Main Differences Between Autism And Down Syndrome
What Is The Population Of People With Down Syndrome
1. The Centers for Disease Control in 2011 estimated the frequency of Down syndrome in the US is 1 in 691 live births
2. The estimate that 90% of pregnant women in the U.S. who get a diagnosis of Down syndrome through amniocentesis choose to terminate IS INACCURATE.
- This statistic is based on studies done that merged findings from the U.S., UK and Europe in the mid- to late 1990s. The numbers do not represent the attitudes of the US population then or today.
- A more targeted 2012 review of just United States data and termination rates following a prenatal diagnosis for Down syndrome estimates termination rates from 1995 2011 were about 67%.
3. Surprisingly, The population of people in the US with Down syndrome is currently unknown. What we do know is:
Some Perspective On Autism
Autism used to be seen as a behavior disorder. In the past, people saw these differences and thought they should be punished.
Nowadays, we know that these things help autistic people feel comfortable. Fidgeting helps them stay calm. Enjoying their interests isnt wrong, and it can be fun to join them.
Besides, some parts of autism are good. I had several autistic friends in college. They were fun, creative, and unique people who made me laugh. If I needed an opinion, then I knew I could count on them to tell the truth. Whatever I did, they didnt judge me for being different.
Above all, its important to respect who they are.
Don’t Miss: Does Autism Qualify For Disability
Autism Vs Down Syndrome: What Should Parents Know
In the last few years, there has been a noticeable increase in the number of children with Down syndrome who are also being diagnosed with autism spectrum disorder . Children who have autism, as well as Down syndrome, have a dual diagnosis. They have two co-existing conditions.
Earlier, many experts and parents believed that children couldn’t have autism and Down syndrome together. This concept is gradually becoming dated with the continuous publication of longitudinal research on the behavior and affects of children with Down syndrome and ASD.
As of 2021, psychiatrists diagnose approximately 1 in 44 children in the US with Autism Spectrum Disorder . Every year, around 6000 babies are born with Down Syndrome in the US. Experts working with children with Down syndrome and ASD report that approximately 18% to 20% of all children with Down syndrome also have autism.
It makes Autism Spectrum Disorder and Down syndrome equal opportunity conditions. These disorders can affect any child irrespective of their geographic location, race, and socioeconomic status. While both these conditions can be difficult to manage, a dual diagnosis poses a unique set of challenges for the parents.
While Autism Spectrum Disorder and Down syndrome are developmental conditions, they have different causes, symptoms, treatment, and management.
Difference Between Autism And Down Syndrome

Autism vs Down Syndrome
Autism and Down syndrome are well known causes of mental retardation. There are other causes of mental retardation, as well. However, these two are important because Down syndrome represents the pure genetic end of the spectrum while autism represents the purely psychological end. Even though some studies have suggested a genetic link to autism, it remains very doubtful to this date. This article will talk about both autism and Down syndrome in detail highlighting the differences in clinical features, symptoms, causes, tests and investigation, prognosis, and the course of treatment they require.
Autism and Autism Spectrum Disorders
The cause of autismand autism spectrum disorders is due to abnormal development of the nervous system. Autism first appears in childhood or infancy. There are three main symptoms of autism. They are poor social interactions, impairment of communication, and restricted interests and repetitive behaviors. Due to poor interactions, autistic children fail to make friends, play alone, and remain possessive. They find it difficult to speak and express feelings through body language. They develop a unique set of behaviors that they hardly ever change. They like to stack objects up, line up toys and adhere strictly to a daily routine. Autism symptoms become apparent around one to two years of age. Some children develop normally before regressing. During adulthood, the signs of autism are rather muted.
Down Syndrome
Read Also: What To Do When Autistic Child Throws Things
A Down Syndrome Vs Autism: Autistic Spectrum Disorder
Autism spectrum disorder is a disorder that is associated with brain development and how a person interacts and socializes with others. Symptoms can include poor communication skills and repetitive behaviours.
The conditions in autistic spectrum disorder are autism, Asperger syndrome, childhood disintegrative disorder, and an unspecified form of pervasive developmental disorder or atypical autism.
Autistic spectrum disorder is detected in young children and it can cause deficits in social relatedness, especially in school and work.
