What Is The Difference Between Autism And Autism Spectrum Disorder
The term autism was changed to autism spectrum disorder in 2013 by the American Psychiatric Association. ASD is now an umbrella term that covers the following conditions:
- Autistic disorder.
- Pervasive developmental disorder not otherwise specified .
- Asperger syndrome.
People with ASD have trouble with social interactions and with interpreting and using non-verbal and verbal communication in social contexts. Individuals with ASD may also have the following difficulties:
- Inflexible interests.
- Insistence on sameness in environment or routine.
- Repetitive motor and sensory behaviors, like flapping arms or rocking.
- Increased or decreased reactions to sensory stimuli.
How well someone with ASD can function in day-to-day life depends on the severity of their symptoms. Given that autism varies widely in severity and everyday impairment, the symptoms of some people arent always easily recognized.
How Is Asd Treated
There arent any standardized treatment recommendations for different levels of ASD. Treatment depends on each persons unique symptoms.
People with different levels of ASD may all need the same kinds of treatment, but those with level 2 or level 3 ASD will likely need more intensive, long-term treatment than those with level 1 ASD.
Potential ASD treatments include:
Are Siblings At Greater Risk For Autism Spectrum Disorder
The truth is that genetics do play a role in autism. When one child is diagnosed with ASD, the next child to come along has about a 20% greater risk of developing autism than normal. When the first two children in a family have both been diagnosed with ASD, the third child has about a 32% greater risk of developing ASD.
You May Like: What Is The Life Expectancy Of People With Autism
Implications Of Changes In Dsm
Differences in DSM-5 criteria for ASD in comparison to DSM-IV have led to debates regarding the impact on the prevalence of the disorder, as well as the diagnosis, and subsequently clinical practice.
The DSM-5 taxonomy offers more stringent criteria for a diagnosis of ASD. The literature raises concern that individuals who used to get the diagnosis of Aspergers disorder, or Pervasive Developmental Disorder Not Otherwise Specified under DSM-IV, are now less likely to meet criteria for the ASD diagnosis by using DSM-5 and therefore will not be eligible for services. Studies also support the notion that young children and females may be at higher risk of being underdiagnosed according to the DSM-5 criteria. These results are of concern as children who are less impaired are more likely to benefit from early intervention, may now be least likely to qualify for such services.
It is however important to note before the publication of DSM-5, there was a growing consensus among clinicians that subcategories of pervasive developmental disorders in DSM IV cannot be reliably diagnosed., Thus, despite the concerns of being a stringent criteria, efforts to conceptualize autism as a broad spectrum of disorders in the DSM-5 had met with less criticism by professionals. Several groups investigating the validity of shifting from a triadic model to a two-factor model have also yielded support for it.,
Symptoms Of Autism Spectrum Disorder In Adults
Common symptoms of autism in adults include:
- Difficulty interpreting what others are thinking or feeling
- Trouble interpreting facial expressions, body language, or social cues
- Difficulty regulating emotion
- Trouble keeping up a conversation
- Inflection that does not reflect feelings
- Difficulty maintaining the natural give-and-take of a conversation; prone to monologues on a favorite subject
- Tendency to engage in repetitive or routine behaviors
- Only participates in a restricted range of activities
- Strict consistency to daily routines; outbursts when changes occur
- Exhibiting strong, special interests
Autism spectrum disorder is typically a life-long condition, though early diagnosis and treatment can make a tremendous difference.
Read Also: Does Lionel Messi Have Autism
Pervasive Developmental Disorder Not Otherwise Specified
Pervasive developmental disorder not otherwise specified described children who didn’t fully fit the criteria for other specific autism diagnoses ;but still had some symptoms of autism. Essentially, PDD-NOS was a “catchall” term for disorders with autism-like symptoms that didn’t fit the full criteria for;another diagnosis.
Because there was no easy way to define the symptoms of PDD-NOS, which may range from very mild to very severe, the diagnostic category no longer exists, though a new diagnosis introduced in the DSM-5, social communication disorder, may become a similar catchall category.;
Treatment Considerations: Asha’s Position
Several treatment options and approaches lack scientific evidence of validity and are not endorsed by ASHA. They are Auditory Integration Training , Facilitated Communication , and Rapid Prompting Method . Below are brief descriptions of these treatments, along with ASHA’s position on each. Click on the hyperlinks provided to read ASHA’s full position statements.
