What Are The Most Common Risk Factors For Autism
ASD occurs among all racial, ethnic, and socioeconomic groups.
Common risk factors for autism spectrum disorder include:
- Having a twin with ASD, or other family history.
- Boys are about 4 times more likely to develop ASD than girls.
- Parents who have had a child with ASD have a 2% to 18% chance of having another child with the disorder.
- Children born to older parents also seem to have a higher risk, but more research is necessary.
- About 10% of children with autism also have certain genetic disorders like Rett Syndrome or fragile X syndrome, or tuberous sclerosis, where benign tumors develop in the brain.
- Preterm babies born before 26 weeks of gestation may have an elevated risk of autism spectrum disorder.
- Over 80% of children diagnosed with ASD also have a psychiatric, neurologic, chromosomal, or genetic diagnosis.
What Are The Causes Of Autism
Its natural to want to know what causes autism, however it is likely that there is not one single cause. While genetic differences are known to cause some types of autism, the causes of autism are largely unknown.
We do know that autism is a neurobiological difference, meaning that the brain processes information differently for people with autism, than it does for people who do not have autism.
We also know that parenting styles do not cause a child to develop autism.
Autism is not caused by vaccinations during or before pregnancy, and the falsely-reported link between the measles-mumps-rubella immunisation and autism has been retracted from the paper it was published in, and completely discredited by the research, scientific and medical community.
For more information about the current studies being undertaken into the causes of autism, visit our what causes autism section.
How Is Autism Spectrum Disorder Diagnosed
There are no laboratory tests to determine ASD. However, certain healthcare providers receive specific training and can do screenings and evaluations if needed and who might ask parents or teachers to record observations. These providers might include specialized physicians, psychologists and speech-language pathologists.
Also Check: How To Tell If My Baby Is Autistic
Theories And Empirical Research
Confucianism
is a study and theory of relationships especially within hierarchies. Social harmonyâthe central goal of Confucianismâresults in part from every individual knowing his or her place in the social order, and playing his or her part well. Particular duties arise from each person’s particular situation in relation to others. The individual stands simultaneously in several different relationships with different people: as a junior in relation to parents and elders; and as a senior in relation to younger siblings, students, and others. Juniors are considered in Confucianism to owe their seniors reverence and seniors have duties of benevolence and concern toward juniors. A focus on mutuality is prevalent in East Asian cultures to this day.
Minding relationships
The mindfulness theory of relationships shows how closeness in relationships may be enhanced. Minding is the “reciprocal knowing process involving the nonstop, interrelated thoughts, feelings, and behaviors of persons in a relationship.” Five components of “minding” include:
Screening By Age Group
Children Younger Than Age 18 Months
Earlier diagnosis of ASD may lead to earlier treatment. The M-CHAT is the most studied and widely used tool for screening toddlers for ASD. Additional tools are under investigation and are listed in as promising autism screening tests. Language delay can be identified by using the Infant and Toddler Checklist in low-risk infants and toddlers between 12 and 18 months of age., This questionnaire might be useful in identifying infant siblings of children with ASD who are at increased risk for ASD. Additional research may allow for screening of toddlers as young as 12 months by using parent-administered questionnaires such the Communication and Symbolic Behavior Scales Development Profile and the Infant and Toddler Checklist.
Primary care providers are tasked with identifying all children who would benefit from early intervention, not just children at risk for ASD . It is important to identify all clinically significant delays in children with referral for appropriate diagnostic evaluation and intervention. Problems with sleep, eating, constipation, and state regulation are common in the general population but may be particularly challenging in young children with ASD. Pediatricians can help families with management of these symptoms.
Children Ages 18 to 30 Months
Children Older Than 30 Months
Also Check: Life Expectancy For Autism
What Is Autism Spectrum Disorder
Autism spectrum disorder is a developmental disability;that can cause significant social, communication and behavioral challenges. There is often nothing about how people with ASD look that sets them apart from other people, but people with ASD may communicate, interact, behave, and learn in ways that are different from most other people. The learning, thinking, and problem-solving abilities of people with ASD can range from gifted to severely challenged. Some people with ASD need a lot of help in their daily lives; others need less.
A diagnosis of ASD now includes several conditions that used to be diagnosed separately: autistic disorder, pervasive developmental disorder not otherwise specified , and Asperger syndrome. These conditions are now all called autism spectrum disorder.
Causes And Risk Factors
We do not know all of the causes of ASD. However, we have learned that there are likely many causes for multiple types of ASD. There may be many different factors that make a child more likely to have an ASD, including environmental, biologic and genetic factors.