Children within the age of 1 showcase symptoms of autism spectrum disorder. A small percentage of children show no autistic symptoms in the first year and develop later by 18 -24 months.
Till now there is no cure for autism spectrum disorder although early intervention through intensive behavioural treatment can bring some change in the affected.
Structural Language And False Belief Understanding Differences
Our results indicated that the poorer structural language skills of individuals with DS relative to those with FXS are likely a consequence of their lower level of NV cognition. Or put differently, when statistically matched on NV cognition, the two groups are equally impaired in terms of virtually all structural language variables examined.
The present findings regarding structural language contrast with the findings of several previous investigations that have suggested a weakness in expressive syntax for participants with DS relative to participants with FXS, even when the groups are matched on cognitive functioning . Because the present project utilized multiple measures of structural language, including syntax measured in a standardized test and in a structured naturalistic conversation and with similar results across measures, the difference between our findings relative to other studies are not likely to be due to task or context . Instead, it is more likely that the difference between our findings and those of previous studies is due to differences in participant characteristics, such as age, sex distributions, or language criteria for enrollment.
Pragmatic Skills Differences
Also Check: Why Do People Joke About Autism
What Is The Behavior Of Down Syndrome
The most common mental health concerns include: general anxiety, repetitive and obsessive-compulsive behaviors oppositional, impulsive, and inattentive behaviors sleep related difficulties depression autism spectrum conditions and neuropsychological problems characterized by progressive loss of cognitive skills.
General Themes Across Different Clinical Conditions
The second general issue is whether the language symptoms appear to be delayed or deviant relative to normal development. Although this issue has been most explicitly investigated for the condition of SLI, it is also intrinsic to the interpretive issues that apply to other conditions of language disorders. In the delayed scenario, the language impairments can seem to share many points of similarity with younger, typically developing children, as if the language system is chronologically guided such that by a certain age level typically developing children have acquired a set of particular language skills, whereas the language of children with language impairments reflects a less mature pattern very similar to younger children. In contrast, in the deviant scenario the language system of children with language impairments might not parallel that of younger children. Instead, the kinds of errors and limitations in language use and competency are inconsistent with what is known about any given level of typical language acquisition. The distinction between delayed and deviant bears on interpretation of the language impairment and possible etiological considerations: Are the linguistic systems of affected children fundamentally similar to unaffected children, or are the systems fundamentally different? Are underlying neurocognitive processes and mechanisms fundamentally similar or different? This issue will be highlighted when appropriate in the following review.
You May Like: Where Does Autism Gene Come From
Down Syndrome Disintegrative Disorder: A Clinical Regression Syndrome Of Increasing Importance
POTENTIAL CONFLICT OF INTEREST: Dr Skotko has received payment for expert witness testimony related to Down syndrome the other authors have indicated they have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE: The authors have indicated they have no financial relationships relevant to this article to disclose.
Pediatrics
Mattia Rosso, Ellen Fremion, Stephanie L. Santoro, Nicolas M. Oreskovic, Tanuja Chitnis, Brian G. Skotko, Jonathan D. Santoro Down Syndrome Disintegrative Disorder: A Clinical Regression Syndrome of Increasing Importance. Pediatrics June 2020 145 : e20192939. 10.1542/peds.2019-2939
Srs Scores In Ds: Comparisons To The Normative Sample
Group-wise, participants showed elevated overall SRS scores, indicated by the mean total T-score of 60.57 , which is just above the normal range and into the clinically significant mild-to-moderate category of ASD symptomatology. Further, a one-sample t-test comparing participants T-scores to the mean value from the normative sample was significant, t=6.16, p=< .001.
An examination of SRS T-scores by subscale revealed that the mean T-scores for Autistic Mannerisms and Social Cognition were beyond the normal range cutoff of T=60. The mean scores for the other subscales were just below this cutoff, with the range of scores spanning above and below 60 for every subscale. See Figure for the distribution of T-scores into each clinical category by subscale. One-sample t-tests comparing participants subscale T-scores to the mean value from the normative sample were all statistically significant such that, for each subscale, the mean score of study participants was significantly higher than that of the normative sample .