Auditory Integration Training
Auditory Integration Training is a type of sensory integration treatment that involves exercising the middle ear muscles and auditory nervous system to treat a variety of auditory and nonauditory disorders, including auditory processing problems, dyslexia, learning disabilities, attention-deficit disorders, and ASD. The treatment typically involves listening to specially filtered and modulated music for two 30-minute sessions per day for 10 consecutive days. The objective is to reduce distortions in hearing and hypersensitivity to specific frequencies so that the individual will be able to perceive soundsâincluding speechâin a normal fashion.
According to ASHA’s position statement titled, Auditory Integration Training, “The 2002 ASHA Work Group on AIT, after reviewing empirical research in the area to date, concludes that AIT has not met scientific standards for efficacy that would justify its practice by audiologists and speech-language pathologists” .
Facilitated Communication
Rapid Prompting Method
You May Like: Aspergers Life Expectancy
What Research Is Being Done
The mission of the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke is to seek fundamental knowledge about the brain and nervous system and to use that knowledge to reduce the burden of neurological disease. The NINDS is a component of the National Institutes of Health , the leading supporter of biomedical research in the world.; NINDS and several other NIH Institutes and Centers support research on autism spectrum disorder.;
Nearly 20 years ago the NIH formed the Autism Coordinating Committee to enhance the quality, pace, and coordination of efforts at the NIH to find a cure for autism. The NIH/ACC has been instrumental in promoting research to understand and advance ASD. The NIH/ACC also participates in the broader;Federal Interagency Autism Coordinating Committee , composed of representatives from various U.S. Department of Health