Online Mendelian Inheritance In Man
| Content |
|---|
| Catalog of all known human genes and genetic phenotypes. |
| Data types |
Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man is a continuously updated catalog of and and , with a particular focus on the . As of 28 June 2019, approximately 9,000 of the over 25,000 entries in OMIM represented the rest represented , many of which were related to known phenotypes.
Genetic Causes Of Autism
Most of the researchers on ASD think that the genes may play an important role in the development of ASD. Latest researches estimate that the scientists have been able to discover dozens of genes that contribute to ASD. Studies have shown that the twins and siblings are affected by ASD in many cases. So, the researchers started twin studies which have found a large influence of the gene as causes of autism.
Taking a family health history would be important, because if there is already someone with autism spectrum disorders, and the study is correct, then the likelihood of another person having it in the family is higher. Charis Eng, MD, PhD.
Followings are the common opinions of the genetics researchers regarding autism at different times :
- Autism is clearly among the most heritable of all psychiatric disorders
- Autism is one of the most heritable complex disorders, with compelling evidence for genetic factors and little or no support for environmental influence
- Autism spectrum disorders are considered to be among the most heritable of all mental disorders. recent reviews estimate the heritability of autistic disorder to be more than 90%.
- ASDs are known to be highly heritable .
Limitations Of Current Research
Compared to genetic studies of ASD, studies of environmental risk factors are in their infancy. Many previous studies of environmental risk factors have been limited by small sample size, retrospective or cross-sectional design, indirect measurement of exposure, and inability to ascertain exact timing of exposure with relation to a critical neurodevelopmental period. Moreover, for various reasons, most previous studies have not investigated important factors that might explain the heterogeneity of ASD such as differences in risk between males and females, differences between subtypes, and relation of symptom severity to risk factors. Importantly, the definition of ASD is very broad and encompasses multiple subtypes of the disorder, mirroring the etiological heterogeneity of the condition.
You May Like: Can You Self Diagnose Autism
Postnatal Risk Factors: Lesser
Postnatal risk factors have crucial roles in susceptibility to autism, and a set of them is mentioned in . Low birth weight, jaundice, and postnatal infection are some of the most significant risk factors. A neonate with birth weight, which is the result of three potential factors minor than 2500 g considered as low birth weight and associated with a two-fold increase in the risk of autism. Postnatal jaundice is a result of high bilirubin production caused by increased breakdown of fetal erythrocytes and a low hepatic excretory capacity resulting from general immaturity of the liver and it can be associated with death during a sensitive period or susceptibility to mental disorders, especially a four-fold increase in autism if survive. In addition to prenatal maternal infection during pregnancy, postnatal infections such as meningitis mumps, varicella, unknown fever, and ear infections on the first 30 days of life are correlated with high risk of autism.
Transcriptional Regulation And Chromatin
The processes that encompass transcriptional regulation and chromatin-remodeling are complex. In short, these two processes control which genes can be expressed to form the corresponding protein.
Accurate follow-through of these processes is important as, if any of the steps involved during either transcriptional regulation or in the chromatin remodeling pathway are affected, it will bring rise to the formation of risk genes, some of which have been potentially linked to autism.
For example, the process of transcriptional regulation converts DNA to RNA. Once RNA is transcribed, it goes through cellular processes to coordinate cellular activity. When RNA is transcribed, RNA editing or modification can occur whereby discrete changes can take place within the RNA molecule. In the study by Tran et al. , it was found that mutations such as FMRP and FXRP1 can cause abnormal RNA modification activity.
According to Rylaarsdam, et al. , the genes that impact transcription and chromatin-remodeling pathways include MeCP2, UBE3A, chromodomain helicase DNA binding protein 8 , activity dependent neuroprotector homeobox , pogo transposable element derived with ZNF domain , fragile X mental retardation protein , and RNA binding forkhead box genes.
Also Check: What Is The Life Expectancy Of People With Autism
You May Like: Autistic Phenotype
Nebula Genomics Dna Report For Autism
Is autism genetic? We created a DNA report based on a study that attempted to answer this question. Below you can see a SAMPLE DNA report. To get your personalized DNA report, purchase our Whole Genome Sequencing!
| This information has been updated to reflect recent scientific research as of April 2021. |
Recommended Reading: What Is The Life Expectancy Of People With Autism
Study Illustrates A Quicker And Less Expensive Way To Explore Gene
- Date:
- Johns Hopkins University Bloomberg School of Public Health
- Summary:
- Researchers have shown in a brain organoid study that exposure to a common pesticide synergizes with a frequent autism-linked gene mutation.
