How Is Autism Spectrum Disorder Treated
ASD is most often a life-long condition. Both children and adults with autism benefit from behavioral interventions or therapies that can teach new skills to address the core deficits of autism and to reduce the core symptoms. Every child and adult with autism is unique. For this reason, the treatment plan is individualized to meet specific needs. It is best to begin interventions as soon as possible, so the benefits of therapy can continue on throughout the course of life.
Many people with ASD often have additional medical conditions, such as gastrointestinal and feeding issues, seizures and sleep disturbances. Treatment can involve behavioral therapy, medications or both.
Early intensive behavioral treatments involves the entire family and possibly a team of professionals. As your child ages and develops, treatment may be modified to cater to their specific needs.
During adolescence, children benefit from transition services that promote skills of independence essential in adulthood. The focus at that point is on employment opportunities and job skill training.
Identify Characteristics Of Autism In Your Child
The major characteristics of autism are behavior problems, communication problems, social interaction problems and sensory sensitivity problems. These characteristics of autism prevail in the children as a spectrum which includes a wide range of disorders. As such it is called autism spectrum disorders . The characteristics of autism and the severity of the autistic individuals vary widely across these four core areas.
The peculiarity of ASD is that the sign and symptoms of these disorders in one individual does not match with others. No two autistic individuals have identical characteristics of autism.
If youve met one individual with autism, youve met one individual with autism.Dr. Stephen M. Shore
There are different types of developmental disorders like Attention Deficit Disorder , Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder , Autism Spectrum Disorders , Bipolar Disorders, Seizure Disorders, Mental Retardation, Cerebral Palsy, Down Syndrome, Angelman Syndrome and so on. Autism is a kind of developmental disorders among them.
At the early life, an autistic child faces a delay in different developmental milestone and gradually starts showing different characteristics of autism as s/he grows up. Similarly, my autistic son Mahi was delayed in different developmental milestones in his childhood and subsequently different characteristics of autism prevailed in him in course of time.
Social Behavior And Traits
Just as motor skills vary based on the severity of the case of ASD, social behavior will vary as well. Social skills can improve over time with the proper therapy and intervention from professionals. Social behaviors that can signal Autism Syndrome Disorder includes:
- Aggressive social behavior such as rough play, hitting, scratching or inappropriate aggression towards their peers.
- Inappropriate language, actions or gestures may be common for individuals with ASD. These inappropriate actions can include lewd language, gestures that are aggressive or sexual in nature or actions that are unfitting for the situation they are in.
- Feelings, body language and actions can easily be misinterpreted with an individual with ASD. They may take a sentence or action out of context and respond accordingly.
- Socially, individuals on the Autism spectrum may seem awkward or uncomfortable. They will likely not pursue any sort of social activity on their own and may respond to social interactions in a timid or hostile way.
We hope that this information about the different types of Autism will help you differentiate between the three different categories of Autism. We want to encourage you to embrace all people, whether they have a disability or not, and show them all the same respect. We feel that everyone is just as important and special as the next!
Read Also: Is Dr Shaun Murphy Really Autistic
Autistic Disorder Vs Asperger Syndrome
Autistic individuals and those with Aspergers are commonly known to have difficulty in social and behavioral situations, as well as in forming and maintaining relationships. They may both struggle with picking up on social cues or reading body language. Autistic people who are higher-functioning and those with Aspergers often excel in academics compared to those who are not considered high-functioning. The biggest difference between autism and Aspergers is that symptoms are less severe in those with Aspergers and there are not typically language delays.3 Aspergers individuals also tend to have interests in particular subjects that border on obsessive.
Restrictive / Repetitive Behaviors May Include:
- Repeating certain behaviors or having unusual behaviors. For example, repeating words or phrases, a behavior called echolalia
- Having a lasting intense interest in certain topics, such as numbers, details, or facts
- Having overly focused interests, such as with moving objects or parts of objects
- Getting upset by slight changes in a routine
- Being more or less sensitive than other people to sensory input, such as light, noise, clothing, or temperature
People with ASD may also experience sleep problems and irritability. Although people with ASD experience many challenges, they may also have many strengths, including:
- Being able to learn things in detail and remember information for long periods of time
- Being strong visual and auditory learners
- Excelling in math, science, music, or art
Recommended Reading: Stage 2 Autism
An Insight Into The Various Types Of Autism
Let us now get a deeper insight into each of the following forms of Autism.