and Human Services agencies, the Department of Education, and other governmental organizations, as well as public members, including individuals with ASD and representatives of patient advocacy organizations. One responsibility of the IACC is to develop a strategic plan for ASD research, which guides research programs supported by NIH and other participating organizations.
What Role Do Genes Play
Twin and family studies strongly suggest that some people have a genetic predisposition to autism. Identical twin studies show that if one twin is affected, then the other will be affected between 36 to 95 percent of the time. There are a number of studies in progress to determine the specific genetic factors associated with the development of ASD. In families with one child with ASD, the risk of having a second child with the disorder also increases. Many of the genes found to be associated with autism are involved in the function of the chemical connections between brain neurons . Researchers are looking for clues about which genes contribute to increased susceptibility. In some cases, parents and other relatives of a child with ASD show mild impairments in social communication skills or engage in repetitive behaviors. Evidence also suggests that emotional disorders such as bipolar disorder and schizophrenia occur more frequently than average in the families of people with ASD.
Read Also: Symettra Autism
Autism Aspergers Advocacy Australia
By Aaron Kandola, Reviewed by Karen Gill, MD
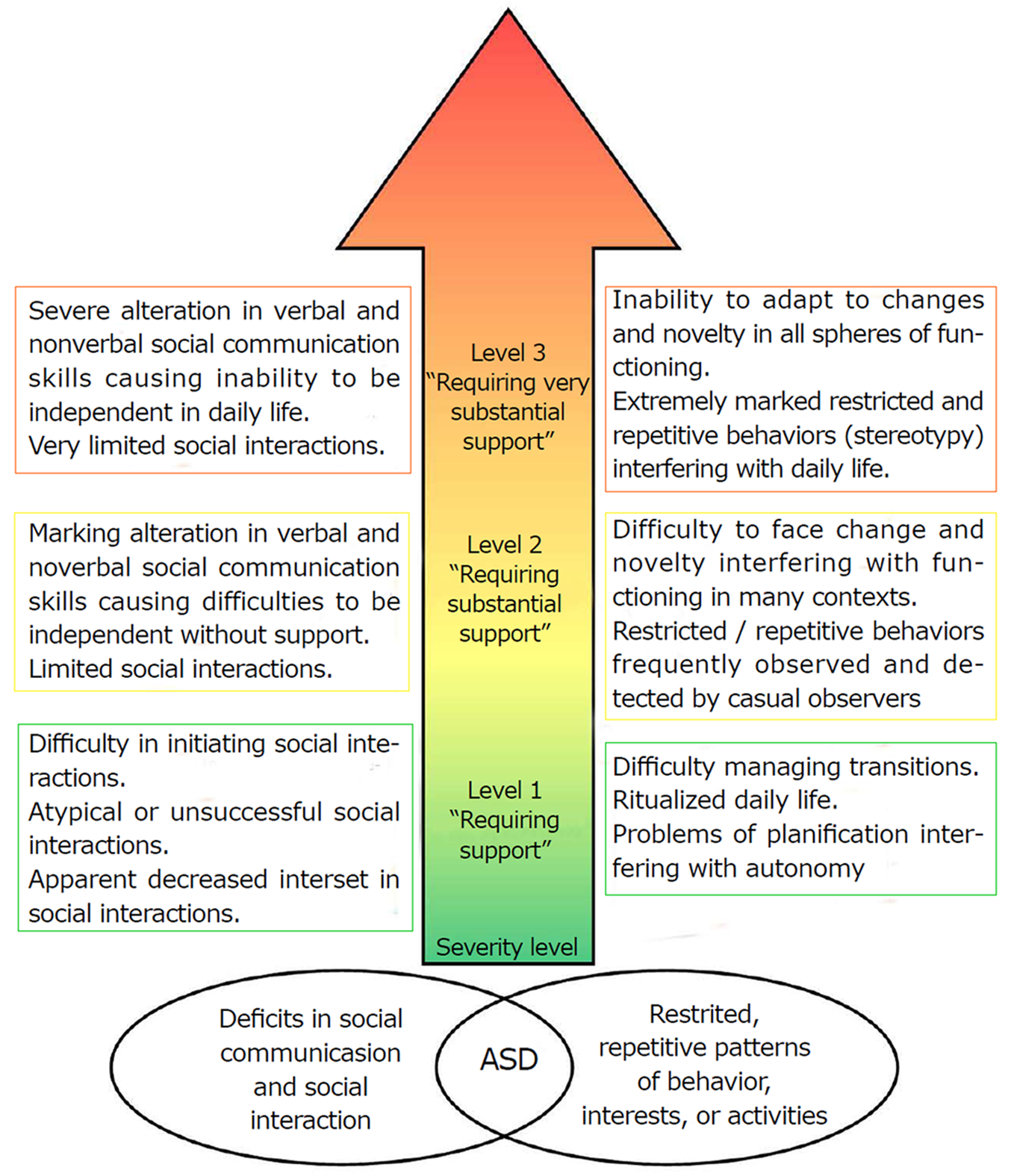
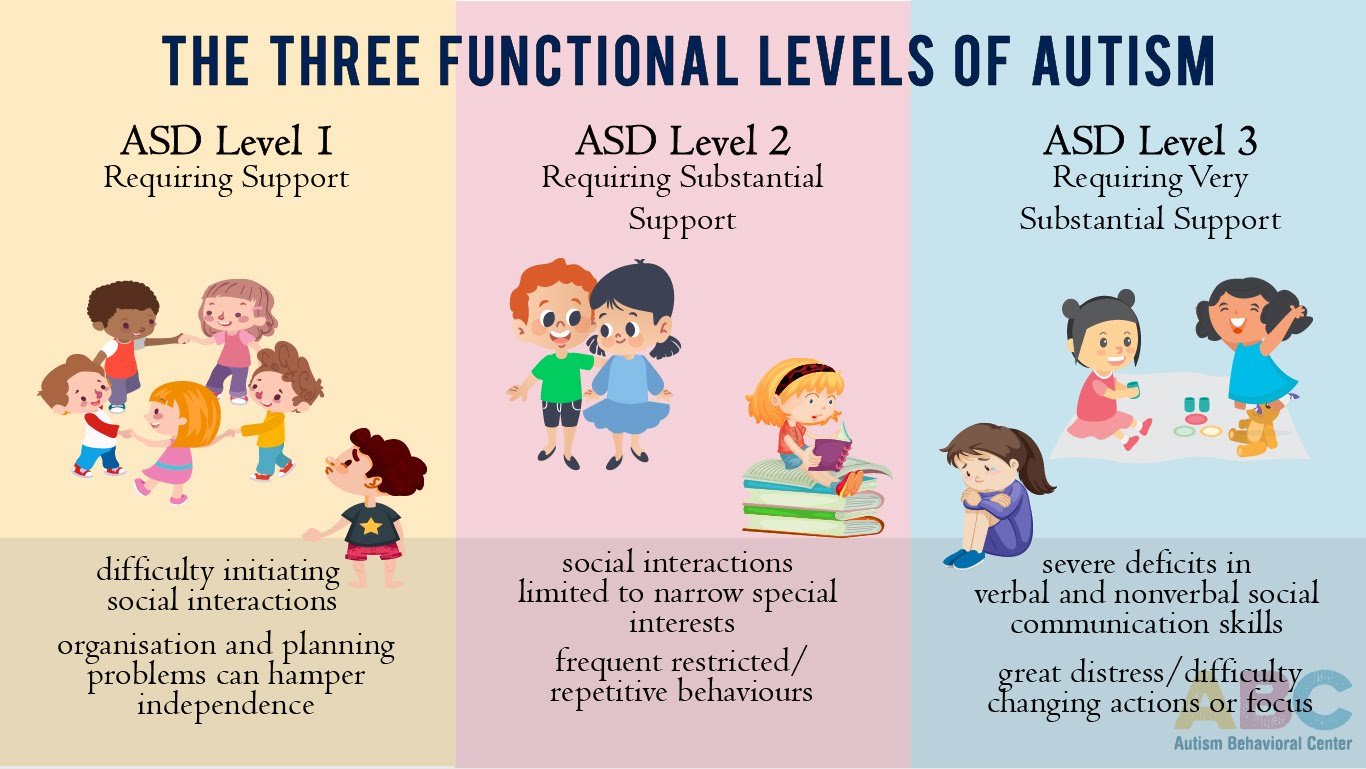
Autism is a spectrum disorder that causes social and behavioral problems. There are three different levels of autism, which range from mild to severe.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention , about one in 59 children have autism. Signs of the condition are usually present at a young age, but occasionally people do not receive a diagnosis until adulthood.