Figure 1
Recommended Reading: What Environmental Factors Cause Autism
The Causes Of Autism Vs Down Syndrome
There are various causes of autism, and the illness mainly stems from developmental issues in the brain. Nevertheless, autism is associated with several underlying health disorders, such as:
- Hereditary infections in a pregnant mother, for instance, German measles , Toxoplasmosis, and Cytomegalovirus
- Lack of enzymes necessary for metabolic activity, for example, failure to treat phenylketonuria
- Fragile X Syndrome and Tuberous sclerosis, which are rare genetic disorders
- Brain inflammations, including bacterial meningitis and Encephalitis, which are neurological syndromes that occur after birth
On the other hand, Down syndrome arises when an abnormality in cell division occurs, resulting in an extra partial or fullreplica of genetic information from chromosome 21. The additional chromosome can cause defects as physical features and brain develop. There is no medical link of Down syndrome to anything in the internal environment or parents faults.
A Few Differences Between Autism And Down Syndrome
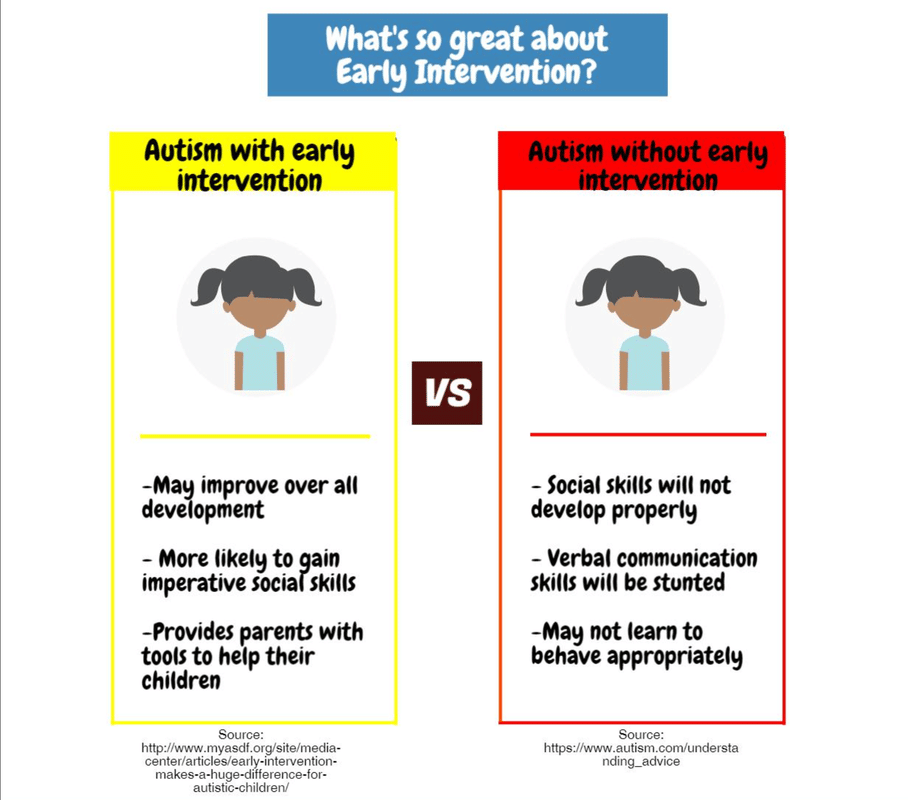
Some of the main differences between Down syndrome and autism include:
- Intellectual disability
Looks: People with Down syndrome look different. You can almost always tell at a glance. Meanwhile, autistic people look like everyone else.
Intellect: Almost all people with Down syndrome have an intellectual disability. Thus, things like counting change, reading large books, and understanding the world are harder. Meanwhile, autism doesnt lower your IQ. Autistic people can have any level of intelligence.
Body language: Down syndrome doesnt change body language. Autistic people tend to fidget and avoid eye contact. This helps them feel better, so dont tell them to stop.
Of course, you cant always tell. For example, if someone has mosaic Down syndrome, then some of their cells have Down syndrome and some dont. That means the signs might be subtler. Autistic people can also mask or hide their natural behavior. However, this is bad for their mental health.
These signs are there, whether theyre obvious or not. If someone is open about it, then it means they trust you with who they are.
Also Check: Advanced Autism Center For Treatment
Down Syndrome Vs Autism: Differences And Similarities
Do you also use the terms down syndrome and autism alternately?
