What Is Public Health Surveillance
Public Health Surveillance is defined as the tracking and forecasting of any health event or health determinant through the on-going collection of data their integration, analysis and interpretation and, the communication of results for public information, policy and decision-making.
Surveillance is a core function of public health and PHAC and, is viewed as an integral component of any public health strategy.
Recognizing shared responsibility with provinces and territories on public health issues, PHAC works to build an effective public health system that enables Canadians to achieve better health and well-being. In this capacity, PHAC plays a unique role in leading and coordinating national public health initiatives.
How Many People In Canada Are On The Autism Spectrum
In March 2018, theNational Autism Spectrum Disorder Surveillance System released the most up-to-date Canadian prevalence rate:1 in 66Canadian children and youth are diagnosed with Autism Spectrum Disorder . According to theCanadian Medical Association Journal,approximately 1 – 2% of the Canadian population is on the autism spectrum which means there areapproximately 135,000 autistic people in Ontario.
As more research is being done on the intersections of autism and race, gender, sexuality and social locations, more information is being made available online which is increasing the rates of autism diagnosis in children and adults. This in turn is placing a larger demand on education, healthcare, and social service systems, highlighting glaring gaps in the supports available especially for autistic adults, people with lower incomes, people in rural areas, and Black, Indigenous and people of colour.
Having these numbers helps us advocate to the appropriate government ministries for the individual needs of all people on the autism spectrum and their families throughout the life course.
What Are Good Job Options For Autistic People
The passions and fixations that are a hallmark of autism can translate into valuable skills in the workforce. People who are drawn to patterns or puzzles may excel at software testing, quality control, or other roles in the technology sector. Other positions in autism-friendly companies include working on stockroom operations, production lines, data entry, and accounting. Autistic people should explore how their natural interests and talents overlap with the needs of particular positions in the job market.
Also Check: What Is The Difference Between Sensory Processing Disorder And Autism
Variability In Adults With Autism
Not all adults with autism are alike.
- Some adults with autism have successful careers in demanding fields such as information technology, robotics, and video game production.
- Some work part-time while also taking advantage of day programs and resources.
- Some are unable to function in the workplace and spend their days in sheltered settings.
- Some adults on the spectrum are happily married or partnered.
- Others have romantic friendships.
- A significant number are unable to form meaningful, reciprocal relationships with peers.
These vast differences make it just as tough to define or provide services for adults with autism as for children on the spectrum.
Recommended Reading: Symmetra Overwatch Autistic
What Research Is Being Done
The mission of the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke is to seek fundamental knowledge about the brain and nervous system and to use that knowledge to reduce the burden of neurological disease. The NINDS is a component of the National Institutes of Health , the leading supporter of biomedical research in the world. NINDS and several other NIH Institutes and Centers support research on autism spectrum disorder.
Nearly 20 years ago the NIH formed the Autism Coordinating Committee to enhance the quality, pace, and coordination of efforts at the NIH to find a cure for autism. The NIH/ACC has been instrumental in promoting research to understand and advance ASD. The NIH/ACC also participates in the broader Federal Interagency Autism Coordinating Committee , composed of representatives from various U.S. Department of Health and Human Services agencies, the Department of Education, and other governmental organizations, as well as public members, including individuals with ASD and representatives of patient advocacy organizations. One responsibility of the IACC is to develop a strategic plan for ASD research, which guides research programs supported by NIH and other participating organizations.
