Causes And Neurological Aspects Of Autism
Many non-specific biological causes have been identified in autism. Some problems of pregnancy and birth and some problems that may be seen in the neonatal period It has been reported that it is more common in children with autistic symptoms. However, these problems are not specific to autism, nor are they specific to autism.
Neurological and genetic diseases that cause autism or autistic symptoms include some genetic syndromes such as Fragile X, diseases that affect the skin and the brain , diseases that disrupt brain structure , acquired processes , encephalitis, passing rubella in the womb), metabolic diseases .
There are also many data about autism as a genetic disease. Studies on the genetic basis of autism suggest that autism is a disease in which many multi-factor genes are responsible.
Gender Differences In Males And Females With Asd
The above information provides an overview of just some of the differences found in the symptoms of autism spectrum disorder when comparing males and females.
In summary, males and females differ in the following ways when looking at the diagnosis of ASD:
- males are diagnosed at a 4:1 ratio when compared to females
- at a young age , females seem to have more motor deficits and lesson communication deficits when they are identified as meeting criteria for an ASD diagnosis at that time
- as intelligence level increases, females are less likely to be diagnosed with ASD which may have to do with their ability to develop coping strategies to manage their life experiences despite having ASD
- females may display different types of restrictive or repetitive behaviors as compared to males sometimes these behaviors are less noticeable to outside observers
Reference:
Halladay, A.K., Bishop, S., Constantino, J.N. et al. Sex and gender differences in autism spectrum disorder: summarizing evidence gaps and identifying emerging areas of priority. Molecular Autism6, 36 doi:10.1186/s13229-015-0019-y
Matheis, M., Matson, J.L., Hong, E. et al. J Autism Dev Disord 49: 1219. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-018-3819-z
Current Understanding Of Social Perception In Asd
The social brain is of great research interest because the social difficulties characteristic of ASD are thought to relate closely to the functioning of this brain network. Functional magnetic resonance imaging and event-related potentials are complementary brain imaging methods used to study activity in the brain across the lifespan. Each method measures a distinct facet of brain activity and contributes unique information to our understanding of brain function.
FMRI uses powerful magnets to measure the levels of oxygen within the brain, which vary according to changes in neural activity. As the neurons in specific brain regions work harder, they require more oxygen. FMRI detects the brain regions that exhibit a relative increase in blood flow while people listen to or view social stimuli in the MRI scanner. The areas of the brain most crucial for different social processes are thus identified, with spatial information being accurate to the millimeter.
In contrast, ERP provides direct measurements of the firing of groups of neurons in the cortex. Non-invasive sensors on the scalp record the small electrical currents created by this neuronal activity while the subject views stimuli or listens to specific kinds of information. While fMRI provides information about where brain activity occurs, ERP specifies when by detailing the timing of processing at the millisecond pace at which it unfolds.
Read Also: Adhd And Dyslexia Comorbidity
Toys For Brain Development And Neurological Improvement
Stages Learning Materials Language Builder Flashcards, Noun Flashcards, Autism Learning Picture Cards
It is one of the most recommended toys that you can find on Amazon. There are different card games available in it in order to improve your childs brain connections, language development, etc. It will be very beneficial whether your child on the autism spectrum or not. It has realistic and attractive pictures. Your child is not going to be bored at all. It has a different category with different stimuli such as colors, sizes, designs, etc. It is developed based on ABA therapy. Overall, it is a very useful toy for your child.
Autism Supplies And Developments Plastic Visual ASD Behavior Keyring
These cards are designed based on the needs of children on the autism spectrum. These symbols are chosen in order to fit most of the people. Individuals on the autism spectrum can learn the symbols on these cards in order to express their desires, wants, and thought. They will boost their brain connections and make their lives easier. Overall, both individuals with autism and the people around them will be very satisfied with these cards.
Coogam Wooden Tetris Puzzle, Brain Teasers, Toy, Tangram, Jigsaw
BizyBeez Magnetic Building Blocks Set Special Needs Toys for Kids with Autism
Magz-Bricks 40 Piece Magnetic Building Set, Magnetic Building Blocks
Autism: Insights From The Study Of The Social Brain
Yale University
People with autism spectrum disorder suffer from a profound social disability. Social neuroscience is the study of the parts of the brain that support social interactions or the social brain. This module provides an overview of ASD and focuses on understanding how social brain dysfunction leads to ASD. Our increasing understanding of the social brain and its dysfunction in ASD will allow us to better identify the genes that cause ASD and will help us to create and pick out treatments to better match individuals. Because social brain systems emerge in infancy, social neuroscience can help us to figure out how to diagnose ASD even before the symptoms of ASD are clearly present. This is a hopeful time because social brain systems remain malleable well into adulthood and thus open to creative new interventions that are informed by state-of-the-art science.