Researchers at Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health have shown in a brain organoid study that exposure to a common pesticide synergizes with a frequent autism-linked gene mutation.
The results represent one of the clearest pieces of evidence yet that genetic and environmental factors may be able to combine to disturb neurodevelopment. Researchers suspect that genetic and environmental factors might contribute to the increased prevalence of autism spectrum disorder, a developmental disorder characterized by cognitive function, social, and communication impairments.
The study’s use of brain organoids also points the way towards quicker, less expensive, and more human-relevant experimentation in this field when compared to traditional animal studies.
The study, which appears online July 14 in Environmental Health Perspectives, is the first to show in a human model that an environmental risk factor can amplify the effect of genetic risk factor for autism.
“This is a step forward in showing an interplay between genetics and environment and its potential role for autism spectrum disorder,” says study lead Lena Smirnova, PhD, a research associate in the Department of Environmental Health and Engineering at the Bloomberg School.
Story Source:
Also Check: What Is The Best Pet For An Autistic Child
Asd And Associated Genetic Conditions
Autism Spectrum Disorder and features of ASD can occur as part of some genetic conditions. Approximately 20% of children with ASD will have a diagnosable genetic syndrome. These syndromes can be due to missing or extra stretches of DNA, misspellings in genes, or biochemical abnormalities.
Some of these conditions are easy for a general pediatrician to recognize , while other conditions can be subtle and require specialized testing . For this reason, the American College of Medical Genetics recommends that anyone with an ASD diagnosis receive an evaluation by a clinical geneticist. Accurate diagnosis is important because there can be other health implications for the affected child, as well as differences in the risk of having another child on the autism spectrum.
In addition to genetic causes of ASD, exposure to certain medications during pregnancy can cause ASD. During your childs visit with a clinical geneticist, they will review any medications that you may have taken during pregnancy.
Examples of genetic abnormalities that can be associated with ASD are listed below.
22q deletion syndrome
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
Fragile X
Fragile X syndrome is a genetic condition that causes a range of developmental delay. Usually males are more severely affected than females. Children may be hyperactive or have a secondary diagnosis of ADHD.
Prader-Willi syndrome
Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome
What Are Environmental Factors
STAT News explains that in autism diagnoses and therapy, the term environmental factors is often used incorrectly.
In a colloquial sense, environment can refer to natural settings and the contamination thereof by pollutants, which is itself a factor in the development of autism spectrum disorder . However, scientists and doctors use the term environmental factor to mean anything that produces a biological or behavioral response that cannot be strictly attributed to genetic factors .
In this context, environmental factors can mean anything from food and drink, to air quality, to anything that comes in contact with the skin that causes a biological or behavioral response.
Read Also: Level 2 Autism Spectrum Disorder
Autism Awareness Month Spotlights The Next Generation Of Researchers
In a symposium of early-career researchers and a seminar, scientists shared their work on the role of environmental factors in autism risk.
NIEHS marked Autism Awareness Month with a mini-symposium April 12 showcasing NIEHS-funded research, as well as a guest lecture April 28 that presented a new hypothesis about how microbes in the gut are linked to the disorder.
Autism, also known as autism spectrum disorder , is a broad range of conditions affecting the way people communicate, behave, or interact with others. Once considered rare, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention now estimates that autism affects about 1 in 54 children in the United States.
There is a strong genetic contribution to autism, but we know a lot less about the nongenetic or environmental factors that might be at play, said Cindy Lawler, Ph.D., head of the NIEHS Genes, Environment, and Health Branch.
During the mini-symposium, six early-stage researchers presented their efforts to study those environmental factors, describing a variety of approaches from epidemiology to laboratory-based studies of biological mechanisms that may be at play.
