Pregnancies Less Than A Year Apart
From the Study to Explore Early Development spacing out a second pregnancy in under 18 months can cause ASD. Doctors have always recommended keeping pregnancies spaced further apart.
This study can be found here. Its interesting reading, but it doesnt give any reasons why this is occurring, its basically statistics.
How Can I Spot Signs Of Autism
The earlier treatment for autism spectrum disorder begins, the more likely it is to be effective. Thatâs why knowing how to identify the signs and symptoms is so important.
Make an appointment with your childâs pediatrician if they donât meet these specific developmental milestones, or if they meet but lose them later on:
- Smiles by 6 months
- Imitates facial expressions or sounds by 9 months
- Coos or babbles by 12 months
- Gestures by 14 months
- Speaks with single words by 16 months and uses phrases of two words or more by 24 months
- Plays pretend or âmake-believeâ by 18 months
Show Sources
What Are Causes And Symptoms Of Autism
Articles On Autism
Autism spectrum disorder can look different in different people. Its a developmental disability that affects the way people communicate, behave, or interact with others.
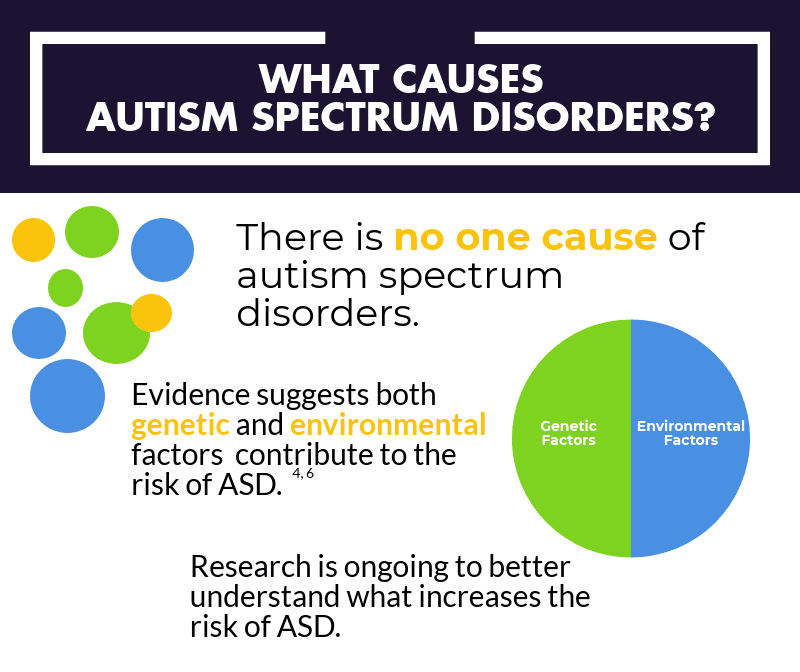
What Are the Causes of Autism?
Experts dont fully understand all of the causes of autism spectrum disorder. It seems to be genetic, but things such as parental age and prescription medications taken during pregnancy may be involved.
For instance:
- A person is more likely to be on the spectrum if a brother, sister, or parent is. But it doesnt always run in families.
- About 10% of kids with ASD have a form of genetic disorder such as Down syndrome and fragile X syndrome.
- A large Danish study found a link between ASD and advanced parental age of either parent.
- Women prescribed opioids just before pregnancy are likelier to have a child with ASD.
ishonestNo.251 – Scars
Some children who are on the spectrum start showing signs as young as a few months old. Others seem to have normal development for the first few months or years of their lives and then they start showing symptoms.
But up to half of parents of children with ASD noticed issues by the time their child reached 12 months, and between 80% and 90% noticed problems by 2 years. Children with ASD will have symptoms throughout their lives, but its possible for them to get better as they get older.
How Does Autism Affect a Childs Social Skills?
How Does Autism Affect Communication?
ishonestNo.171 – Pre-Sun Exposure
Don’t Miss: What Does Hypersensitivity Mean In Autism
Autism Screening And Diagnosis
It can be hard to get a definite diagnosis of autism. Your doctor will focus on behavior and development.
For children, diagnosis usually takes two steps.
