Managing Autism Spectrum Disorder
Numerous therapies and behavioral interventions can help improve the specific challenges that autistic people face.
Healthcare professionals often recommend that ASD therapies begin as soon as possible after a child receives their diagnosis. Early intervention can reduce their difficulties, allowing them to adapt and learn new skills.
Management strategies for ASD may include:
- educational and developmental therapy
- behavioral therapy to help learn life skills and overcome other challenges
- speech, language, and occupational therapy to help with social, communication, and language skills
- medication to tackle accompanying mental health issues, such as irritability, aggression, repetitive behavior, hyperactivity, attention issues, anxiety, and depression
- psychotherapy to help a person increase or build upon their strengths
- supplements or changes in diet
It is important to note that ASD is a spectrum disorder, meaning people can experience a varying range of these differences. After an ASD diagnosis, many children go on to live productive, independent, and fulfilling lives.
Do Treatment Options Differ For Aspergers And Autism
Neither what was previously diagnosed as Aspergers nor autism is a medical condition that needs to be treated.
Those diagnosed with autism are considered neurodivergent. Autistic behaviors arent considered whats socially typical. But that doesnt mean that autism indicates theres anything wrong with you.
Whats most important is that you or someone in your life whos been diagnosed with autism know that theyre loved, accepted, and supported by the people around them.
Not everyone in the autism community agrees that autistic people dont need medical treatment.
Theres an ongoing debate between those who see autism as a disability that needs medical treatment and those who see autism treatment in the form of securing disability rights, like fair employment practices and healthcare coverage.
Here are some
What Is Autism Spectrum Disorder Previously Called Autism And Pervasive Developmental Disorders
Autism spectrum disorder is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by the following:
- Difficulties in social communication differences, including verbal and nonverbal communication.
- Deficits in social interactions.
- Restricted, repetitive patterns of behavior, interests or activities and sensory problems
Many of those with ASD can have delayed or absence of language development, intellectual disabilities, poor motor coordination and attention weaknesses.
You May Like: Does Jerry Seinfeld Have Autism
Social Communication And Interaction Skills
Social communication and interaction skills can be challenging for people with ASD.
Examples of social communication and social interaction characteristics related to ASD can include:
- Avoids or does not keep eye contact
- Does not respond to name by 9 months of age
- Does not show facial expressions like happy, sad, angry, and surprised by 9 months of age
- Does not play simple interactive games like pat-a-cake by 12 months of age
- Uses few or no gestures by 12 months of age
- Does not share interests with others
- Does not point or look at what you point to by 18 months of age
- Does not notice when others are hurt or sad by 24 months of age
- Does not pretend in play
- Shows little interest in peers
- Has trouble understanding other peoples feelings or talking about own feelings at 36 months of age or older
- Does not play games with turn taking by 60 months of age
No Link Between Autism And Immunisation
Any link between immunisation and autism has been completely discredited.
During the 1990s, concern in the community about a possible link between the measles, mumps, rubella vaccine and autism was generated by the findings of research conducted in London in 1998. The Wakefield study has since been discredited and withdrawn by the journal that originally published it. Dr Wakefields registration as a doctor in the United Kingdom has also been cancelled.
Extensive research conducted globally for a decade did not establish any link between vaccines and autism.
Recommended Reading: Are Stuttering And Autism Related
Social Communication / Interaction Behaviors May Include:
- Making little or inconsistent eye contact
- Tending not to look at or listen to people
- Rarely sharing enjoyment of objects or activities by pointing or showing things to others
- Failing to, or being slow to, respond to someone calling their name or to other verbal attempts to gain attention
- Having difficulties with the back and forth of conversation
- Often talking at length about a favorite subject without noticing that others are not interested or without giving others a chance to respond
- Having facial expressions, movements, and gestures that do not match what is being said
- Having an unusual tone of voice that may sound sing-song or flat and robot-like
- Having trouble understanding another persons point of view or being unable to predict or understand other peoples actions
Forms Of Relation And Interaction
According to , forms of relation and interaction in sociology and may be described as follows: first and most basic are animal-like , i.e. various physical movements of the body. Then there are movements with a meaning and purpose. Then there are , or social actions, which address other people, which solicit a response from another agent.