Fig 3:
As mentioned at the beginning of this article, the various types of autism spectrum disorders present a significant overlap with one another. The following 3 characteristics are carefully evaluated to arrive at the right conclusion:
- Social skills within families coping with Autism and externally
- Autism Communication Skills
For example, it is extremely hard to discriminate between mild PDD and moderate Aspergers symptoms as a patient may demonstrate both characteristics in the autism spectrum quotient.
Social Communication / Interaction Behaviors May Include:
- Making little or inconsistent eye contact
- Tending not to look at or listen to people
- Rarely sharing enjoyment of objects or activities by pointing or showing things to others
- Failing to, or being slow to, respond to someone calling their name or to other verbal attempts to gain attention
- Having difficulties with the back and forth of conversation
- Often talking at length about a favorite subject without noticing that others are not interested or without giving others a chance to respond
- Having facial expressions, movements, and gestures that do not match what is being said
- Having an unusual tone of voice that may sound sing-song or flat and robot-like
- Having trouble understanding another persons point of view or being unable to predict or understand other peoples actions
Don’t Miss: Can Speech Delay Mimic Autism
What Is The Outlook For People With Autism Spectrum Disorder
In many cases, the symptoms of ASD become less pronounced as a child gets older. Parents of children with ASD may need to be flexible and ready to adjust treatment as needed for their child.
People with ASD may go on to live typical lives, but there is often need for continued services and support as they age. The needs depend on the severity of the symptoms. For most, it’s a lifelong condition that may require ongoing supports.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Through research, there has been much that has been learned about autism spectrum disorder over the past 20 years. There is ongoing active research on the causes of ASD, early detection and diagnosis, prevention and treatments.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 12/29/2020.
References
Social Behavior And Social Understanding
Basic social interaction can be difficult for children with autism spectrum disorders. Symptoms may include:
- Unusual or inappropriate body language, gestures, and facial expressions .
- Lack of interest in other people or in sharing interests or achievements .
- Unlikely to approach others or to pursue social interaction comes across as aloof and detached prefers to be alone.
- Difficulty understanding other peoples feelings, reactions, and nonverbal cues.
- Resistance to being touched.
- Difficulty or failure to make friends with children the same age.
Also Check: Can You Outgrow Autism
Causes And Risk Factors
We do not know all of the causes of ASD. However, we have learned that there are likely many causes for multiple types of ASD. There may be many different factors that make a child more likely to have an ASD, including environmental, biologic and genetic factors.
- Most scientists agree that genes are one of the risk factors that can make a person more likely to develop ASD.4, 19
- Children who have a sibling with ASD are at a higher risk of also having ASD. 5-10
- Individuals with certain genetic or chromosomal conditions, such as fragile X syndrome or tuberous sclerosis, can have a greater chance of having ASD. 11-14, 20
- When taken during pregnancy, the prescription drugs valproic acid and thalidomide have been linked with a higher risk of ASD.15-16
- There is some evidence that the critical period for developing ASD occurs before, during, and immediately after birth. 17
- Children born to older parents are at greater risk for having ASD. 18
ASD continues to be an important public health concern. Like the many families living with ASD, CDC wants to find out what causes the disorder. Understanding the factors that make a person more likely to develop ASD will help us learn more about the causes. We are currently working on one of the largest U.S. studies to date, called Study to Explore Early Development . SEED is looking at many possible risk factors for ASD, including genetic, environmental, pregnancy, and behavioral factors.
Social Communication And Interaction Skills
Social communication and interaction skills can be challenging for people with ASD.
Examples of social communication and social interaction characteristics related to ASD can include:
- Avoids or does not keep eye contact
- Does not respond to name by 9 months of age
- Does not show facial expressions like happy, sad, angry, and surprised by 9 months of age
- Does not play simple interactive games like pat-a-cake by 12 months of age
- Uses few or no gestures by 12 months of age
- Does not share interests with others
- Does not point or look at what you point to by 18 months of age
- Does not notice when others are hurt or sad by 24 months of age
- Does not pretend in play
- Shows little interest in peers
- Has trouble understanding other peoples feelings or talking about own feelings at 36 months of age or older
- Does not play games with turn taking by 60 months of age
Don’t Miss: Do People With Autism Die Early
Types Of Autism Spectrum Disorders Explained
There can be a bit of confusion surrounding autism and its various types. Leaving aside the entire vaccinations-causing-autism-in-children clusterf*ck , there was a diagnostic shift in 2013 that may have left some disorder in its wake. The DSM, or Diagnostic Statistical Manual, is used to define psychiatric disorders worldwide, and has been through many different editions â and its 2013 edition decided to make a classification change. Instead of disorders like Asperger’s and Childhood Disintegrative Disorder being treated as separate problems, they’ve all been dissolved and put under one label: autism spectrum disorder.