- A developmental screening will tell your doctor whether your child is on track with basic skills like learning, speaking, behavior, and moving. Experts suggest that children be screened for these developmental delays during their regular checkups at 9 months, 18 months, and 24 or 30 months of age. Children are routinely checked specifically for autism at their 18-month and 24-month checkups.
- If your child shows signs of a problem on these screenings, theyâll need a more complete evaluation. This might include hearing and vision tests or genetic tests. Your doctor might want to bring in someone who specializes in autism disorders, like a developmental pediatrician or a child psychologist. Some psychologists can also give a test called the Autism Diagnostic Observation Schedule .
If you werenât diagnosed with autism as a child but notice yourself showing signs or symptoms, talk to your doctor.
Symptoms And Signs Of Autism Spectrum Disorders
Autism spectrum disorders may manifest during the first year of life, but, depending on severity of symptoms, diagnosis may not be clear until school age.
Two main features characterize autism spectrum disorders:
-
Persistent deficits in social communication and interaction
-
Restricted, repetitive patterns of behavior, interests, and/or activities
Both of these features must be present at a young age and must be severe enough to significantly impair the child’s ability to function at home, school, or other situations. Manifestations must be more pronounced than expected for the childs developmental level and adjusted for norms in different cultures.
Examples of deficits in social communication and interaction include
-
Deficits in social and/or emotional reciprocity
-
Deficits in nonverbal social communication
-
Deficits in developing and maintaining relationships
The first manifestations noticed by parents may be delayed language development, lack of pointing at things from a distance, and lack of interest in parents or typical play.
Examples of restricted, repetitive patterns of behavior, interests, and/or activities include
-
Stereotyped or repetitive movements or speech
-
Inflexible adherence to routines and/or rituals
-
Highly restricted, abnormally intense, fixated interests
-
Extreme over- or under-reaction to sensory input
Some affected children injure themselves. About 25% of affected children experience a documented loss of previously acquired skills.
You May Like: I Think I Have Adhd What Should I Do
How Are Autism And Adhd Related
ASD can be a stand-alone disorder, or it may coexist with other disorders. One study found that children with ADHD are up to 20 times more likely to exhibit some signs of ASD than are their neurotypical peers1. Autism is generally characterized by social and communication difficulties, and by repetitive behaviors. ADHD is marked by inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity, though social challenges are often part of the ADHD equation as well.
To differentiate ADHD from ASD, many clinicians work to determine whether weak social skills derive from an executive-function impairment or from a broken or missing developmental building block. For example, is a child having difficulty taking turns because he simply wants to play next, or because he doesnt grasp the nature of the game?
Its important to separate difficulties that mimic autism from actual symptoms. Early detection and treatment of the correct condition are crucial. A professional who is familiar with ASD, ADHD, and other similar neurological conditions can use clinical skill and experience to find the true source of a patients challenges.
FREE EBOOK
1 Dennis Thompson. More Links Seen Between Autism, ADHD. HealthDay. . Web.
Treatments Supported By Scienftic Evidence
- Early intensive behavioral intervention programs
- Applied Behavior Analysis , including Discrete Trial Training and Functional Communication Training
- Cognitive Behavior Therapy , especially self-management
- Social skills training, including peer-based strategies, social sto- ries, and social skills groups
- Visual supports and schedules
- PECS when taught through ABA strategies
- Medication for attention, mood, aggression, and rigid behavior
Read Also: Is Add A Form Of Autism
Disorders Of Amino Acid Metabolism
Epigenetic mechanisms may increase the risk of autism. Epigenetic changes occur as a result not of DNA sequence changes but of chromosomal histone modification or modification of the DNA bases. Such modifications are known to be affected by environmental factors, including nutrition, drugs, and mental stress. Interest has been expressed in imprinted regions on chromosomes 15q and 7q.
Most data supports a polygenic, epistatic model, meaning that the disorder is caused by two or more genes and that those genes are interacting in a complex manner. Several genes, between two and fifteen in number, have been identified and could potentially contribute to disease susceptibility. However, an exact determination of the cause of ASD has yet to be discovered and there probably is not one single genetic cause of any particular set of disorders, leading many researchers to believe that epigenetic mechanisms, such as genomic imprinting or epimutations, may play a major role.