- Most scientists agree that genes are one of the risk factors that can make a person more likely to develop ASD.4, 19
- Children who have a sibling with ASD are at a higher risk of also having ASD. 5-10
- Individuals with certain genetic or chromosomal conditions, such as fragile X syndrome or tuberous sclerosis, can have a greater chance of having ASD. 11-14, 20
- When taken during pregnancy, the prescription drugs valproic acid and thalidomide have been linked with a higher risk of ASD.15-16
- There is some evidence that the critical period for developing ASD occurs before, during, and immediately after birth. 17
- Children born to older parents are at greater risk for having ASD. 18
ASD continues to be an important public health concern. Like the many families living with ASD, CDC wants to find out what causes the disorder. Understanding the factors that make a person more likely to develop ASD will help us learn more about the causes. We are currently working on one of the largest U.S. studies to date, called Study to Explore Early Development . SEED is looking at many possible risk factors for ASD, including genetic, environmental, pregnancy, and behavioral factors.
Recommended Reading: Autistic In Hindi
Autism Diagnosis: Poor Social Skills
A major part of the diagnosis of autism is determining social skills. Some features of many children with autism are their inability to look another person in the eye, even the eyes of their parents. Children with autism often focus on objects and do so intently, virtually ignoring other people or other stimuli for long time periods. If children with autism do communicate, it is often robot-like without facial expressions or gestures. Ages and Stages Questionnaires can be helpful in evaluating a child’s communication, gross motor, fine motor, problem-solving, and personal adaptive skills.
Risk And Prognostic Factors
The best established prognostic factors for individual outcome within autism spectrum disorder are presence or absence of associated intellectual disability and language impairment and additional mental health problems. Epilepsy, as a comorbid diagnosis, is associated with greater intellectual disability and lower verbal ability.
Environmental. A variety of nonspecific risk factors, such as advanced parental age, birth weight, or fetal exposure to valproate, may contribute to risk of autism spectrum disorder.
Genetic And Physiological. Heritability estimates for autism spectrum disorder have ranged from 37% to higher than 90%, based on twin concordance rates. Currently, as many as 15% of cases of autism spectrum disorder appear to be associated with a known genetic mutation, with different de novo copy number variants or de novo mutations in specific genes associated with the disorder in different families. However, even when an autism spectrum disorder is associated with a known genetic mutation, it does not appear to be fully penetrant. Risk for the remainder of cases appears to be polygenic, with perhaps hundreds of genetic loci making relatively small contributions.
You May Like: Is Level 2 Autism High Functioning
Can Diet Have An Impact On Autism
Theres no specific diet designed for autistic people. Nevertheless, some autism advocates are exploring dietary changes as a way to help minimize behavioral issues and increase overall quality of life.
A foundation of the autism diet is the avoidance of artificial additives. These include preservatives, colors, and sweeteners.
An autism diet may instead focus on whole foods, such as:
Some autism advocates also endorse a gluten-free diet. The protein gluten is found in wheat, barley, and other grains.
Those advocates believe that gluten creates inflammation and adverse bodily reactions in certain autistic people. However, scientific research is inconclusive on the relationship between autism, gluten, and another protein known as casein.
Autism Spectrum Disorder Diagnostic Criteria 29900
A. Persistent deficits in social communication and social interaction across multiple contexts, as manifested by all of the following, currently or by history :
1. Deficits in social-emotional reciprocity, ranging, for example, from abnormal social approach and failure of normal back-and-forth conversation; to reduced sharing of interests, emotions, or affect; to failure to initiate or respond to social interactions.
2. Deficits in nonverbal communicative behaviors used for social interaction, ranging, for example, from poorly integrated verbal and nonverbal communication; to abnormalities in eye contact and body language or deficits in understanding and use of gestures; to a total lack of facial expressions and nonverbal communication.
3. Deficits in developing, maintaining, and understanding relationships, ranging, for example, from difficulties adjusting behavior to suit various social contexts; to difficulties in sharing imaginative play or in making friends; to absence of interest in peers.
Specify current severity: Severity is based on social communication impairments and restricted, repetitive patterns of behavior .
