Conflict Of Interest Statement
The author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
Pexman, P. M., Zdrazilova, L., McConnachie, D., Deater-Deckard, K., and Petrill, S. A. 2009. That was smooth, mom: childrens production of verbal and gestural irony. Metaphor Symbol 24:23748. doi: 10.1080/10926480903310286
Harris, M., and Pexman, P. M. 2003. Childrens perceptions of the social functions of verbal irony. Discourse Process. 36:14765. doi: 10.1207/S15326950DP3603_1
Climie, E. A., and Pexman, P. M. 2008. Eye gaze provides a window on childrens understanding of verbal irony. J. Cogn. Dev. 9:25785. doi: 10.1080/15248370802247939
Nicholson, A., Whalen, J. M., and Pexman, P. M. 2013. Childrens processing of emotion in ironic language. Front. Dev. Psychol. 4:691. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2013.00691
Pexman, P. M., Rostad, K. R., McMorris, C. A., Climie, E. A., Stowkowy, J., and Glenwright, M. R. 2011. Processing of ironic language in children with High Functioning Autism Spectrum Disorder. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 41:1097112. doi: 10.1007/s10803-010-1131-7
Shamay-Tsoory, S. G., Tomer, R., Berger, B. D., Goldsher, D., and Aharon-Peretz, J. 2005. Impaired affective theory of mind is associated with right ventromedial prefrontal damage. Cogn. Behav. Neurol. 18:5567. doi: 10.1097/01.wnn.0000152228.90129.99
What Can Autistic Teens Do
Helping Activities for Autistic Teenager in HomeHelping Activities for Autistic Teenager in Home. Have Your Teen Read Simple, but Interesting Books. Encourage Your Teen to Listen to Music or Take Part in Music Therapy. Give Your Teen Puzzles to Do in Their Free Time. Encourage Your Teen to Draw.May 15, 2019
Brains Of People With Autism Show Altered Growth With Age
Suzanne Tucker /Shutterstock.comRevealing scans: People with autism miss out on the steady increase in whole brain volume that typically occurs throughout childhood.
Several brain regions in people with autism become enlarged earlier than usual during childhood and shrink too soon during adulthood, finds a study published 7 November in Autism Research1.
The study used magnetic resonance imaging to track brain volume in 100 males with autism and 56 controls, all ranging in age from 3 to 35 years, over an eight-year span.
Total brain volume in boys with autism tends to be larger than that of controls before age 10. This difference fades between ages 10 and 15, as brain volume in controls increases. After this period, controls continue to show gains in brain volume until their mid-20s, whereas the brains of people with autism begin shrinking.
People with autism miss the increase in brain volume in those younger years, says lead investigator Nicholas Lange, associate professor of psychiatry at Harvard Universitys McLean Hospital. That coincides with the transition into adulthood, which is particularly challenging for some people with the disorder. They are faced with new demands, and they have less brain resources to deal with that, Lange says.
Also Check: Autistic Puzzle Piece Symbol
The Brain Of An Autistic Person Simply Works Differently
Autistic people can find communicating and engaging with others hard. But a typical autistic person does not exist, and autistic traits may be in all of us.
Pi: Some autistic people can memorize numbers very well
A whole range of different conditions belong to the autism spectrum disorder or autism, a life-long neurodevelopmental disorder that affects how people communicate and interact with the world.
One in 160 children has autism but several recent studies have reported rates that are substantially higher, according to the World Health Organization .
ASD is considered a developmental disorder because although it can be diagnosed later in life it begins in early childhood and tends to persist into adolescence and adulthood.
The level of intellectual functioning in autistic people varies hugely, ranging from profound impairment to superior non-verbal cognitive skills. It is estimated that around 50% of people with autism also suffer from an intellectual disability, according to the WHO.
There is a wide range of symptoms in autistic people. Some of the main symptoms include communication problems like delayed speech development, and difficulty in social interactions, such as making friends, maintaining eye contact, reading people’s body language or facial expressions, and expressing how they feel. Repetitive behaviors and strict routines may also be noticed, like repetitive body movements or finding it difficult to adjust even to small changes.