Next are , a pair of social actions, which form the beginning of social interactions. Social interactions in turn form the basis of social relations. Symbols define social relationships. Without symbols, our social life would be no more sophisticated than that of animals. For example, without symbols people would have no aunts or uncles, employers or teachers-or even brothers and sisters. In sum, symbolic integrations analyze how social life depends on the ways people define themselves and others. They study , examining how people make sense out of life, how they determine their relationships.
Also Check: Can Autism Be Passed Down
Symptoms Of Autism Spectrum Disorder In Adults
Common symptoms of autism in adults include:
- Difficulty interpreting what others are thinking or feeling
- Trouble interpreting facial expressions, body language, or social cues
- Difficulty regulating emotion
- Trouble keeping up a conversation
- Inflection that does not reflect feelings
- Difficulty maintaining the natural give-and-take of a conversation prone to monologues on a favorite subject
- Tendency to engage in repetitive or routine behaviors
- Only participates in a restricted range of activities
- Strict consistency to daily routines outbursts when changes occur
- Exhibiting strong, special interests
Autism spectrum disorder is typically a life-long condition, though early diagnosis and treatment can make a tremendous difference.
Read Also: Does Lionel Messi Have Autism
Family Support & Involvement
Your family is your childs microcosm of society. Since communication doesnt happen in a vacuum, the therapist will train the whole family in techniques, strategies, games, tools, etc., to help you communicate with your child. This practice will pay off in your childs interactions with other social groups and communities, too.
Recommended Reading: Where To Get Tested For Autism
How Have People Responded To The Change
While shifting to “autism spectrum disorder” has generally received the support of the medical community, the revision of the term Aspergers syndrome to autism spectrum disorder was met with uncertainty in the autism community.3 Although the change took place nearly ten years ago, many people with autism continue to refer to themselves as having Aspergers or being Aspies.
Research shows that some autistic people strongly identified with an Aspie identity, and some viewed the diagnostic shift as taking away our identity.4 From celebrities such as Chris Packham and Elon Muskwho continue to refer to themselves as having Aspergersto the wide range of blogs and books which continue to use the term, its evident that for many, there is some kind of desire for this particular identity.
What Research Is Being Done
The mission of the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke is to seek fundamental knowledge about the brain and nervous system and to use that knowledge to reduce the burden of neurological disease. The NINDS is a component of the National Institutes of Health , the leading supporter of biomedical research in the world. NINDS and several other NIH Institutes and Centers support research on autism spectrum disorder.
Nearly 20 years ago the NIH formed the Autism Coordinating Committee to enhance the quality, pace, and coordination of efforts at the NIH to find a cure for autism. The NIH/ACC has been instrumental in promoting research to understand and advance ASD. The NIH/ACC also participates in the broader Federal Interagency Autism Coordinating Committee , composed of representatives from various U.S. Department of Health and Human Services agencies, the Department of Education, and other governmental organizations, as well as public members, including individuals with ASD and representatives of patient advocacy organizations. One responsibility of the IACC is to develop a strategic plan for ASD research, which guides research programs supported by NIH and other participating organizations.
Read Also: Adhd And Asd Comorbidity
Vaccines Dont Cause Autism
No link has been found between vaccines and autism, despite many scientific studies. Researchers have scrutinized the measles, mumps, and rubella vaccine since a 1998 British report raised concerns. That report has been retracted by the Lancet medical journal for poor science and fraud. Thimerosol, a form of mercury, was removed from childhood vaccines in 2001 as a precaution â though no good evidence ever linked it to autism.
How Is Asd Treated
There arent any standardized treatment recommendations for different levels of ASD. Treatment depends on each persons unique symptoms.
People with different levels of ASD may all need the same kinds of treatment, but those with level 2 or level 3 ASD will likely need more intensive, long-term treatment than those with level 1 ASD.
Potential ASD treatments include:
Read Also: Do Nonverbal Autistic Ever Talk
Differentiating Between Borderline Personality Disorder And Autism
By Andréas RB Deolinda, BA, BSc
Studies have discovered that some individuals with autism spectrum disorder also present with a form of personality disorder. Of the various forms of personality disorders, borderline personality disorder and autism as a combination seem to be the most prevalent.