B. Restricted, repetitive patterns of behavior, interests, or activities, as manifested by at least two of the following, currently or by history :
1. Stereotyped or repetitive motor movements, use of objects, or speech .
2. Insistence on sameness, inflexible adherence to routines, or ritualized patterns of verbal or nonverbal behavior .
Specify if:
Also Check: What Is The Life Expectancy Of People With Autism
What Role Do Genes Play
Twin and family studies strongly suggest that some people have a genetic predisposition to autism. Identical twin studies show that if one twin is affected, then the other will be affected between 36 to 95 percent of the time. There are a number of studies in progress to determine the specific genetic factors associated with the development of ASD. In families with one child with ASD, the risk of having a second child with the disorder also increases. Many of the genes found to be associated with autism are involved in the function of the chemical connections between brain neurons . Researchers are looking for clues about which genes contribute to increased susceptibility. In some cases, parents and other relatives of a child with ASD show mild impairments in social communication skills or engage in repetitive behaviors. Evidence also suggests that emotional disorders such as bipolar disorder and schizophrenia occur more frequently than average in the families of people with ASD.
What Causes Autism Spectrum Disorder

There is no clear-cut cause of ASD. Some causes that are supported by research include genetic and some environmental factors. Specific genetic causes can only be identified in 10% to 20% of cases. These cases include specific genetic syndromes associated with ASD and rare changes in the genetic code.
Risk factors include older parental age, low birth weight, prematurity and maternal use of valproic acid or thalidomide during pregnancy, among others. This field of study is an active one for reasearch.
Don’t Miss: Freddie Highmore Really Autistic
Signs And Symptoms Of Autism Spectrum Disorders
Autism spectrum disorder is a developmental disability caused by differences in the brain. Some people with ASD have a known difference, such as a genetic condition. Other causes are not yet known. Scientists believe there are multiple causes of ASD that act together to change the most common ways people develop. We still have much to learn about these causes and how they impact people with ASD.
There is often nothing about how people with ASD look that sets them apart from other people. They may behave, communicate, interact, and learn in ways that are different from most other people. The abilities of people with ASD can vary significantly. For example, some people with ASD may have advanced conversation skills whereas others may be nonverbal. Some people with ASD need a lot of help in their daily lives; others can work and live with little to no support.
ASD begins before the age of 3 years and can last throughout a persons life, although symptoms may improve over time. Some children show ASD symptoms within the first 12 months of life. In others, symptoms may not show up until 24 months or later. Some children with ASD gain new skills and meet developmental milestones, until around 18 to 24 months of age and then they stop gaining new skills, or they lose the skills they once had.
What Are The Symptoms Of Autism Spectrum Disorder
Children with autism often show symptoms before they are two years old. Some children begin to lose language or social skills at the age of one or two. Autism looks different in each child. Not every child shows every symptom, and some have more severe symptoms.
Symptoms of ASD are grouped into two categories:
Social Communication and Social Interaction
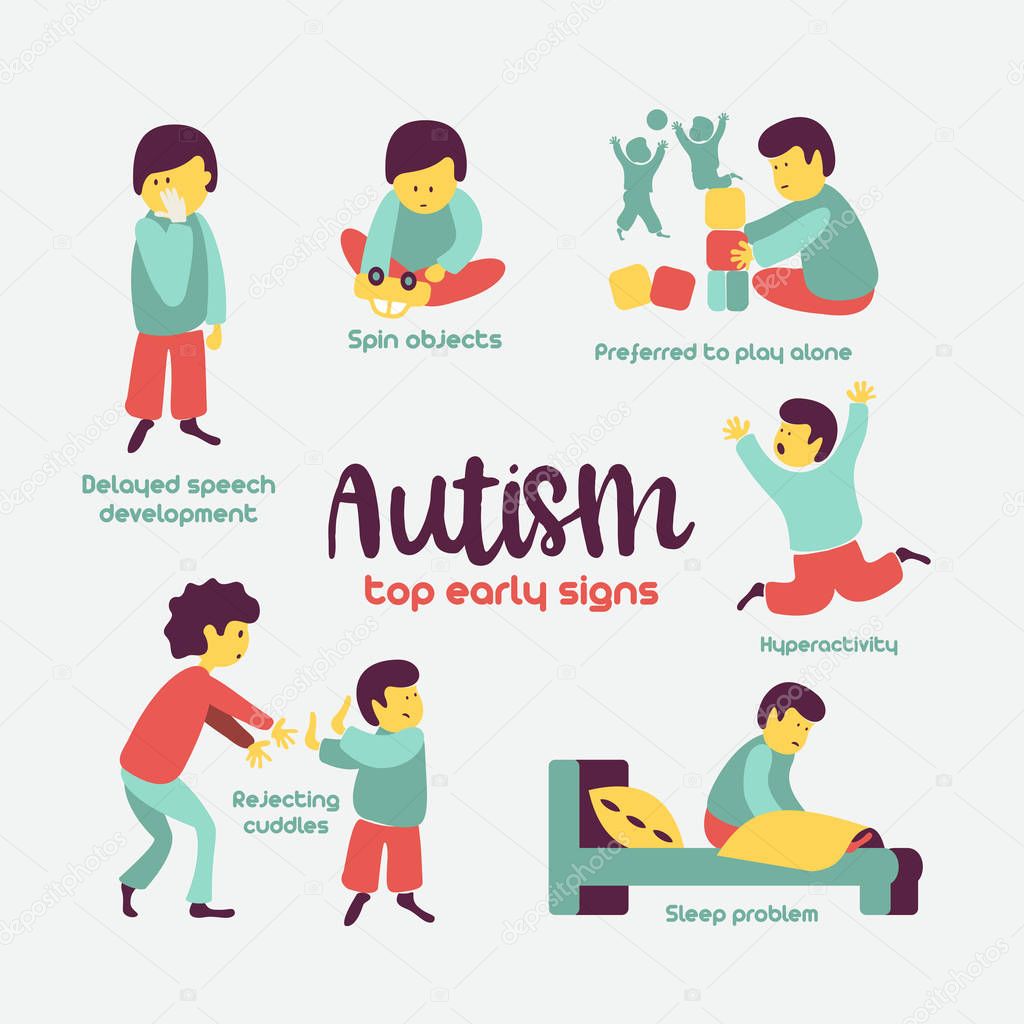
- Doesnt like to cuddle or hug
- Likes to play alone
- Hasnt spoken a word by 18 months
- Cannot say two-word phrases by two years old