Changes In Autism Severity Over Time
The white matter research builds on a previous MIND Institute study, which found that while many children experience fairly stable levels of autism symptoms throughout childhood, a significant portion can be expected to increase or decrease in their symptom severity over time.
This new analysis provides an important clue about the brain mechanism that may be involved in some of these changes, said Amaral.
Read Also: High Performance Autism
The Potential For Treatment Not Management
In this article we will explain why we believe that discoveries made using molecular neuroimaging offer the promise of a new approach to treating autism during critical periods of brain development. In the past two decades, scientists have made substantial advances in understanding autism and how it affects brain development and behavior. Research in genetics, functional neuroimaging, and cognitive neuroscience has rovided helpful knowledge about potential causes of autism, as well as the range of behavioral effects. Although these studies -have been invaluable in understanding more about the disorder, it is research at a more basic level that may provide the start for a new and unique method of treatment.
Recent research using molecular neuroimaging has provided critical information about how the processes in the developing brain of an autistic child differ from those in the brain of a child without the disorder.
One of the biggest problems in succinctly dening autismand consequently in recommending treatmentis that the disorder exhibits such a broad array of characteristics.
Careful study of the details of these differences in brain development may provide a basis for designing new drug treatments for autism, treatments that would not manage behavior, as is the case now, but rather would work directly to bring the brain development of the autistic child closer to the normal range.
Bringing The Brain Of The Child With Autism Back On Track
What if we could identify some common process that goes awry in the developing brain of a child and leads to errors in wiring that cause the devastating symptoms of autism? What if, understanding that malfunction, we could intervene with drugs and behavioral therapies that dont just mask symptoms but actually bring the childs brain development back on course? Wayne State University professor of pediatrics and radiology Diane C. Chugani, Ph.D., describes new insights achieved through molecular neuroimaging that mayrepeat, maychange how we understand and treat autism.
Many parents of autistic children speak about their child in terms of before and after. They reminisce about their childs babyhood, full of play, smiles, and the early developmental milestones so easily reached. But then, they say, seemingly overnight, things dramatically changed.
The lively sounds that so closely resembled speech never quite evolved into actual words instead they regressed into grunts and nonsense noises. The child who was once content to be held in Mamas arms now recoiled from her touch, and any small change in routine could result in inconsolable screams. Many say that it was almost as if their child had suddenly and mysteriously changed into an entirely different person.
Don’t Miss: Aspergers Hereditary From Mother Or Father
How Does Autism Affect The Brain
- Open annotations. The current annotation count on this page is being calculated.
Image credit: CC0
Autism is a brain disorder that affects how people interact with others. It occupies a spectrum, with severe autism at one end and high-functioning autism at the other. People with severe autism usually have intellectual impairments and little spoken language. Those with high-functioning autism have average or above average IQ, but struggle with more subtle aspects of communication, such as body language. As well as social difficulties, many individuals with autism show repetitive behaviors and have narrow interests.
The brains of people with autism process information differently to those of people without autism. The brain as a whole shows less coordinated activity in autism, for example. But whether individual brain regions themselves also work differently in autism is unclear. Watanabe et al. set out to answer this question by using a brain scanner to compare the resting brain activity of high-functioning people with autism to that of people without autism.