You May Like: Symbol For Autism Awareness
Exploring Diversity In Asd
Because of the limited quality of the behavioral methods used to diagnose ASD and current clinical diagnostic practice, which permits similar diagnoses despite distinct symptom profiles , it is possible that the group of children currently referred to as having ASD may actually represent different syndromes with distinct causes. Examination of the social brain may well reveal diagnostically meaningful subgroups of children with ASD. Measurements of the where and when of brain activity during social processing tasks provide reliable sources of the detailed information needed to profile children with ASD with greater accuracy. These profiles, in turn, may help to inform treatment of ASD by helping us to match specific treatments to specific profiles.
The integration of imaging methods is critical for this endeavor. Using face perception as an example, the combination of fMRI and ERP could identify who, of those individuals with ASD, shows anomalies in the FG and then determine the stage of information processing at which these impairments occur. Because different processing stages often reflect discrete cognitive processes, this level of understanding could encourage treatments that address specific processing deficits at the neural level.
Diagnostic Models Based On Imaging Genetics
Imaging genetics in ASD has proven useful, and pathways that include common genetic variation in TD individuals at risk of developing ASD have been characterized. Prenatal transcription regulation and synapse formation in the developing brain is impacted by the genes associated with ASD . Alteration in frontal WM connectivity and structure and disturbance in the frontal, temporal, and occipital circuits involved in visual and language processing was found to be associated with NRXN superfamily genes. Neuropeptide signaling and emotional functioning was found to be influenced by the oxytocin and arginine vasopressin receptor genes via structural and functional modification in the amygdalahypothalamus circuitry. One study showed a relationship between frontal lobe connectivity and common genetic variants in CNTNAP2 using a functional neuroimaging study and the study found that ASD and TD individuals who were nonrisk allele carriers showed more reduction in the activation of mPFC during an fMRI task as compared to risk allele carriers. Another study showed decreased functional connectivity in the prefrontal cortex, cortical spinal tract, corpus callosum, and decreased integrity of WM in children and adolescents carrying MET rs1858830, C risk allele. Such studies suggest that the genes affect the brain regions that are involved in social and emotional processing.
Also Check: Symmetra Comic Autism
Study Provides Evidence That Autism Affects Functioning Of Entire Brain
Previous View Held Autism Limited to Communication, Social Behavior, and Reasoning.
A recent study provides evidence that autism affects the functioning of virtually the entire brain, and is not limited to the brain areas involved with social interactions, communication behaviors, and reasoning abilities, as had been previously thought. The study, conducted by scientists in a research network supported by the National Institutes of Health , found that autism also affects a broad array of skills and abilities, including those involved with sensory perception, movement, and memory.
The findings, appearing in the August Child Neuropsychology, strongly suggest that autism is a disorder in which the various parts of the brain have difficulty working together to accomplish complex tasks.
The study was conducted by researchers in the Collaborative Program of Excellence in Autism , a research network funded by two components of the NIH, the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development and the National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders.
These findings suggest that further understanding of autism will likely come not from the study of factors affecting one brain area or system, but from studying factors affecting many systems, said the director of NICHD, Duane Alexander, M.D.
We set out to find commonalities across a broad range of measures, so that we could make inferences about whats going on in the brain, Dr. Minshew said.
What’s It Like To Have Autism Spectrum Disorder
A kid with autism might have trouble:
- talking and learning the meaning of words
- making friends or fitting in
- dealing with changes
- dealing with loud noises, bright lights, or crowds
Kids also might move in an unusual way or do the same thing over and over .
A kid with autism may have a little trouble with these things, or a lot. Some kids need only a little bit of help, and others might need a lot of help with learning and doing everyday stuff.
Also Check: What Is The Life Expectancy Of People With Autism
Tpc Is Disordered In Asd
See , Box 3.
TPC broadly comprises superior temporal regions and adjacent inferior parietal regions, and is generally taken to encompass BAs 41, 42, 22, 43, 40 ), and 39 ). TPC subregions are commonly disrupted in ASD, as evidenced next.
In a meta-analysis of functional neuroimaging studies, the findings included that the superior temporal gyrus and inferior parietal cortex were hypoactive in ASD groups relative to TD comparison groups . In a further meta-analysis that concerned language processing tasks, hypoactivation of middle temporal gyrus across diverse language tasks, as well as abnormalities in STG , were found in ASD groups relative to TD controls . In addition, a magnetoencephalographic study found the perisylvian cortex, which includes TPC, to frequently display epileptiform activity in ASD children . A further observation noted earlier is that in a group of unaffected siblings of ASD children, STS manifested increased activations relative to the two comparison groups, suggesting that STS can mediate compensatory processes in ASD .
