An Insight Into The Various Types Of Autism
Let us now get a deeper insight into each of the following forms of Autism.
Fig 3:
As mentioned at the beginning of this article, the various types of autism spectrum disorders present;a significant overlap with one another. The following 3 characteristics are carefully evaluated to arrive at the right conclusion:
- Social skills within families;coping with Autism;and externally
- Autism Communication Skills
For example, it is extremely hard;to discriminate between mild PDD and moderate Aspergers symptoms as a patient may demonstrate both characteristics in the autism spectrum quotient.
Cultural And Linguistic Considerations
Awareness of individual and cultural differences is essential for accurate diagnosis. For example, direct eye contact with an authority figure may be considered disrespectful in some cultures, and silence may be valued as a sign of respect. In a U.S. school system, these behaviors could easily be misinterpreted as socially inappropriate.
The core characteristics of ASD may be viewed through a cultural lens leading to under-, over-, or misdiagnosis . Signs and symptoms that are clearly “red flags” in the U.S. health care or educational system may not be viewed in the same way by someone from a culture that does not formally define the disorder.
Cultural and linguistic variables may contribute to the disparity in the diagnosis of ASD among some racial/ethnic groups . For example, Begeer et al. found that Dutch pediatricians might be inclined to attribute social and communication problems of non-European minority groups to their ethnic origin, while attributing these same characteristics to autistic disorders in children from majority groups.
Benefits Of Early Accurate Diagnosis
An early, accurate diagnosis of ASD can help families and caregivers access appropriate services, provide a common language across interdisciplinary teams, and establish a framework to help families and caregivers understand the child’s difficulties. Any diagnosis of ASDâparticularly of young childrenâis periodically reviewed by members of the interdisciplinary team because diagnostic categories and conclusions may change as the child develops.
The identification of early behavioral indicators can help families and caregivers obtain appropriate diagnostic referrals and access early intervention services, even before a definitive diagnosis is made . Furthermore, early intervention can improve long-term outcomes for many children . A number of researchers have been reporting the benefits of providing intervention to at-risk infants that targets pre-linguistic communication .
Don’t Miss: Symmetra Hindi Voice Lines
Treatment Considerations: Transitioning Youth And Adults
The core challenges associated with ASD can have an impact on the ability to succeed in postsecondary educational programs, employment, and social relationships, and to acquire the skills needed to live independently .
Individuals with ASD who are transitioning to young adulthood experience high rates of unemployment and underemployment and may have difficulty maintaining employment once secured . Socially, they may discontinue friendships, participate in fewer social activities , and experience social isolation .
These findings highlight the need for continued support to facilitate a successful transition to adulthood. SLPs are involved in transition planning in high school and may be involved, to varying degrees, in other support services beyond high school.
Transition planning for individuals with ASD may include
- determining the need for continued therapy, if appropriate;
- identifying career goals and educational needs;
- providing academic or career counseling;
- providing opportunities for work experience;
- discussing housing options; and
- facilitating community networking .
Effective transition planning involves the student as an active and respected member of the team as well as their family, who can provide valuable information about the student’s needs. See ASHA’s resource on transitioning youth.
Where Can I Get More Information
For more information on neurological disorders or research programs funded by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, contact the Institute’s Brain Resources and Information Network at:
Office of Communications and Public LiaisonNational Institute of Neurological Disorders and StrokeNational Institutes of HealthBethesda, MD 20892
NINDS health-related material is provided for information purposes only and does not necessarily represent endorsement by or an official position of the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke or any other Federal agency. Advice on the treatment or care of an individual patient should be obtained through consultation with a physician who has examined that patient or is familiar with that patient’s medical history.
All NINDS-prepared information is in the public domain and may be freely copied. Credit to the NINDS or the NIH is appreciated.