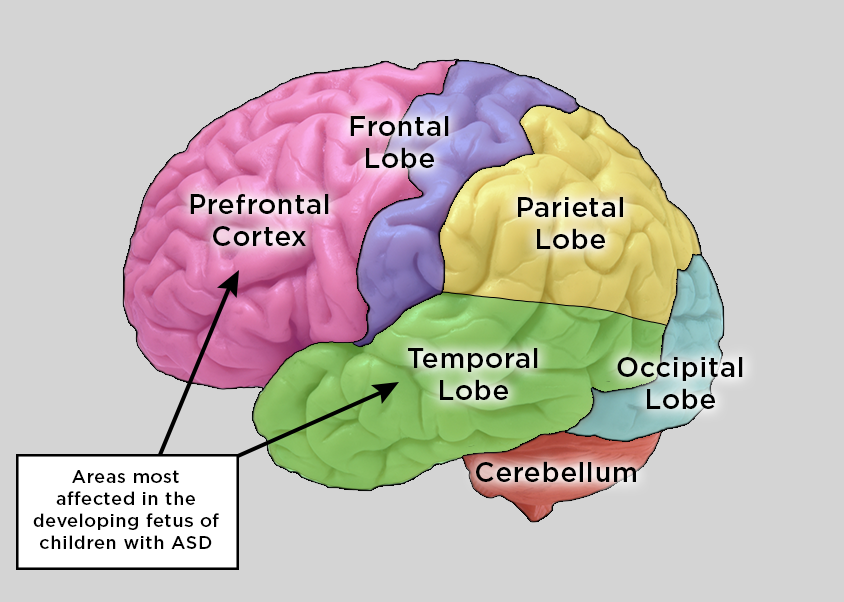
Autism & The Lobes Of The Brain
Additionally, within each hemisphere of the brain, there are four lobes: the frontal, parietal, occipital, and temporal lobes. Within these lobes are structures that control everything the body does, from movement to thinking. On top of the lobes is the cerebral cortex, where information processing takes place.
The greater the surface area of the cerebral cortex, the more information the brain is capable of processing. The brain has folds, to add to the surface area of the cerebral cortex. Researchers at San Diego State University have found evidence that suggests that the folds develop differently in people with autism. In autistic brains, there is much more folding in some of both the left and right lobes.
The changes have been connected to modifications in network connectivity in neurons. The weaker a connection, the deeper the folds are. Other research has indicated that language production and processing are altered.
Yet, says PsyCom, the neurobiology of an autistic brain is still hidden. Some experts have said that the more they study brains affected by autism, the more they realize that it may not be so much about the hardware as the software. It may be that the timing of the brain activity is different, affecting how the signals from one region of the brain being sent to another get distorted. It might be that as the autistic brain ages, the aging process brings about more changes that impact the development of autistic symptoms.
Don’t Miss: Do Autistic Toddlers Dance
Functional And Physiological Differences In The Brain Of A Child With Autism
Have you ever felt perplexed by your childs overly intense reactions to things that your other son or daughter hardly notices? Or maybe you find your child has virtually no reaction to things that would stir excitement and curiosity in another child?
As extremely different as these responses are, they are equally startling to a new parent.
While there is still much we dont know about the brain, recent research suggests that very specific functional and physiological differences in the brain of children with autism may be able to account for behaviors that were previously shrouded in mystery.
There is something about understanding the background of problem behaviors that can sometimes help alleviate some of the frustration. Even though you might not be able to immediately change the situation, there can be solace in understanding, especially when you know the issue is rooted more in physiology and mechanics than psychology.
What might it sound like if someone with autism could articulate what is happening inside their brain?
A Whole New Perspective
These findings, which were consistent with data from the ABIDE study, may explain why people with autism can experience distress when exposed to numerous stimuli at once, the research team believes.
Individuals with autism who have greater social dysfunction have an increase in synched activity in their scans, notes postdoctoral researcher Jace King, first author of the study paper.
Now that we are looking at finer timescales, weve found a consistent story. It provides us with new tools to figure out the mechanisms that may underlie autism, King adds.
Nevertheless, the researchers note that their study faced one fundamental limitation namely that it worked with male participants only, which may not offer the full picture of what characterizes autism in the brain. Still, they will not stop at this study and hope to expand this research.
We want to compare the results from this analysis to more traditional methods. This is a whole new perspective into how autism works in the brain and can help us develop strategies for treatment and finding medications that might be more effective to ease the symptoms of the disorder.