Also Check: Comorbid Autism And Adhd
What Role Do Genes Play
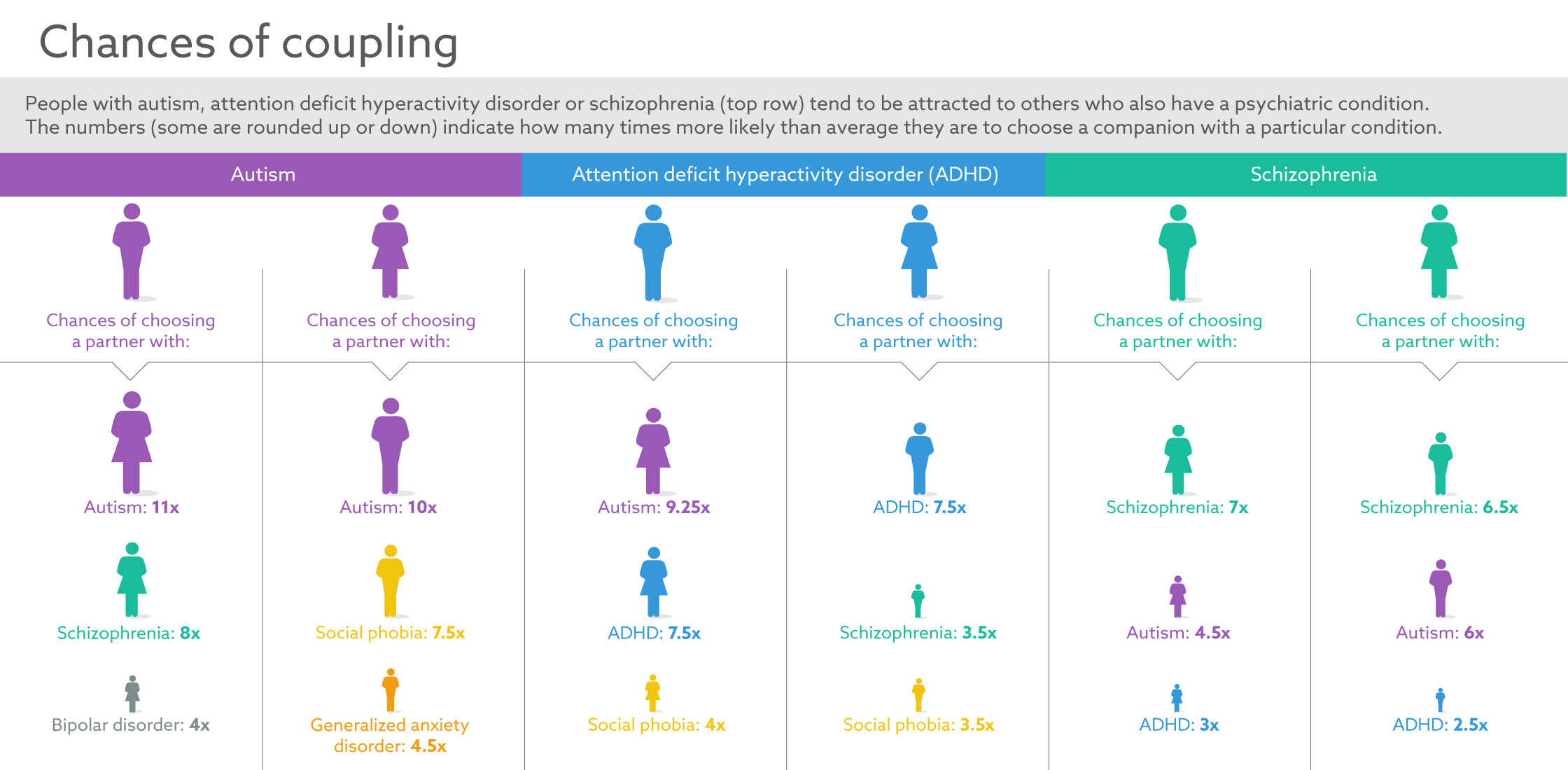
Twin and family studies strongly suggest that some people have a genetic predisposition to autism. Identical twin studies show that if one twin is affected, then the other will be affected between 36 to 95 percent of the time. There are a number of studies in progress to determine the specific genetic factors associated with the development of ASD. In families with one child with ASD, the risk of having a second child with the disorder also increases. Many of the genes found to be associated with autism are involved in the function of the chemical connections between brain neurons . Researchers are looking for clues about which genes contribute to increased susceptibility. In some cases, parents and other relatives of a child with ASD show mild impairments in social communication skills or engage in repetitive behaviors. Evidence also suggests that emotional disorders such as bipolar disorder and schizophrenia occur more frequently than average in the families of people with ASD.
What Is Autism Spectrum Disorder
ASD is a neurodevelopmental disorder that includes impairments in language, communication skills, and social interactions combined with restricted and repetitive behaviours, interests or activities.Footnote 1 Signs of ASD are typically detected in early childhood, with boys four to five times more frequently diagnosed with ASD than girls.Footnote 2
Each person with ASD is unique and will have different symptoms, deficits and abilities. Because of the range of characteristics, this condition is named a “spectrum” disorder, where ones’ abilities and deficits can fall anywhere along a spectrum, and thereby, support needs may range from none to very substantial. It is a complex life-long condition that impacts not only the person with ASD, but their families, caregivers and communities.
In Canada, the diagnosis of ASD is usually provided by medical doctors or psychologists. ASD diagnostic assessments typically use both direct observation and developmental interviews to inform the diagnosing clinician’s clinical judgement based on ASD criteria from the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders .Footnote 3
Also Check: Good Doctor Autism
A Violent Turning Point
One night, after several weeks in which hed not said much of anything to me, I asked him to come to bed with me. He agreed. Giddy for a little attention, I showered, lit a few candles and changed into a pretty nightgown. An hour went by, then more than an hour, and there he sat glued to his screen. I was so desperate for love that I became manic. I hurled insults at him. He jumped up, his agitation grew violent as he grabbed his lounge chair and hurled it across the room at me. I ran out, and the wooden chair leg pierced a deep gouge into the door, slamming it shut.