Autism spectrum disorder is not a personality disorder in itself. ASD is characterized by persistent difficulties in social communication and interaction, as well as repetitive/restrictive interests and behaviors. The difficulty with social etiquette is particularly highlighted as some individuals find challenges with social approach to conversation, difficulties integrating communication etiquettes, difficulty making eye contact, and difficulty understanding and using gestures. Autism is a heterogeneous condition given the variety in experiences across the spectrum.
Borderline personality disorder is a condition characterized by impairments in interpersonal functioning, and mostly includes experiencing emotions intensely. Because of this, many individuals with BPD experience emotional dysregulation.
Due to the rise in interest and research, in this article, well look at what borderline personality disorder is, break down the difference between BPD and ASD, and explore the existing overlap between the two. The article also aims to answer whether some autistic individuals are misdiagnosed with BPS.
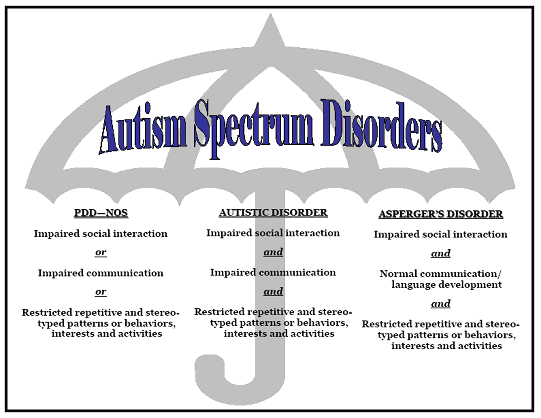
What Conditions Are Considered Spectrum Disorders
Until recently, experts talked about different types of autism, such as autistic disorder, Aspergerâs syndrome, pervasive developmental disorder not otherwise specified . But now they are all called âautism spectrum disorders.â
If you still hear people use some of the older terms, youâll want to know what they mean:
Asperger’s syndrome. This is on the milder end of the autism spectrum. A person with Asperger’s may be very intelligent and able to handle their daily life. They may be really focused on topics that interest them and discuss them nonstop. But they have a much harder time socially.
Pervasive developmental disorder, not otherwise specified . This mouthful of a diagnosis included most children whose autism was more severe than Asperger’s syndrome, but not as severe as autistic disorder.
Autistic disorder. This older term is further along the autism spectrum than Aspergerâs and PDD-NOS. It includes the same types of symptoms, but at a more intense level.
Childhood disintegrative disorder. This was the rarest and most severe part of the spectrum. It described children who develop normally and then quickly lose many social, language, and mental skills, usually between ages 2 and 4. Often, these children also developed a seizure disorder.
Don’t Miss: Is Level 2 Autism High Functioning
Getting The Right Environment
Environment is important to quality of life for autistic people. There are ways you can adapt and improve your environment to make it as comfortable and supportive as possible for you or your child.
The social model of disability is a way of looking at the world that treats the difficulties people with disabilities have as being caused by barriers in society, rather than just the disabilities themselves. These barriers can be physical for example, buildings not having accessible toilets. Barriers can also be caused by peoples attitudes for example, many people will assume someone is lying because they dont make eye contact while talking.
The social model of disability can be a helpful way of considering the difficulties someone faces, and how to adapt their environment so it works for them.
Common changes to an environment that can help autistic people include:
- sensory changes for example, being given a quiet space to work, being able to use sensory toys like fidget spinners, or being allowed to make noises while working
- communication changes for example, using email or apps to communicate, using very clear language, allowing additional time to ask questions, or using visual communication such as photos or pictures as well as written words
- routine keeping to a regular routine and giving warning of any changes as far in advance as possible
- infections
Restricted Or Repetitive Behaviors Or Interests
People with ASD have behaviors or interests that can seem unusual. These behaviors or interests set ASD apart from conditions defined by only problems with social communication and interaction.