- Speaks differently than other children:
- Sounds like a robot when speaking
- Speaks in a very singsong way
- Repeats phrases or puts words in the wrong order
- Can recite information but not use it to solve problems or have a conversation
- Rarely or never makes eye contact
- Has trouble carrying on a conversation and letting the other person talk
Repetitive Behaviors
- Repeats the same action over and over again
- Focuses on small details and nothing else
- Struggles with changes in their routine
- Puts toys in order instead of playing with them
- Gets extremely focused on specific topics or objects
Additionally, children with autism are often sensitive to sounds, lights, textures or smells. This is called asensory processing problem. For example, loud noises or bright lights can make them very uncomfortable. Or, they may need more sensations to feel comfortable, so they will try to bump into things or constantly touch or smell things.
Recommended Reading: Is The Good Doctor Actor Really Autistic
Autism Spectrum Disorder Among Siblings
Autism spectrum disorders diagnoses have increased over the years. Researchers have found that autism runs in families and younger siblings of an autistic sibling have an 18.7% risk of also having autism. Identical twins have the highest percentage of autism occurrence, about a 75% chance that both will develop autism if one twin has autism. As previously mentioned, boys are about four to five times more likely to develop autism.
Restricted Or Repetitive Patterns Of Behavior Or Activities
These can include:
- an increase or decrease in sensitivity to specific sensory information from their surroundings, such as a negative reaction to a specific sound
- fixated interests or preoccupations
Autistic people are evaluated within each category, and the intensity of their symptoms is noted.
To receive an autism diagnosis, a person must display all three symptoms in the first category and at least two symptoms in the second category. Get more information on symptoms and how they may manifest in kids.
The exact cause of ASD is unknown. The most current research demonstrates theres no single cause.
Some suspected risk factors for ASD include:
- having an immediate family member whos autistic
- genetic mutations
An ASD diagnosis involves several screenings, genetic tests, and evaluations.
Read Also: Stuttering And Autism
What Disorders Are Related To Asd
Certain known genetic disorders are associated with an increased risk for autism, including Fragile X syndrome and tuberous sclerosis each of which results from a mutation in a single, but different, gene. Recently, researchers have discovered other genetic mutations in children diagnosed with autism, including some that have not yet been designated as named syndromes. While each of these disorders is rare, in aggregate, they may account for 20 percent or more of all autism cases.
People with ASD also have a higher than average risk of having epilepsy. Children whose language skills regress early in life before age 3 appear to have a risk of developing epilepsy or seizure-like brain activity. About 20 to 30 percent of children with ASD develop epilepsy by the time they reach adulthood. Additionally, people with both ASD and intellectual disability have the greatest risk of developing seizure disorder.
What Started This Concern
A study published in The Lancet in 1998 stated incorrect findings over an association between the MMR vaccine and autism. Since this time, the majority of the authors and The Lancet have retracted the findings.
In the U.S., many legal cases were brought forth over a supposed link between autism and the MMR vaccine. However, according to the Omnibus Autism Proceeding, it was ruled that the MMR vaccine, either given alone or in conjunction with thimerosal-containing vaccines, was not a causal factor in the development of autism.
Related: Childhood vaccines: Tough questions, straight answers
Also Check: Autism Life Expectancy