I grew despondent. He retreated further into his interest.And a new cycle of verbal violence emerged.
Read Also: Do Autistic Toddlers Dance
Study Finds Higher Rates Of Gender Diversity Among Autistic Individuals
A published in Nature Communications found that transgender and gender-diverse individuals have higher rates of autism than their cisgender peers.
Researchers found that transgender and gender-diverse individuals were 3 to 6 percent more likely to be diagnosed with autism with scores higher in areas of sensory sensitivity and autistic traits and lower in empathetic traits. They found their participants experienced challenges outside of autism, citing other psychiatric conditions that play a role in their everyday lives.
This research is crucial to understanding the need transgender and gender-diverse people have for appropriate medical and mental health care that can improve their quality of life, said Thomas W. Frazier, Ph.D., chief science officer at Autism Speaks. By looking at groups of autistic people across several different types of data collected, this study gives us a more realistic idea of how much gender identity and autism overlap.
The study analyzed data from 641,860 participants across five datasets, including survey data, population studies and online questionnaires. Researchers found that 24 percent of the gender-diverse and transgender respondents were autistic compared with 5 percent of the studys cisgender participants.
Researchers concluded that current medical and mental health care for transgender and gender-diverse autistic people is inadequate.
You May Like: Symmetra Hindi Voice Lines
Sen Support & Ehc Plans
Special educational needs and disability is a legal term. It details needs of a child who has a disability or learning difficulty which makes it harder for them to learn than other children of the same age.
In January 2020 of the pupils in England 1,079,000 were identified as having SEN support. An increase from 11.9% in 2019.
If a student has SEN but needs assistance over and above what the school or setting is able to provide or needs to attend a specialist setting they may require an Education Health and Care Plan . Across all schools, the number of pupils with an EHC plan has increased by 8.7%, from 271,200 to 294,800 in January 2020. This represents 3.3% of all pupils, an increase from 3.1% last year. From 2007-2017 this percentage had remained at 2.8%.
EHC plans should be issued within 20 weeks of the initial request for a needs assessment. Only 60% of new EHC plans in 2019 were issued within the 20 week time limit.
Autism is the highest primary type of need for pupils with EHC plans at 30% . Of pupils with SEN support 6.8% have autism as the primary type of need.
The Myth Of The 80% Divorce Rate
Researchers in Baltimore investigated the supposed 80 percent divorce rate for parents of a child with autism spectrum disorder . Unlike other studies, this one was particularly large using data from almost 78,000 parents, 913 of whom had a child with autism and included families from across the United States. The bigger the study, the less likely the results are due to chance or something unique about the pool of people studied. The researchers, from Kennedy Krieger Institute and Johns Hopkins University, found no evidence of an 80 percent divorce rate.9
In fact, parents of children with autism split up as often as parents of children who dont have autism, according to their research. In this study, about two-thirds of the children lived with their two biological or adoptive parents. That was true whether the children had autism or not. The severity of a childs autism symptoms had no effect on the likelihood that parents would go their separate ways.9
While there are indeed stressors in parenting a child with autism, it doesnt necessarily result in the family breaking up more often than would occur in another family, Dr. Freedman has said. Still, he added, its important for health care professionals to provide these families with support and training to handle the stresses they do face.10
Regardless, its clear that raising a child with autism can affect a couple, in ways large and small.
Recommended Reading: Average Lifespan Of An Autistic Person
Are The Numbers Really True
Its been circulating that 80 to 90 percent of parents with autistic children get divorced, but are these numbers actually true? Weve conducted our own research and have come up with conflicting data.
A study published in theJournal of Autism and Development Disorders, evaluated data from nearly 78,000 children from the 2007 National Survey of Childrens Health, and it did not find any evidence to suggest that the parents of autistic children had an increased chance ofdivorce.
However, a 2010 study conducted by the University of Wisconsin at Madison found that parents with ASD children were nearly twice as likely to get divorced than couples without disabled children. The study revealed something interesting: the divorce rates in parents with disabled children did not increase until the children became teens or adults.
After closely evaluating the two above studies,Psychology Today had this to say, Even if statistics conflict, neither study suggests that the divorce rate is anywhere close to 80 percent for parents of ASD kids.
Recommended Reading: How To Make A Visual Schedule For Autism
Unreliable And Biased Tests May Have Underrepresented Autism Intelligence
In the decades before autism was officially recognized and diagnosed, most autistic patients were relegated to general diagnoses that included intellectual disabilities, and in milder cases, learning disabilities.
But the true links between autism and intelligence are more complicated and much more fascinating.
Today, autism is considered a neurological disorder separate from intellectual disabilities. Among the general population, intellectual disability rates run at about 1 percent among ASD patients, the rate is closer to 40 percent according to the Center for Autism Research.