Examples of restricted or repetitive interests and behaviors related to ASD can include:
- Lines up toys or other objects and gets upset when order is changed
- Repeats words or phrases over and over
- Plays with toys the same way every time
- Is focused on parts of objects
- Gets upset by minor changes
- Has obsessive interests
- Flaps hands, rocks body, or spins self in circles
- Has unusual reactions to the way things sound, smell, taste, look, or feel
Also Check: Is Level 2 Autism High Functioning
Level : Requiring Very Substantial Support
The communication issues a person with Level 3 ASD may face include:
- severe issues in both verbal and nonverbal social communication, which severely impair functioning
- very limited initiation of social interactions
- minimal response to social interaction from others
- using few words of intelligible speech
- unusual methods of meeting social needs and responding to only very direct approaches
The repetitive behavioral issues a person with Level 3 ASD may face include:
- inflexible behavior
The levels of ASD correspond to the severity of the autism symptoms described above and the degree of support required.
In addition, it is important to keep in mind that the amount of support an autistic person needs can vary according to different ages or situations.
Causes And Risk Factors
While scientists dont know the exact causes of ASD, research suggests that genes can act together with influences from the environment to affect development in ways that lead to ASD. Although scientists are still trying to understand why some people develop ASD and others dont, some risk factors include:
- Having a sibling with ASD
- Having older parents
- Having certain genetic conditionspeople with conditions such as Down syndrome, fragile X syndrome, and Rett syndrome are more likely than others to have ASD
- Very low birth weight
Read Also: What Does It Mean To Be Mildly Autistic
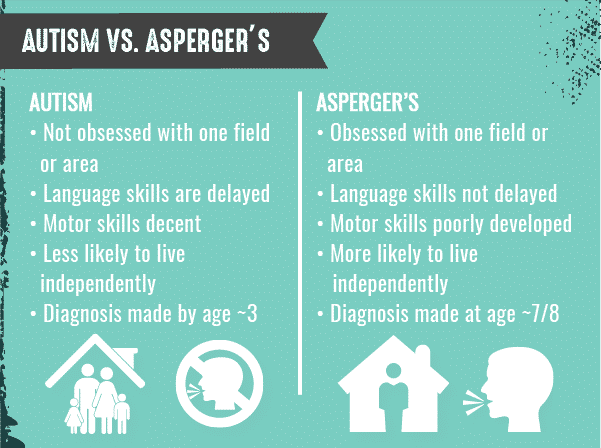
What Is The Difference Between Autism And Aspergers
The difference between autism and Aspergers is a question that often features in discussions about autism.
Aspergers was included in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 4th Edition for the first time in 1994, where it appeared as a separate presentation of a pervasive developmental disorder.
Key characteristics associated with Aspergers syndrome in DSM-4 were:
- Difficulties with social interaction and social communication
- Restricted and repetitive behaviours
- No intellectual disability, and
- No delay in verbal speech development.
Other diagnoses that were thought to be different categories of autism were included in DSM-4 under the umbrella title of Pervasive Developmental Disorders. These included:
- Autistic Disorder
- Pervasive Developmental Disorder Not Otherwise Specified, known as PDD-NOS.
Signs Of Autism In Teenagers And Adults
The characteristics of autism can affect you differently as you get older you may also recognise some of the signs of autism in children in yourself as an adult. Many people are diagnosed with autism as teenagers or adults based on noticing that they think and behave differently from most other people.
Signs of autism in teenagers
As you age and experience different environments, you might notice different signs of autism.
As an autistic teenager, you might:
As an autistic teenager, you might:
- find eye contact uncomfortable, or struggle to know how much eye contact to use
- do well when youre in your routine, but find it difficult when routines change changes might make you feel anxious, make it hard to concentrate, or mean you have to work harder on things itd normally be easy to do
- struggle to imagine things that you havent experienced before for example, if youre going to a party for the first time, it might be hard for you to imagine what will happen and what youll be expected to do
- find yourself making social mistakes without realising why for example, during conversations you might not realise there are things other people would rather not talk about, or dont think are important to talk about
As an autistic teenager, you might:
As an autistic teenager, you might:
As an autistic teenager, you might:
Signs of autism in adults
As an autistic adult, you might:
As an autistic adult, you might:
As an autistic adult, you might:
As an autistic adult, you might:
Also Check: What Is The Symbol For Autism