Dr. Jeff Anderson
You May Like: What Is The Life Expectancy Of People With Autism
Is Autism Inherited From The Mother Or Father
Clues to the first two questions come from studies that have shown that at least 30% of individuals with autism have spontaneous de novo mutations that occurred in the fathers sperm or mothers egg and disrupt genes important for brain development, these spontaneous mutations likely cause autism in families where
Understanding The Complicated Effects Of Autism
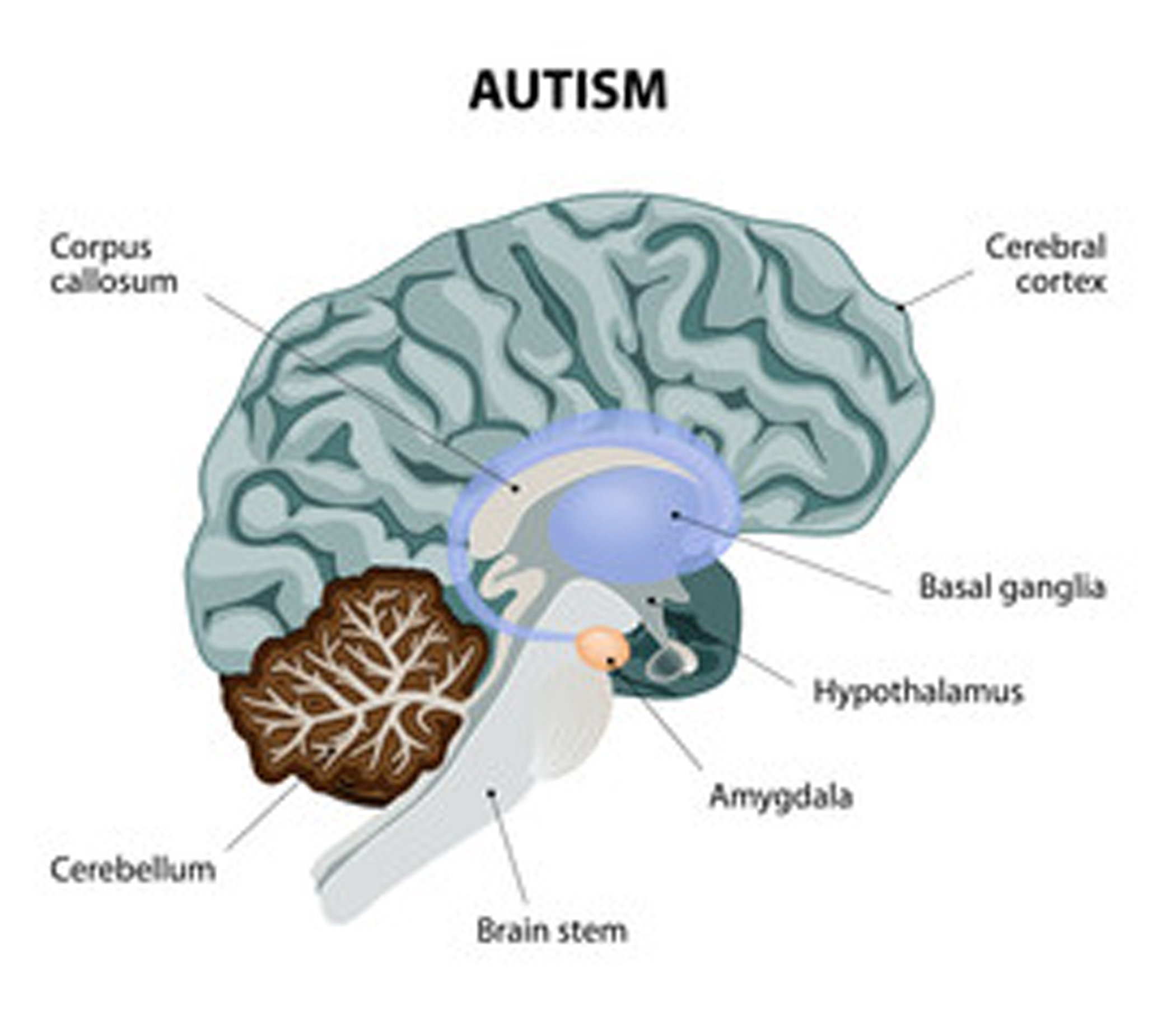
Other research has also supported the theory that abnormalities of the cerebellum are associated with autism. A study published in Frontiers in Systems Neuroscience posited that impaired circuitry activity in the cerebellum could partially underlie symptoms of autism, including but not limited to restricted motor functioning and cognitive deficits, specifically with regard to attention span, language development, and executive functioning.