According to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders 5 , doctors categorize autism by assigning level 1, 2, or 3 to two of the domains of symptoms.
One severity score is for impairment in social function, while a second severity score is for restrictive, repetitive behaviors. The levels the doctor assigns depend on the severity of the symptoms.
A correct autism diagnosis that includes the levels of severity can help doctors and other specialists work with the individual to provide the right treatment and support. In this article, learn more about the levels of autism.
The Challenges Of Living With High
Steven Gans, MD, is board-certified in psychiatry and is an active supervisor, teacher, and mentor at Massachusetts General Hospital.
Autism is a spectrum disorder. This means people with autism have a wide range of symptoms and abilities. High-functioning autism is often considered mild, but that’s not necessarily true.
People with HFA can struggle significantly. They may not need the same level of support as people with more severe autism. However, it can still have a major impact on their daily lives.
This article discusses the common challenges of living with high-functioning autism.
Read Also: Does Autism Affect Life Expectancy
Where Can I Get More Information
For more information on neurological disorders or research programs funded by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, contact the Institute’s Brain Resources and Information Network at:
Office of Communications and Public LiaisonNational Institute of Neurological Disorders and StrokeNational Institutes of HealthBethesda, MD 20892
NINDS health-related material is provided for information purposes only and does not necessarily represent endorsement by or an official position of the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke or any other Federal agency. Advice on the treatment or care of an individual patient should be obtained through consultation with a physician who has examined that patient or is familiar with that patient’s medical history.
All NINDS-prepared information is in the public domain and may be freely copied. Credit to the NINDS or the NIH is appreciated.
Autism Symptoms In Adults At Work
Symptoms of ASD vary greatly from person to person based on the severity of the condition. These or similar manifestations of ASD may be apparent at work:
- When youre having a conversation with your boss, you prefer to look at the wall, her shoes, or anywhere but directly into her eyes.
- Your co-workers say that you speak like a robot.
- Each item on your desk has a special place, and you dont like when the cleaning company rearranges it to dust.
- You are really good at math, or software coding, but struggle to succeed in other areas.
- You talk to your co-workers the same way you talk with your family and friends.
- During meetings, you find yourself making involuntary noises, like clearing your throat over and over.
- When talking with your boss, you have difficulty telling if he is happy with your performance or mad at you.
In addition, individuals with ASD may exhibit extraordinary talents in visual skills, music, math, and art. And roughly 40 percent of individuals with ASD have average or above-average intelligence.
If you experience these or similar symptoms of ASD, consult a doctor or mental-health professional for a formal autism evaluation and learn more about treatment options for autism symptoms in adults.
Also Check: How To Make A Visual Schedule For Autism
What Causes Autism Spectrum Disorder
There is no clear-cut cause of ASD. Some causes that are supported by research include genetic and some environmental factors. Specific genetic causes can only be identified in 10% to 20% of cases. These cases include specific genetic syndromes associated with ASD and rare changes in the genetic code.
Risk factors include older parental age, low birth weight, prematurity and maternal use of valproic acid or thalidomide during pregnancy, among others. This field of study is an active one for reasearch.
Why Is It Important To Understand The Levels Of Autism
Autism spectrum is quite wide. While some people with autism can perform complex tasks and are brilliant at certain subjects, others can be intellectually challenged or may not even speak.