You May Like: Is Spd On The Autism Spectrum
What Is Developmental Screening
Developmental screening is a short test that checks to see if a child is learning basic skills when he should, or if there are delays. During developmental screening, your babys provider does a short checkup to look for signs of problems. During screening, the provider may ask you some questions or talk and play with your baby to see how he plays, learns, speaks, behaves and moves. A delay in any of these areas could be a sign of a problem. The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends that all children be screened for developmental delays and disabilities during regular well-child visits at:
- 24 or 30 months
If your childs provider doesnt do this kind of developmental screening, you can ask the provider that it be done. Some babies may need extra screening if theyre at high risk for developmental problems because they were born prematurely or with low birthweight or because of other reasons, like having a brother or sister with ASD. If the provider thinks your baby may have ASD, she needs a full evaluation before a diagnosis can be made.
Also Check: What Are The 5 Disorders On The Autism Spectrum
Autism Spectrum Disorders : Causes Symptoms And Treatments
Autism spectrum disorders are neurodevelopmental disorders that affect communication and social interaction skills, as well as other behaviors. There are numerous forms of ASD, which all fall under the umbrella term autism spectrum disorder .
Autism has come to be widely understood as one end of the autism spectrum, but all forms of ASD share certain symptoms or characteristics, including repetitive and restricted behavior patterns, impaired language skills, and impairments in understanding nonverbal social cues such as facial expressions and body language.
The degree to which these symptoms are present determines the severity of an individuals condition.
You May Like: Is Biting A Sign Of Autism
What Is The Outlook For People With Autism Spectrum Disorder
In many cases, the symptoms of ASD become less pronounced as a child gets older. Parents of children with ASD may need to be flexible and ready to adjust treatment as needed for their child.
People with ASD may go on to live typical lives, but there is often need for continued services and support as they age. The needs depend on the severity of the symptoms. For most, it’s a lifelong condition that may require ongoing supports.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Through research, there has been much that has been learned about autism spectrum disorder over the past 20 years. There is ongoing active research on the causes of ASD, early detection and diagnosis, prevention and treatments.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 12/29/2020.
References
You May Like: Can Autism Be Cured Permanently
Endogenous Opiate Precursor Theory
In 1979, Jaak Panksepp proposed a connection between autism and opiates, noting that injections of minute quantities of opiates in young laboratory animals induce symptoms similar to those observed among autistic children. The possibility of a relationship between autism and the consumption of gluten and casein was first articulated by Kalle Reichelt in 1991.
Opiate theory hypothesizes that autism is the result of a metabolic disorder in which opioid peptides gliadorphin and casomorphin, produced through metabolism of gluten and casein , pass through an abnormally permeable intestinal wall and then proceed to exert an effect on neurotransmission through binding with opioid receptors. It has been postulated that the resulting excess of opioids affects brain maturation, and causes autistic symptoms, including behavioural difficulties, attention problems, and alterations in communicative capacity and social and cognitive functioning.
A Parents Guide To Autism Spectrum Disorders

Millions of people globally have autism spectrum disorders , also known as autism, which are neurological conditions that can affect the way people communicate, socialize, and behave. The disorders also affect parents and other loved ones who might wonder how they can find assistance.
We often hear about autism, but we might not know what it is. It could be useful to describe the condition and how it affects the people with it as well as the people who love them.
You May Like: What Type Of Disability Is Autism
Getting An Autism Spectrum Disorder Diagnosis
The road to an ASD diagnosis can be difficult and time-consuming. In fact, it is often two to three years after the first symptoms of ASD are noticed before an official diagnosis is made. This is due in large part to concerns about labeling or incorrectly diagnosing the child. However, an ASD diagnosis can also be delayed if the doctor doesnt take a parents concerns seriously or if the family isnt referred to health care professionals who specialize in developmental disorders.
If youre worried that your child has ASD, its important to seek out a clinical diagnosis. But dont wait for that diagnosis to get your child into treatment. Early intervention during the preschool years will improve your childs chances for overcoming their developmental delays. So look into treatment options and try not to worry if youre still waiting on a definitive diagnosis. Putting a potential label on your kids problem is far less important than treating the symptoms.