Several Biological Pathways Identified
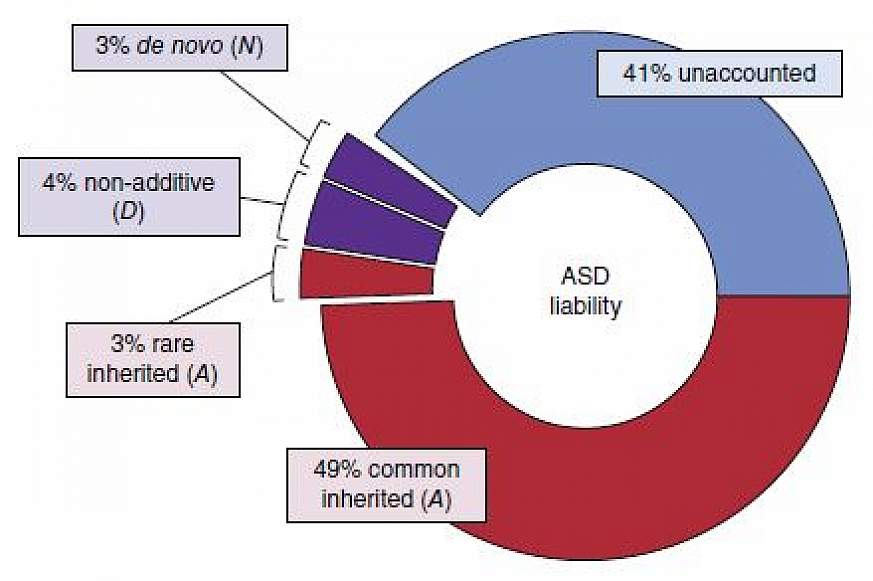
Individuals with ASD vary in language ability, ranging from absent speech to fluent language, and in cognitive development, ranging from profound intellectual disability to above-average intellectual functioning. Individuals may also show associated medical comorbidities including epilepsy and minor physical anomalies, as well as psychiatric comorbidities, thus showing a wide clinical heterogeneity. The clinical heterogeneity of autism has long been a hindrance to understanding the pathophysiological mechanisms involved. However, although many questions remain and new questions are being raised, the last several years of investigation have brought important pieces to the autism puzzle. Indeed, the identification of specific alleles contributing to ASD has shed light on pathogenic mechanisms.
Going back to an individual approach, already used in mental retardation, the search for rare mutations or chromosomal rearrangements was then used, allowing new hypotheses about the mechanisms involved in autism. While the existence of many genetic syndromes associated with autism first led to considering the existence of genetic heterogeneity mirroring the clinical variability, genetic studies in idiopathic autism confirmed the existence of different defects in common pathways. The results suggest that autism may be caused by a multitude of genetic alterations that ultimately affect only limited biological pathways of brain development and plasticity.
Also Check: What Does It Mean To Be Mildly Autistic
The Genetic Architecture Of Asd
Autism spectrum disorder defines a broad group of NDDs characterized by young age of onset, impairment in communication and social abilities, restricted interests and repetitive behaviors, and symptoms that affect patients function in various areas of their life . Symptoms severity varies widely and is often compounded by significant comorbidities, especially intellectual disability, epilepsy, anxiety, sleep, and gastrointestinal disorders .
There Is No Scientific Evidence That Vaccines Cause Autism
A much-talked-about report from the 1990s claimed there may be a link between certain vaccinations given during infancy and autism. Those claims have since been debunked by subsequent studies and the evidence behind those earlier claims has been found to be unreliable.
The American Academy of Pediatrics has compiled a list of dozens of studies that have found there is NO connection between childhood vaccines and autism. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has said the same.
Veenstra-Vanderweele says that this train of thought is dangerous. Vaccinate your children. He says there is no scientific evidence that pinpoints vaccinations as a cause of autism.
Recommended Reading: Schedule Boards For Autism
Study Of Environmental Factors In Autism
Various countries have reported an increase in the prevalence of autism. While its cause is uncertain, many researchers of psychiatry are examining environmental factors as the reason for the increase. Since there has never been a study report with a 100% agreement rate for monozygotic twins to date, the possibility of environmental factors contributing to the prevalence of autism cannot be ruled out. However, some researchers consider that the major reason for the increase of the morbidity rate is due to relaxing diagnostic criteria and applying it to lower levels of intelligence, other medical conditions, and chromosomal abnormalities. When considering environmental factors in autism, the key issue is at what point do they start to affect the central nervous system, causing the onset of abnormal changes in development? Since it was discovered that autism manifests itself before the age of 3 years, environmental risk factors from conception to immediately after birth have been investigated. The following examples are some of the known risk factors.