Many people with autism have severe communication problems in their daily lives. On the other hand, some people with autism grow up to be exceptional public speakers or successful business owners.
The levels of support for autism spectrum disorder were developed to address this issue of variety. The DSM-5 diagnostic criteria include three functional levels.
Each of these levels is determined based on the amount of support that an individual with autism required to function in their lives.
Assigning a functional level with an autism spectrum diagnosis could provide a clearer picture of an individuals abilities and needs.
This also gives the families and caregivers of the individual with autism a sense of direction on what to do next to provide the most comfortable life for the autistic person.
Come along with 200k+ families!
Explore the endless possibilities of learning!
Their inflexible behaviors or other restricted and repetitive behaviors appear frequently enough to be apparent to those around them. Compared to Level 1 ASD, people with Level 2 ASD struggle more with their restricted and repetitive behaviors.
Routines and habits may feel like a must-do for people with Level 2 ASD. If these are interrupted, they become upset and uncomfortable.
Also Check: What Is The Life Expectancy Of People With Autism
Autism Spectrum Disorder Level : Requiring Substantial Support
According to DSM-5, individuals with level 2 autism require substantial support. Generally, they need more support than individuals with level 1 autism. Even with support, they might have a hard time adjusting to changes in the environment around them.
There are a variety of therapies can help them. For example, sensory integration therapyhelps individuals learn how to deal with sensory input. In other respect, individuals with level 2 autism tend to benefit from occupational therapy. This type of therapy helps them develop the skills that they need to complete daily tasks in order to make easier their daily routines, such as decision-making or job-related skills.
A person with level 2 autism, meaning that with moderate autism, may exhibit normal or below normal mental functioning. They may have some degree of mental retardation or they may have a normal IQ of about 100. This person with level 2 autism might find self-care tasks difficult and challenging.
The symptoms which are associated with level 2 autism include more severe lack of both verbal and nonverbal communication skills compared to level 1 autism. To put it in a different way, they have a significant lack of verbal and nonverbal communication skills. They might have an unusual or reduced response to social cues, communication or interactions. They mostly use overly simple sentences during the conversation.
Signs And Symptoms Of Asd
Those diagnosed with ASD have difficulty with social communication and interaction, restricted interests, and repetitive behaviors. The list below gives some examples of the types of behaviors that are seen in those diagnosed with ASD. While not everyone with ASD will show all behaviors, most will show several.
Also Check: Creating A Visual Schedule Autism
How Is Asd Diagnosed
ASD symptoms can vary greatly from person to person depending on the severity of the disorder. Symptoms may even go unrecognized for young children who have mild ASD or less debilitating handicaps.
Autism spectrum disorder is diagnosed by clinicians based on symptoms, signs, and testing according to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders-V, a guide created by the American Psychiatric Association used to diagnose mental disorders. Children should be screened for developmental delays during periodic checkups and specifically for autism at 18- and 24-month well-child visits.
Very early indicators that require evaluation by an expert include:
- no babbling or pointing by age 1
- no single words by age 16 months or two-word phrases by age 2
- no response to name
- excessive lining up of toys or objects
- no smiling or social responsiveness
Later indicators include:
- impaired ability to make friends with peers
- impaired ability to initiate or sustain a conversation with others
- absence or impairment of imaginative and social play
- repetitive or unusual use of language
- abnormally intense or focused interest
- preoccupation with certain objects or subjects
- inflexible adherence to specific routines or rituals
Social Communication / Interaction Behaviors May Include:
- Making little or inconsistent eye contact
- Tending not to look at or listen to people
- Rarely sharing enjoyment of objects or activities by pointing or showing things to others
- Failing to, or being slow to, respond to someone calling their name or to other verbal attempts to gain attention
- Having difficulties with back and forth of conversation
- Often talking at length about a favorite subject without noticing that others are not interested or without giving others a chance to respond
- Having facial expressions, movements, and gestures that do not match what is being said
- Having an unusual tone of voice that may have an irregular pitch, or come across flat and robot-like
- Having trouble understanding another persons point of view or being unable to predict or understand other peoples actions
Recommended Reading: What Causes Autism Exploring The Environmental Contribution
Wilderness Adventure Therapy And Specialized Residential Programs As Treatment For Level 1 Autism
Additionally, for teens with level 1 autism, a credible wilderness adventure therapy program, such as Vantage Point by Aspiro, or a smaller residential programs such as Daniels Academy or Black Mountain Academy, can be a highly effective treatment option in helping these individuals improve their social skills, establish healthier patterns, and learn how to make smooth transitions.