It was a controversial decision, and it makes talking about “types” of autism a bit trickier. According to the organization Autism Spectrum, labels like Asperger’s have now been left in favor of diagnosis in terms of severity on two levels: “deficits in social communication, and fixated interests and repetitive behavior”. It seems, however, that medical organizations and autism charities still find the old categories helpful to talk about kinds of autism: places like the National Autistic Society and Autism Speaks still use them. So bear in mind that any guide to the “types” of autism is always going to be subject to argument.
Pervasive Development Disorder Not Otherwise Specified
This mouthful is one of those strange parts of autistic diagnosis that shows why the DSM thought it might be a good idea to reorganize the whole disorder: it’s literally defined as “not fitting into the other categories properly”. It’s regarded as one of the “milder” forms of autism, and is sometimes called atypical autism, but exactly why is, well, complicated.
Basically, people with PDD-NOS don’t quite fit into a diagnosis either of full Asperger’s or of autistic disorder. They tend to be high-functioning, but their particular symptoms include childhood developmental delay, which means Asperger’s isn’t the right diagnosis. They may also have a range of autistic disorder symptoms, but only in mild forms or have some of the symptoms, but not enough of them to fully qualify. Basically, it’s the outlier. PDD-NOS children and adults are often socially oriented, for instance, but it’s tricky to outline exactly what the symptoms are because there’s so much variation.
Recommended Reading: Dyslexia Adhd Autism
What Are The Symptoms Of Autism
The most obvious symptoms tend to involve communication and interaction with others.
Autistic people may have different ways of learning, thinking, and problem-solving. Intellectually, autistic people can fall on a range from severely challenged to gifted.
Everybody is different. Some people will have many symptoms, and some will have only a few. Signs of autism in a 3-year-old or 4-year-old may look different from those who are teens or adults. Some autistic people may be able to mask their symptoms.
General signs of autism may include:
- not responding to their name
- avoiding eye contact or not showing an awareness when others are speaking
- not understanding sharing or taking turns
- not looking at objects shown to them
- not pointing or responding to pointing
- having difficulty understanding facial expressions
In older children and adults, you might also notice:
- having difficulty reading body language, facial expressions, and other social cues
- not getting sarcasm, teasing, or figures of speech
- speaking in monotone
Late Walkers And Genetic Changes
The later age of walking is not surprising.
The children with mutations did have another notable difference from the comparison group: they took their first steps several months later, between 14.7 and 19 months of age. Dr. Bishop’s team concluded that the age at which a child with autism learns to walk by himself could be a clue of a “potential genetic abnormality.”1
The link between late walking and genetic conditions is not new. Delayed motor skills are often seen in children with genetic disorders such as velocardiofacial, Fragile X, and Noonan syndromes.4 Late walking also is more common in children with intellectual disability, compared to typically developing children and children with autism.1, 5 Autism is more common in people with certain genetic conditions, such as Fragile X, Down, and Phelan-McDermid syndromes and tuberous sclerosis, than in the general population.
“The later age of walking is not surprising,” Dr. Bishop said. “A gross motor milestone delay is very common in kids with genetic syndromes, with or without ASD. In that regard, kids with a de novo mutation look more like kids with a genetic syndrome and autism, than kids without a genetic syndrome, and autism.”
Read Also: High Functioning Autism Prognosis
How Is Autism Managed
If your child is diagnosed with autism, you will be guided through the various treatment options. There are education programs and support services available for children with autism and their parents or caregivers from a number of organisations such as Autism Spectrum Australia.
Treatments used to manage autism are best started as early in a persons life as possible. Specific symptoms and social skills can be improved with the right support and programs. Because everyone with autism is different, the best results are obtained from a treatment program specifically tailored to their individual needs.
Language and social skills are taught through intensive educational programs and behavioural therapies. Speech pathology focuses on developing communication and social skills. Occupational therapy concentrates on sensory motor development, such as learning play and fine motor skills, as well as how to cope in social situations.
Public and private schooling options are available for children with autism. Find out more about schooling options on the Autism Awareness website.
Sometimes claims are made about treatments that are misleading. Avoid treatments that offer a cure or recovery as there is no evidence to support these claims. Ensure that the treatments and supports you choose are informed by evidence.