Autism In The Brain Region By Region
27 February 2017
If the brain were a house with many rooms, you wouldnt find autism in just one of them. Autism has many causes and many forms. But no matter which form it takes, it seems to touch the entire brain. It permeates and perturbs the beams, foundation, wiring and piping of the house, rather than just, say, the kitchen.
Still, autism does have local effects: Different regions of the brain contribute uniquely to autisms impact on cognition, emotion and behavior.
In this special report, we detail the regional consequences of autism, one brain area at a time. Studies of the hippocampus, for example, may help explain the uneven effects of autism on memory. Investigations of the superior temporal sulcus may provide a window into the impact of autism on social perception.
The report is ongoing. Over time, our reporters will step into the various rooms of the brain to probe autisms effect on those regions.
Featured Articles
by Sarah DeWeerdt / 20 August 2020
The brainstem controls such disparate functions as breathing, sensation and sleep all of which can be altered in autism.
by Sarah DeWeerdt / 14 July 2020
The amygdala has long been a focus of autism research. But its exact role in the condition has been unclear.
by Sarah DeWeerdt / 9 March 2020
Long known as the director of movement, the cerebellum may also coordinate social and cognitive abilities, including those central to autism.
by Angie Voyles Askham / 15 October 2020
Recommended Reading: Can A Child With Autism Have Dyslexia
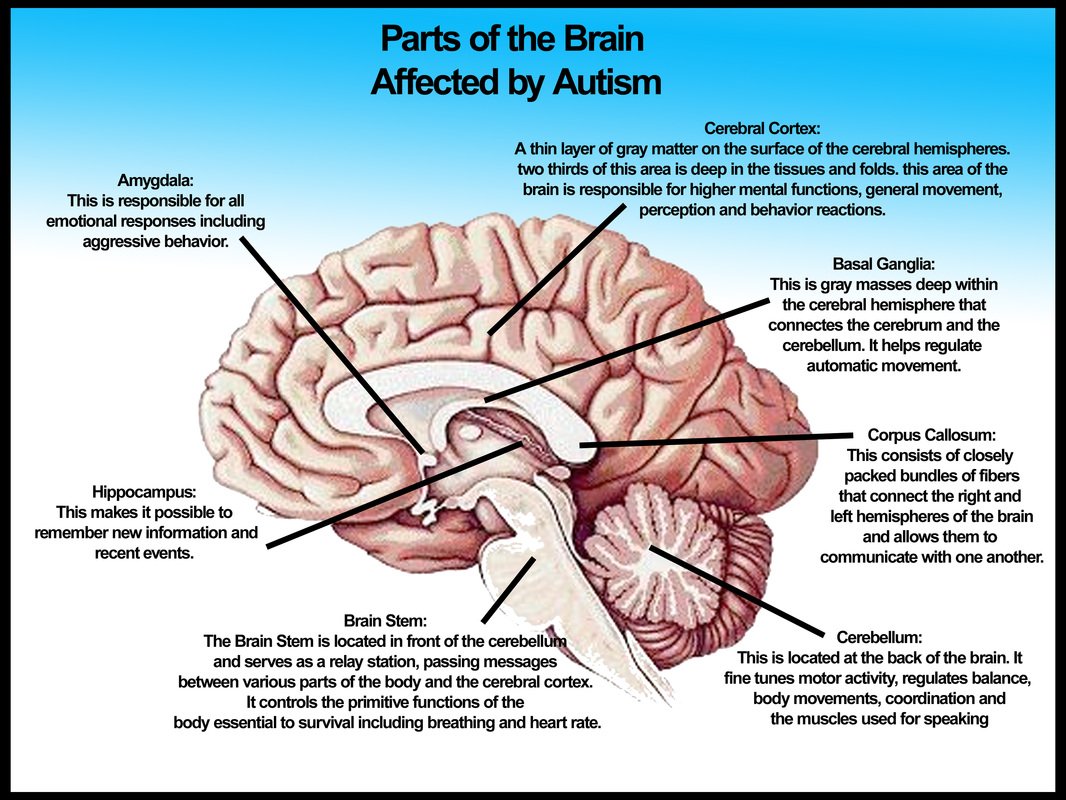
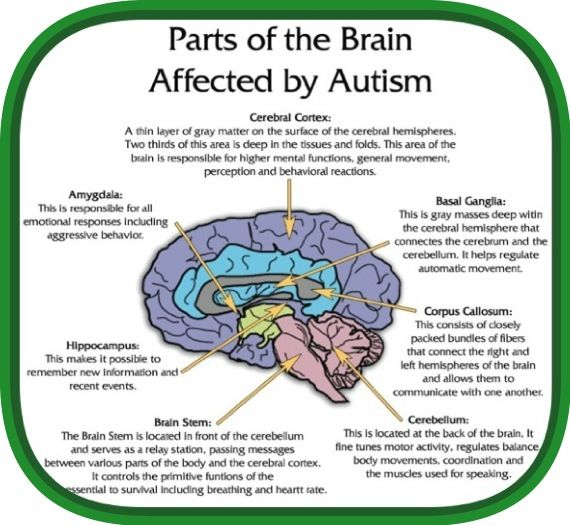
A Look At The Brain Of A Person With Autism
Brain imaging techniques, such as magnetic resonance imaging , havebeen used to examine the brains of people with autism. However, results have been inconsistent. Abnormal brain areas in people with autism include the:
- Cerebellum – reduced size in parts of the cerebellum.