Autism Spectrum Disorders And Depression
Young people and adolescents with ASDs also are more likely to have depression. Researchers have found that people with autism spectrum disorders are four times more likely to have depression during their lives.
In addition to feelings of hopelessness and physical symptoms such as tiredness, depression in people with ASDs can consist of:
- Obsessive behaviors
You May Like: Is Dr Shaun Murphy Really Autistic
Recommended Reading: Can You Die From Autism
Are There Any Treatments Available
There is no one-size-fits-all answer to this question, as the best approach to treatment will vary depending on the individual and the specific symptoms they are experiencing.
However, there are a few general things to keep in mind:
- The earlier children receive intervention services , the better their outcomes tend to be.
- Its important for parents to work with professionals who can help them find treatments that work for their child.
- Educating oneself about ASD and working closely with your childs doctor or therapist is key.
If you suspect that your child might have autism spectrum disorder , youre likely concerned about what treatments are available. While its impossible to provide any blanket advice, its worth noting some important factors:
How Does Autism Affect A Childs Social Skills
A child with ASD has a hard time interacting with others. Problems with social skills are some of the most common signs. They might want to have close relationships but not know how.
If your child is on the spectrum, they might show some social symptoms by the time they’re 8 to 10 months old, including:
- They don’t respond to their name by their first birthday.
- Playing, sharing, or talking with other people donât interest them.
- They prefer to be alone.
- They avoid or reject physical contact, including hugging.
- They avoid eye contact.
- When theyâre upset, they donât like to be comforted.
- They donât understand emotions — their own or othersâ.
- They may not stretch out their arms to be picked up or guided with walking.
You May Like: How To Handle Autistic Child
Understanding Autism Spectrum Disorders
Autism is not a single disorder, but a spectrum of closely related disorders with a shared core of symptoms. Every individual on the autism spectrum has problems to some degree with social interaction, empathy, communication, and flexible behavior. But the level of disability and the combination of symptoms varies tremendously from person to person. In fact, two kids with the same diagnosis may look very different when it comes to their behaviors and abilities.
If youre a parent dealing with a child on the autism spectrum, you may hear many different terms including high-functioning autism, atypical autism, autism spectrum disorder, and pervasive developmental disorder. These terms can be confusing, not only because there are so many, but because doctors, therapists, and other parents may use them in dissimilar ways.
But no matter what doctors, teachers, and other specialists call the autism spectrum disorder, its your childs unique needs that are truly important. No diagnostic label can tell you exactly what challenges your child will have. Finding treatment that addresses your childs needs, rather than focusing on what to call the problem, is the most helpful thing you can do. You dont need a diagnosis to start getting help for your childs symptoms.
What’s in a name?
The Controversy With Asd And Vaccines
In recent years, there has been speculation about whether childhood vaccines might cause autism. Its very important to realize that this has been completely debunked in the scientific literature. Vaccines do not cause autism!
This speculation began in the late 1990s when a paper was published in the Lancet. In that paper, the authors attributed the measles, mumps, and rubella vaccine to potentially being the cause of children developing autism. The study was deeply flawed, and follow-up research discounted the study.
In 2010, the Lancet issued a retraction. Additionally, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control has published a statement explaining clearly that vaccines are not the cause of autism.
Recommended Reading: Is There A Physical Test For Autism
Clinical Implications And Future Perspectives
When autism was first described, it was hypothesized to be an environmentally caused disease. Decades of research have since revealed that autism is a highly heterogeneous and extremely complex genetic condition. Even though great progress had been made in identifying hundreds of risk genes, very little is known about the different types of modifiers that may exacerbate or ameliorate disease severity. Such modifiers could include epigenetics, sex-linked modifiers, CNVs, double-hit mutations, or environmental factors .
Figure 1. Genetic modifiers in autism spectrum disorder. Autism is estimated to be 4080% heritable. However, both genetic and non-genetic factors modulate the penetrance of risk genes, resulting in a highly heterogeneous disease phenotype for similar pathogenic variants. Examples of genetic modulators include CNV, epigenetics, and double-hit mutations. Examples of non-genetic modifiers include environmental exposures and sex-linked modifiers.