Autism Awareness Australia provides self-care tips and helpful links and resources.
The Different Types Of Autism And How To Recognize Each On The Spectrum
When people hear the word autism they often have an idea of an individual in their head. Although those preconceived notions may be true for some people with Autism, not all people fall under that classic Autistic category.Autism often presents itself first and foremost during the pivotal developmental years of a young child, from ages 0-6. During these ages, the child may miss certain milestones that he or she should be hitting for their age, causing concern among their parents and family members.
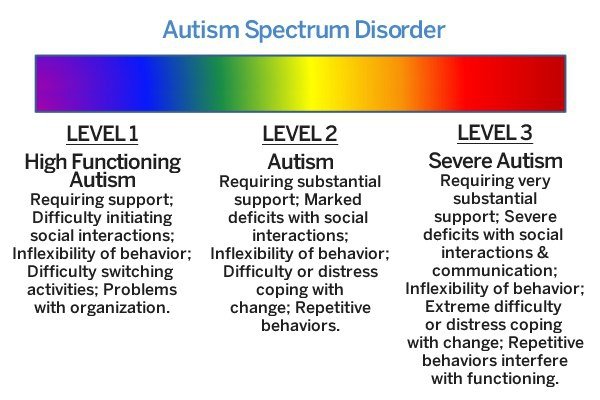
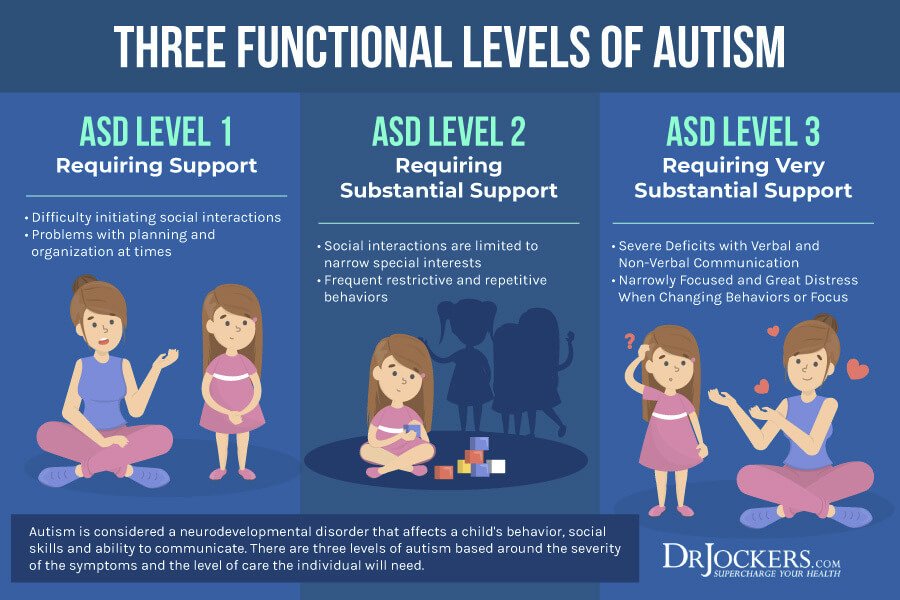
Symptoms and signs of Autism Spectrum Disorder will vary from person to person, as no two cases are the same. Did you know that there are three different types of Autism Spectrum Disorders ? Read below to learn more about each type of Autism and how you can identify it.
You May Like: Life Expectancy Of People With Autism
What Conditions Are Considered Spectrum Disorders
Until recently, experts talked about different types of autism, such as autistic disorder, Aspergerâs syndrome, pervasive developmental disorder not otherwise specified . But now they are all called âautism spectrum disorders.â
If you still hear people use some of the older terms, youâll want to know what they mean:
Asperger’s syndrome. This is on the milder end of the autism spectrum. A person with Asperger’s may be very intelligent and able to handle their daily life. They may be really focused on topics that interest them and discuss them nonstop. But they have a much harder time socially.
Pervasive developmental disorder, not otherwise specified . This mouthful of a diagnosis included most children whose autism was more severe than Asperger’s syndrome, but not as severe as autistic disorder.
Autistic disorder. This older term is further along the autism spectrum than Aspergerâs and PDD-NOS. It includes the same types of symptoms, but at a more intense level.
Childhood disintegrative disorder. This was the rarest and most severe part of the spectrum. It described children who develop normally and then quickly lose many social, language, and mental skills, usually between ages 2 and 4. Often, these children also developed a seizure disorder.