If much remains unknown about autisms effects on the brain and if what is known appears patchy or even contradictory, it is because autism spectrum disorder is complicated, says PsyCom. Even as experts answer some questions about what autism does to the brain, there are further questions raised about other effects, how these effects lead to the development of autism symptoms, and even broader questions about the full scope of the functioning of the human brain itself.
As more and more research is dedicated to the subject, well continue to uncover more about autisms effects on the brain.
Also Check: Is The Good Doctor Autistic
What Is Wrong With An Autistic Brain
Others have found that autistic children have enlarged amygdalae early in development and that the difference levels off over time2,4. Autistic people have decreased amounts of brain tissue in parts of the cerebellum, the brain structure at the base of the skull, according to a meta-analysis of 17 imaging studies5.
References And Further Reading:
Read Also: Can A Child With Autism Have Dyslexia
Brain Study Finds Evidence That Autism Involves Too Many Synapses
Researchers propose that someday it may be possible treat autism with drugs that restore normal pruning of brain-cell connections
A newly published brain-tissue study suggests that children affected by autism have a surplus of synapses, or connections between brain cells. The excess is due to a slowdown in the normal pruning process that occurs during brain development, the researchers say.
The study team also found that the medication rapamycin both restores normal synaptic pruning and reduces autism-like behaviors in a mouse model of autism. They propose that someday a similar medication might be used to treat autism after a child or even adult has been diagnosed.
The report, by neuroscientists at Columbia University Medical Center, appears in the journal Neuron.
Autism Speaks is currently funding several studies on rapamycin. It is also supporting a treatment study using a medication with a very similar action for treatment of autism associated with tuberous sclerosis complex . This rare syndrome often, but not always, involves autism. Indeed, the laboratory mice used in the new Columbia study were developed as an animal model of this syndrome.
The insights from the new study also underscore the vital importance of post-mortem brain donations in advancing research on autism treatments, Dr. Wang adds.
Autism Speaks actively supports autism brain banking through Autism BrainNet.
What Role Do Genes Play
Twin and family studies strongly suggest that some people have a genetic predisposition to autism. Identical twin studies show that if one twin is affected, then the other will be affected between 36 to 95 percent of the time. There are a number of studies in progress to determine the specific genetic factors associated with the development of ASD. In families with one child with ASD, the risk of having a second child with the disorder also increases. Many of the genes found to be associated with autism are involved in the function of the chemical connections between brain neurons . Researchers are looking for clues about which genes contribute to increased susceptibility. In some cases, parents and other relatives of a child with ASD show mild impairments in social communication skills or engage in repetitive behaviors. Evidence also suggests that emotional disorders such as bipolar disorder and schizophrenia occur more frequently than average in the families of people with ASD.
Also Check: Freddie Highmore Disability
Brain Anatomy Of Individuals With Autism Spectrum Disorder
Everyones brain is structured slightly differently based upon genetic composition and changes that occur in the life experiences of the individual.
However, in general, there are some overall similarities in the human brain such as certain parts of the brain being for specific purposes or where particular regions of the brain are located.
Summary And Proposed Pathogenic Mechanism
ASD symptomatology comprises sensory, motor, cognitive, emotional, repetitive behavior, difficulties in daily living, social, and language categories of symptoms, so extends well beyond just social symptoms. Particular symptoms may occur frequently but not universally across ASD individuals, and conversely the pattern of symptoms across ASD individuals is enormously heterogeneous . Further, many studies have reported contradictory findings, in part for methodological reasons. In addition, some symptoms are under-studied, as with abnormalities of interoception of hunger, thirst, body temperature, and other bodily variables, as well as impairments of body representation. Taken together, much has been learned but more remains to be learned about the symptoms and features of ASD.
Summary of disrupted neurocircuitry. Four social brain regions are commonly disrupted and these disruptions and the resulting symptoms drive additional abnormalities of the visual cortex, inferior frontal gyrus, caudate nucleus, and hippocampus. ASD, autism spectrum disorders IFG, inferior frontal gyrus OFC, orbitofrontal cortex TPC, temporoparietal cortex VC, visual cortex.
Recommended Reading: What Does It Mean When Someone Is Brain Dead
Also Check: Does Gestational Diabetes Cause Autism