Despite having some similar symptoms, it is important to understand the difference between Down syndrome vs autism and learn about their differences and similarities.
Doctors have evaluated many children with down syndrome and autism and sometimes either of them. They have observed that every child has its own strength and weakness and different personality. If you are curious to know more about Down syndrome vs autism, stick to the end of the article then.
Know The Signs Of A Dual Diagnosis Of Down Syndrome And Autism Spectrum Disorder
As a parent of a child with Down syndrome , navigating the healthcare system can be difficult and tiring, and finding the appropriate resources and interventions for your child can seem incredibly daunting. Now imagine your child has a dual-diagnosis. Did you know that 2-10% of individuals with Down syndrome also meet criteria for Autism Spectrum Disorder ? What does that mean for families? With a dual-diagnosis of DS and ASD, families have more access to valuable resources and benefits for their child, such as medication and/or behavioral treatment like social skills training and Applied Behavioral Analysis therapy.
With this blog, parents will be able to better understand the differences and similarities between Down syndrome and autism spectrum disorder, consider if their child meets the criteria for a dual-diagnosis, and determine appropriate next steps.
Down Syndrome Characteristics
Down syndrome is a genetic condition that occurs when there are three copies of Chromosome 21. Physical attributes can include small mouth and nose, large tongue, almond-shaped eyes with skin that covers the inner eye, and stunted growth. Individuals with DS often experience physical challenges as well, such as vision and hearing impairments, and weight problems. DS can be detected during pregnancy through prenatal screening and diagnostic testing. According to the National Down Syndrome Society , common behaviors of children with DS include:
Autism Spectrum Disorder Characteristics
Don’t Miss: What It’s Like To Have Autism
D Down Syndrome Vs Autism: Autistic Disorder And Social Interaction
- They will not show any interest or point at objects
- They will not look at objects when someone points at it
- They will be disinterested when other children or other parents are around.
- They will avoid eye contact
- They will not regard othersâ feelings or pay attention to it.
- They will not pay attention when people are talking to them whereas pay attention to background noise.
- They will repeat words or phrases and repeat actions
- It can be difficult for them to express their needs by using words or motions
- They can find it difficult to adapt to routine changes
- They could lose the skills they once had such as stopping repeating words
- They could have unusual reactions to taste, smell, look, feel or sound.
Clinical Research: Down Syndrome Autism Often Coexist
Regression risk: Children who have both autism and Down syndrome are more likely to lose language and other skills than children who have Down syndrome alone.
Nearly 40 percent of people with Down syndrome also meet the criteria for an autism spectrum disorder, suggests a U.K. study of nearly 500 children, published in Autism Research1.
The study found that 38 percent of children with Down syndrome meet a screening test cutoff for either classic autism or another pervasive development disorder on the autism spectrum.
In keeping with the elevated prevalence of autism in males, the study shows that boys with Down syndrome are significantly more likely to meet the criteria for an autism spectrum disorder than girls with Down syndrome.
The study assessed whether children show signs of autism by asking their caregivers to fill out the SocialCommunication Questionnaire , which consists of yes-or-no questions about social and communicative deficits and repetitive and restricted behaviors.
The researchers note that the SCQ does not provide a clinical diagnosis. For example, using the SCQ and an additional questionnaire, a 2010 study initially estimated that 42 percent of children with Down syndrome have an autism spectrum disorder. However, after assessing some participants using more rigorous in-person tests, it downgraded the estimate to 18 percent2.
You May Like: Best Careers For Autistic
C Down Syndrome Vs Autism: Autism Behavior Checklist
An autistic child will showcase these repetitive behaviours such as:
- They can have repetitive motor behaviors such as the use of objects or speech.
- Repetitive body movements such as rocking, and spinning repetitively.
- They could also perform activities that cause self-harm such as biting or headbanging.
- They could be clumsy or keep their body stiff or have very unusual body movements.
- They can be absorbed or fixated on an object or an activity and will focus on it for a very long duration of time.
- They can be sensitive to light, sound, touch, temperature, and pain.
- Autistic children can be very fussy regarding food and they can be eating only a few foods or refuse foods with a certain ingredient.
As they grow up, Autistic children learn to live in society and showcase few behavioural problems. Most children who grow up can lead normal or near-normal lives but continue to face difficulty with spoken language or social interaction.