In addition to having a much higher correlation, there is a lot of speculation that the two conditions may have a causative relationship. Contributing to this belief is the fact that there are well-established connections between other genetic syndromes and intellectual disability Fragile X, Retts, and Downs Syndrome, among others.
However, establishing these numbers and correlations is complicated because the standard methods of IQ testing are not necessarily effective with autistic individuals. More than a decade ago, a study called the Special Needs and Autism Project led by the Department of Psychology and Human Development at the Institute of Education in the UK, concluded that the links between autism and intellectual disability were less common than had been historically assumed.
Also Check: Average Lifespan Of Autistic Person
What Are Some Common Signs Of Asd
Even as infants, children with ASD may seem different, especially when compared to other children their own age. They may become overly focused on certain objects, rarely make eye contact, and fail to engage in typical babbling with their parents. In other cases, children may develop normally until the second or even third year of life, but then start to withdraw and become indifferent to social engagement.
The severity of ASD can vary greatly and is based on the degree to which social communication, insistence of sameness of activities and surroundings, and repetitive patterns of behavior affect the daily functioning of the individual.
Social impairment and communication difficultiesMany people with ASD find social interactions difficult. The mutual give-and-take nature of typical communication and interaction is often particularly challenging. Children with ASD may fail to respond to their names, avoid eye contact with other people, and only interact with others to achieve specific goals. Often children with ASD do not understand how to play or engage with other children and may prefer to be alone. People with ASD may find it difficult to understand other peoples feelings or talk about their own feelings.
What Information Is Counted
NASS is particularly interested in reporting on two indicators with respect to ASD estimates in Canada:
Prevalence: The total number of cases diagnosed compared to the total number of individuals in a population for a specific time period , supporting comparisons by age, sex, region, time and/or other factors.
Incidence: The number of newly diagnosed cases in a specific time period in a defined population. This may inform a more targeted understanding of any changes by age, sex, region, time and/or other factors. For NASS, the incidence year is attributed to the year in which cases are first diagnosed.
Figure 1 – Incidence and prevalence illustration
Figure 1 – Text description
Figure 1 presents a visualization of incidence and prevalence. A container represents the population. Dots outside of, and moving into, the container represent new incidence. These dots blend into the portion of the container that is filled. The filled area of the container represents prevalence. The dots once blended with the filled portion of the container collectively represent prevalence.
For ASD prevalence, the numerator is the total number of identified ASD cases collected from PT data the denominator is the total number of Canadian children and youth at that point in time. Incidence denominator would only include the total number of Canadian children and youth who are not included as ASD cases. Estimates can be expressed as a percentage a rate and, as a ratio .
Recommended Reading: The Good Doctor And Autism
What Methodology Is Used To Collect Data
A number of surveillance methods to estimate the prevalence of ASD were considered, most notably: record-review survey data and administrative data collection methods. Each of these methods uses a different approach to identify information.
A record-review method involves access to all available documents from health and/or education sources to identify children with ASD and/or ASD behaviours. The records are reviewed by trained professionals to classify cases. The survey data collection method involves the direct collection of data through standardized tools that are primarily administered with telephone or electronic questionnaires. The third method involves accessing details from administrativedatabasesNote i that have been designed by government agencies and other organizations to document the provision of health, education and/or social services. These data are then analyzed for surveillance purposes.
The use of an administrative data methodology is a more cost effective approach than either a record review or survey method. Administrative data have been previously and successfully used to describe ASD in Canada, in the National Epidemiological Database for the Study of Autism in Canada .Note ii
Further description of the NASS surveillance methodology is provided in the section entitled, Technical Annex: NASS Surveillance Methods.
Possible Etiologies For The Co
Due to the previous DSM-IV diagnostic constraints, research concerning the possible etiologies of the co-occurrence of ADHD and ASD is scarce. The central focus of available research is in the fields of neuropsychology, genetics, and neuroimaging.
Although there are some important differences between the two disorders, as mentioned in the introduction, ASD and ADHD share many similar impairments in developmental and cognitive domains. Both are more common in males, have a strong comorbidity with intellectual disability, and are also associated with other specific learning and developmental difficulties, notably language, reading, and motor problems. Executive functions deficits are common in both disorders, together with response inhibition deficit. EF measures hardly discriminated between ADHD and HFA, but compared to children with ADHD, the HFA group showed more difficulty with cognitive flexibility and planning . Children with ADHD have pragmatic language difficulties similar to children in the ASD spectrum . Further neuropsychological similarities are suggested by a study of emotional recognition and theory of mind which showed that children with ADHD could not be distinguished from those with ASD .
Don’t Miss: Autism Puzzle Piece Colors Meaning