- Hippocampus and Amygdala – smallervolume. Also, neurons in these areas are smaller and more tightly packed .
- Lobes of the Cerebrum – larger size than normal.
- Ventricles – increased size.
How Does Autism Affect The Brain
- Open annotations. The current annotation count on this page is being calculated.
Image credit: CC0
Autism is a brain disorder that affects how people interact with others. It occupies a spectrum, with severe autism at one end and high-functioning autism at the other. People with severe autism usually have intellectual impairments and little spoken language. Those with high-functioning autism have average or above average IQ, but struggle with more subtle aspects of communication, such as body language. As well as social difficulties, many individuals with autism show repetitive behaviors and have narrow interests.
The brains of people with autism process information differently to those of people without autism. The brain as a whole shows less coordinated activity in autism, for example. But whether individual brain regions themselves also work differently in autism is unclear. Watanabe et al. set out to answer this question by using a brain scanner to compare the resting brain activity of high-functioning people with autism to that of people without autism.
Read Also: How Do Puzzles Help The Brain
You May Like: Is Dr Shaun Murphy Really Autistic
Pet And Spect Studies
In the context of autism, functional neuroimaging studies were performed at rest or during various activities. Injected or inhaled radiopharmaceuticals were applied in positron emission tomography methods. Dissolved radioactive isotopes emit positrons that are detected by the PET camera. Some PET methods measure blood flow, while others measure cerebral metabolic rate .
In PET studies performed with autistic children at rest it has been determined that a decrease in blood flow occurred in the temporal lobes. Functional dysfunction in the temporal lobe was concentrated within the auditory associative cortex and superior temporal sulcus. Functional impairment in the auditory cortex of autistic children may explain initial diagnoses of going deaf and experiencing serious deterioration in communication. It has been suggested that functional deterioration in the superior temporal sulcus might explain emotional and cognitive components of autistic symptoms indirectly, due to these being closely linked with the frontoparietal and limbic regions of the multimodal association .
A PET scan study with high functioning autistic adults which practiced during instruction the tasks of theory of mind identified decreased activity in the medial prefrontal cortex, bilateral superior temporal sulcus and basal temporal area , which are components of the mentalization network .
The Amygdala Is Disordered In Asd
See , Box 1.
The amygdala is a structure of some 12 million neurons in humans that is situated in the temporal lobe in an anterior, medial, and ventral location. The nuclei particularly involved in ASD are the lateral, basal, and accessory basal nuclei, which account for 33%, 27%, and 10% of amygdala cells, respectively . The amygdala is generally disordered in ASD, as evidenced next.
Functional neuroimaging investigations have assessed brain function during face processing and other social tasks, and the findings were that the amygdala was hypoactive in ASD individuals relative to TD controls . A further neuroimaging paradigm examined resting state functional connectivity. It found significantly reduced resting functional connectivity that predominantly involved the amygdala, insula, and OFC in ASD adults relative to TD controls . Amygdala disruption is likely underestimated by fMRI studies, however, due to multiple technical issues, such as magnetic-susceptibility-induced signal loss, and individual differences variables .
Recommended Reading: Do People With Autism Die Earlier
Autism & The Lobes Of The Brain
Additionally, within each hemisphere of the brain, there are four lobes: the frontal, parietal, occipital, and temporal lobes. Within these lobes are structures that control everything the body does, from movement to thinking. On top of the lobes is the cerebral cortex, where information processing takes place.
The greater the surface area of the cerebral cortex, the more information the brain is capable of processing. The brain has folds, to add to the surface area of the cerebral cortex. Researchers at San Diego State University have found evidence that suggests that the folds develop differently in people with autism. In autistic brains, there is much more folding in some of both the left and right lobes.
The changes have been connected to modifications in network connectivity in neurons. The weaker a connection, the deeper the folds are. Other research has indicated that language production and processing are altered.
Yet, says PsyCom, the neurobiology of an autistic brain is still hidden. Some experts have said that the more they study brains affected by autism, the more they realize that it may not be so much about the hardware as the software. It may be that the timing of the brain activity is different, affecting how the signals from one region of the brain being sent to another get distorted. It might be that as the autistic brain ages, the aging process brings about more changes that impact the development of autistic symptoms.