism spectrum disorder.
Although it has no legal status, the DSM by the American Psychiatric Association that defines psychiatric and developmental disorders has a great impact on the diagnosis of autism.
Through guidance of DSM the clinicians, schools, and related service providers understand how to think about and treat autism.
The DSM described the autism spectrum as a disorder that included five distinct diagnoses. Back then people with high functioning autism were considered to have Aspergers syndrome. In the same diagnosis, autistic disorder meant almost the same thing as severe autism.
The previous version of the DSM also described people with not all of the symptoms of autism as Pervasive Developmental Disorder – Not Otherwise Specified . In addition, Rett Syndrome and Fragile X Syndrome were also considered to be part of the ASD.
In 2013, the new manual DSM-5 was published. Unlike the previous edition, DSM-5 defines autism as a single spectrum disorder. These disorders have a set of criteria indicating the symptoms in the areas of behavior, social communication, flexibility, and sensor sensitivity.
How Are Asd Levels Determined
While its difficult to determine a persons ASD level, trained psychologists have some tools that can help them accomplish this, such as the Autism Diagnostic Observation Schedule, Second Edition . This assessment is typically paired with a thorough developmental history.
ASD can be diagnosed as early as 18 months . However, many children, and even some adults, may not be diagnosed until much later.
Being diagnosed at a later age can make treatment more difficult. If you or your childs pediatrician think they may be autistic, consider making an appointment with an ASD specialist. Learn more about testing for ASD.
Also Check: Can Autism Be Passed Down
An Insight Into The Various Types Of Autism
Let us now get a deeper insight into each of the following forms of Autism.
Fig 3:
As mentioned at the beginning of this article, the various types of autism spectrum disorders present a significant overlap with one another. The following 3 characteristics are carefully evaluated to arrive at the right conclusion:
- Social skills within families coping with Autism and externally
- Autism Communication Skills
For example, it is extremely hard to discriminate between mild PDD and moderate Aspergers symptoms as a patient may demonstrate both characteristics in the autism spectrum quotient.
What Disorders Are Related To Asd
Certain known genetic disorders are associated with an increased risk for autism, including Fragile X syndrome and tuberous sclerosis each of which results from a mutation in a single, but different, gene. Recently, researchers have discovered other genetic mutations in children diagnosed with autism, including some that have not yet been designated as named syndromes. While each of these disorders is rare, in aggregate, they may account for 20 percent or more of all autism cases.
People with ASD also have a higher than average risk of having epilepsy. Children whose language skills regress early in life before age 3 appear to have a risk of developing epilepsy or seizure-like brain activity. About 20 to 30 percent of children with ASD develop epilepsy by the time they reach adulthood. Additionally, people with both ASD and intellectual disability have the greatest risk of developing seizure disorder.
Read Also: Is Level 2 Autism High Functioning
Asd Level : Requiring Substantial Support
Social communication and repetitive behaviors present themselves more obviously in children with ASD level 2 than in children with level 1 autism. Children on this level have challenges in verbal and nonverbal communication, as well as reduced or abnormal responses to social cues.
Inflexibility of behavior is also more pronounced than in ASD level 1. Repetitive behaviors appear more frequently and may be obvious to casual observes. Likewise, children with level 2 autism may have difficulty coping with changes in routine, which can cause challenging behavior.
Terms For Types Of Autism That Are No Longer Used Today
When autism was categorized by types, the lines between the different types of autism could be blurry. Diagnosis was, and still is, complicated and often stressful for families.
If you or your child received a diagnosis before the DSM-5 changed, you may still be using the older terminology . Thats OK. Your doctor may continue to use those terms if they help.
You May Like: How To Tell If My Baby Is Autistic
Recommended Reading: Chromosome 9 Autism
Challenges In Severe Autism
According to some researchers, the extreme behaviors seen in severe autism are very often the result of either frustration, sensory overload, or physical pain. Because people with severe autism have such a hard time communicating their needs verbally, they may find expression in behaviors that can be frightening to their caregivers and others.
If the behaviors can’t be addressed or managed, they can actually be dangerous in many cases, it becomes impossible for parents or siblings to live safely with a severely autistic teen or adult.
Asd Level : Requiring Very Substantial Support
ASD level 3 is characterized by severe challenges in social communication as well as extremely inflexible behavior. Children with level 3 autism will be nonverbal or have the use of only a few words of intelligible speech. Initiation of social interaction is very limited, as well as response to others. An individual at this level may interact with others abnormally, and only to meet immediate needs.
Individuals with level 3 autism exhibit marked inflexibility of behavior, with extreme difficulty coping with changes to routine. At this level, restrictive or repetitive behaviors interfere with the individuals ability to function. Changing focus from one activity to another may come at great difficulty and cause significant distress.
Also Check: Is Dr Shaun Murphy Really Autistic
What Are The Three Levels Of Autism
Levels of autism spectrum disorder are defined in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th Edition . The 5th edition criteria for autism diagnosis provides three clear levels based on the patients requirements for support. These levels of autism allow specialists to make more refined diagnoses, allowing for more effective treatment plans and helping caretakers better understand individuals symptoms and needs.