What Are The Symptoms Of Autism
Autism usually develops before 3 years of age and affects each individual differently and to varying degrees. It ranges in severity from relatively mild social and communicative impairments to a severe disability requiring lifelong parental, school and societal support.
The hallmark symptom of autism is impaired social interaction. Children with autism may fail to respond to their name and often avoid eye contact with other people. They have difficulty interpreting what others are thinking or feeling because they dont understand social cues provided by tone of voice or facial expressions and they dont watch other peoples faces to pick up on these cues.
Many children with autism engage in repetitive movements such as rocking, spinning, twirling or jumping, or in self-abusive behavior such as hand biting or head-banging.
Of children being diagnosed now with an autism spectrum disorder, about half will have intellectual disabilities defined by nonverbal IQ testing, and 25 percent will also develop seizures. Though most children show signs of autism in the first year of life, about 30 percent will seem fine and then regress in both their language and social interactions at around 18 months of age.
About 30 percent of children with autism have physical signs of some alteration in early development such as physical features that differ from their parents , small head size or structural brain malformations.
You May Like: Do Kids Outgrow Autism
Autism Is Not An Illness
Being autistic does not mean you have an illness or disease. It means your brain works in a different way from other people.
Its something youre born with or first appears when youre very young.
If youre autistic, youre autistic your whole life.
Autism is not a medical condition with treatments or a cure. But some people need support to help them with certain things.
Environmental Factors Fail To Explain Increased Autism Prevalence
Disclosures: We were unable to process your request. Please try again later. If you continue to have this issue please contact .
Environmental factors linked to autism spectrum disorder did not increase in importance over time and thus are unlikely to explain the increase in ASD prevalence, according to results of a twin design study published in JAMA Psychiatry.
Twin methods provide a tool for testing hypothesis because they can compare the magnitude of genetic and environmental contributions with a trait over different groups, such as individuals born during different periods, of the department of medical epidemiology and biostatistics at Karolinska Institutet in Stockholm, and colleagues wrote. If changes in the environment over time account for the changing prevalence of a trait, then one hypothesis is that the environmental variance would be expected to increase over time. If the underlying genetic variance showed little or no change, then one expectation is that the heritability of a given trait would also decrease.
Taylor and colleagues aimed to assess whether this hypothesis is true for ASD by investigating whether the relative importance of environmental and genetic associations with ASD and autistic traits changed over a 16-year and 26-year period.
Don’t Miss: Best Dogs For Children With Autism
Genetic Testing For Autism Spectrum Disorder
In todays world, unfortunately, there is no genetic testing to detect autism spectrum disorder before birth, when the baby is in the womb.
We need to know that autism spectrum disorder is first and foremost a genetic disorder. Most of the risk of autism comes from genes. Mutation in genes causes this condition. While there are four types of tests that can detect these mutations, there is no definite specific test that can diagnose autism.
Genetic tests used to detect other genetic disorders in the womb cannot be used to diagnose autism. Because environmental factors are involved in autism and a situation after the test can change the result. It does not mean that there are hundreds of mutations that lead to this situation, but not every gene mutated causes autism.
Lets say the genetic test was applied and you got a negative result. But after your baby was born and raised, you learned that he had autism. This is a very livable scenario. The genetic tests in question may not be receiving a particular mutation, or there is no relationship with autism at the time of the test. For this reason, most genetic testing facilities reanaly the results once a year based on the latest findings.
What Are The Genetic Causes Of Autism
Studies have shown that autism may run in families and several different genes seem to be involved in ASD.
ASD can be associated with a genetic disorder like Rett syndrome or fragile X syndrome for some children.
For others, genetic mutations could increase risk of the disorder. Also, other genes may be at play in affecting the brain development.
Genes may also be impacting the way brain cells communicate, or may be determining the symptoms or severity.
Research indicates that some genetic mutations are likely to be inherited, while others occur spontaneously.
When a parent is the carrier of these genes, they may pass it onto the child. In this case, the parent does not have to have autism.
Other times, the genetic mutations could happen in an early embryo or the sperm and/or egg that combine to create the embryo.
However, these gene mutations do not cause autism by themselves, but increase the risk of developing the disorder.
Read Also: Is It Possible To Outgrow Autism