Where Can I Get More Information
For more information on neurological disorders or research programs funded by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, contact the Institute’s Brain Resources and Information Network at:
Office of Communications and Public LiaisonNational Institute of Neurological Disorders and StrokeNational Institutes of HealthBethesda, MD 20892
NINDS health-related material is provided for information purposes only and does not necessarily represent endorsement by or an official position of the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke or any other Federal agency. Advice on the treatment or care of an individual patient should be obtained through consultation with a physician who has examined that patient or is familiar with that patient’s medical history.
All NINDS-prepared information is in the public domain and may be freely copied. Credit to the NINDS or the NIH is appreciated.
Recommended Reading: Is James Holzhauer Autistic
Level : Require Substantial Support
- A deficit with verbal/nonverbal communication skills.
- Limited or no social interaction and no respond to people trying to interact with them
- Interaction is possible up to a limit with non-verbal communication
- Nervousness and shyness when watched by unfamiliar faces
- reduced ability to function and participate in their daily activities
- Repetitive behaviour is obvious
Communication & Language For Moderate To Severe Autism
Communication and language capabilities are generally limited in children with moderate autism. They may acquire language skills later than normal and speak below their age level. In some cases, children with moderate autism are nonverbal and unable to speak words.
Depending on intellectual abilities, children with moderate autism may learn to communicate through pictures, typing, or via other communication devices.
Many children with severe autism have very limited communication and language abilities. If they can speak, they repeat words and phrases they hear others say or say only a few words that do not fit the context.
Despite serious limitations, though, children with severe autism can communicate through sounds, groans, and behaviors. Parents use observation, interaction, and speech therapy to understand their child and discover ways to improve communication and language.
Children with moderate autism may or may not interact with peers. They generally struggle to make eye contact, interpret body language and emotions, and understand figures of speech, and they may simply walk away from conversations that dont involve their favorite topics or interests.
However, children with moderate autism can play near or with peers unless their repetitive behaviors like arm flapping or rocking, limited speech capabilities, and aggression scare peers who dont understand the disorder.
Recommended Reading: Is The Good Doctor Actor Autistic
The Levels Of Autism: Unique Treatment Approaches For Each
Autism is a disorder where people suffer from a range of social, communication, and behavioral problems. The disabilities occur on a spectrum, which is why autism is also known as autism spectrum disorder.
There are three general levels of autism, ranging from mild impairments that require minimal therapy and intervention, to severe impairments that need intensive, multidisciplinary guidance.
Regardless of the level, autism is a lifelong condition. Even those with only a mild form of the disability will require some degree of ongoing therapy and monitoring for many years.
What Are The Signs And Characteristics Of Autism
The developmental differences, signs and characteristics of autism can vary widely in nature and severity from person to person, and can also develop, change and improve over time.
Age, gender and cognitive ability can also have an impact on how the signs or characteristics of autism present themselves in different people, which is something that should also be considered.
While much of the diagnostic process is related to behavioural attributes, it can be difficult to diagnose autism until they are between 18-20 months. For some, the signs of autism may not become apparent until school years, or adult years when demands exceeds capacity.
Nevertheless, if you feel as though you, your child, or someone you love is on the autism spectrum, you may want to start the diagnostic process.
When I met people with autism, I realised how much I related to them, it made me realise that this is what it is like for everyone else all the time.
Dr Damian Milton, National Autistic Society, UK
As autism is a varied spectrum of characteristics it can be difficult to identify if a person is autistic. To help you better understand the signs and characteristics here is a summary of what to look out for, according to the latest diagnostic guidelines, the DSM-5.
Recommended Reading: The Good Doctor Autism Representation
What Conditions Are Considered Spectrum Disorders
Until recently, experts talked about different types of autism, such as autistic disorder, Aspergerâs syndrome, pervasive developmental disorder not otherwise specified . But now they are all called âautism spectrum disorders.â
If you still hear people use some of the older terms, youâll want to know what they mean:
Asperger’s syndrome. This is on the milder end of the autism spectrum. A person with Asperger’s may be very intelligent and able to handle their daily life. They may be really focused on topics that interest them and discuss them nonstop. But they have a much harder time socially.
Pervasive developmental disorder, not otherwise specified . This mouthful of a diagnosis included most children whose autism was more severe than Asperger’s syndrome, but not as severe as autistic disorder.
Autistic disorder. This older term is further along the autism spectrum than Aspergerâs and PDD-NOS. It includes the same types of symptoms, but at a more intense level.
Childhood disintegrative disorder. This was the rarest and most severe part of the spectrum. It described children who develop normally and then quickly lose many social, language, and mental skills, usually between ages 2 and 4. Often, these children also developed a seizure disorder.
Autism Spectrum Disorder 29900
A. Persistent deficits in social communication and social interaction across multiple contexts, as manifested by the following, currently or by history :
Read Also: Prognosis Mild Autism
What Are The 3 Levels Of Autism
Pipkin said the most recent edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders has provided three levels of severity in order to better individualize autism diagnoses and communicate a persons need for support.
She provided helpful markers in better understanding the levels of autism:
At Level One, an individual is expected to need some degree of support based on their degree of impairment related to social communication and restricted or repetitive behaviors, Pipkin said. They may be someone who, with the appropriate supports, can function fairly well in most settings. However, upon closer inspection they may be seen to struggle in the back-and-forth aspects of conversation or lack close friends due to their lack of interest or inability to initiate friendships.
At Level Two, an individual is likely to require substantial support based on their social communication abilities and their restricted or repetitive behaviors, Pipkin explained.
Related: Parents and loved ones of children with autism tell what they wish theyd known earlier.