Read Also: What Is The Life Expectancy Of People With Autism
Modern Interpretation Of Types Of Autism
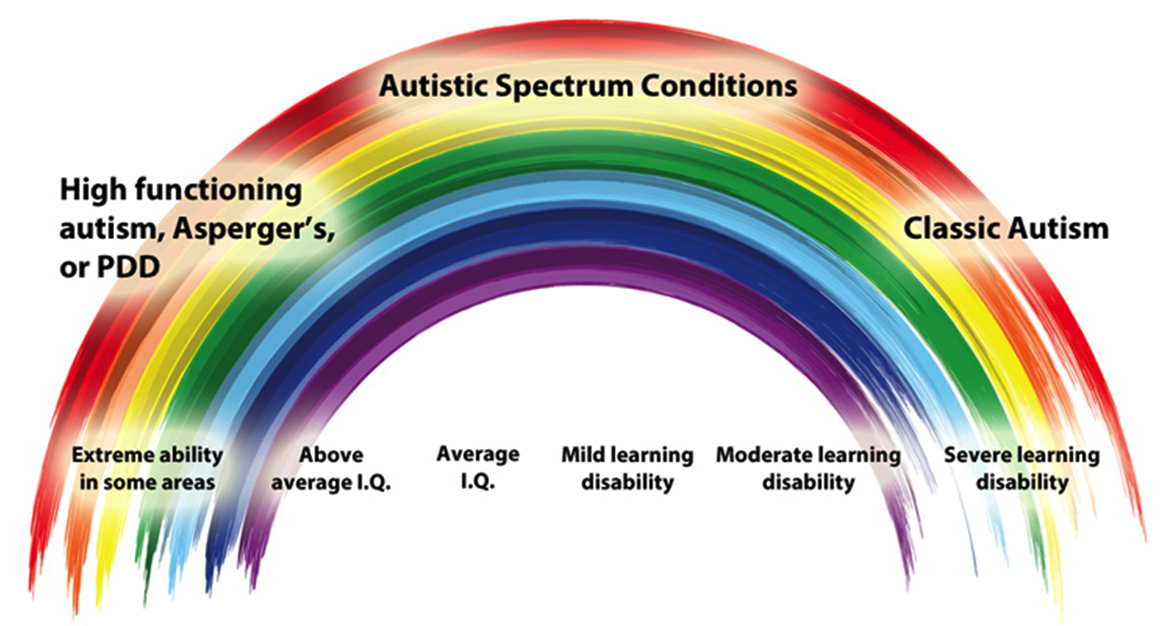
Fig 3
Each type of Autism;demonstrates a;degree of difficulty that a patient;faces with verbal, social and communicative;interactions. Just as a shade in rainbow overlaps and blends to the next one, so does the autism spectrum; thus turning it into a challenging exercise for physicians;to determine where one range in the spectrum;starts and where it ends, comments Mary Alexa, autism therapy specialist.
What Conditions Are Considered Spectrum Disorders
Until recently, experts talked about different types of autism, such as autistic disorder, Aspergerâs syndrome, pervasive developmental disorder not otherwise specified . But now they are all called âautism spectrum disorders.â
If you still hear people use some of the older terms, youâll want to know what they mean:
Asperger’s syndrome. This is on the milder end of the autism spectrum. A person with Asperger’s may be very intelligent and able to handle their daily life. They may be really focused on topics that interest them and discuss them nonstop. But they have a much harder time socially.
Pervasive developmental disorder, not otherwise specified . This mouthful of a diagnosis included most children whose autism was more severe than Asperger’s syndrome, but not as severe as autistic disorder.
Autistic disorder. This older term is further along the autism spectrum than Aspergerâs and PDD-NOS. It includes the same types of symptoms, but at a more intense level.
Childhood disintegrative disorder. This was the rarest and most severe part of the spectrum. It described children who develop normally and then quickly lose many social, language, and mental skills, usually between ages 2 and 4. Often, these children also developed a seizure disorder.
Recommended Reading: How To Make A Visual Schedule For Autism
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Asd
Every person with ASD is unique, so the timing and severity of the first signs and symptoms can vary widely. Some children with ASD show signs within the first few months of life. In others, symptoms may not become obvious until 24 months or later. Some children with ASD appear to develop normally until around 18 to 24 months of age and then stop gaining new skills and/or start losing skills.
During infancy , a child may show symptoms that include:
- Limited or no eye contact
- No babbling
- Appearing not to hear
- Playing with toys in an unusual or limited manner
- Showing more interest in objects instead of people
- Starting language skills but then stopping or losing those skills
- Showing repetitive movements with their fingers, hands, arms or head
Up to 2 years of age, there may be continuing symptoms from infancy. A child may also:
- Focus only on certain interests
- Be unable to have reciprocal social interactions
- Move in unusual ways, such as tilting their head, flexing their fingers or hands, opening their mouth or sticking out their tongue
- Have no interest in playing with other children
- Repeat words or phrases without appearing to understand them
- Have behavioural issues, including self-injury;
- Have trouble controlling their emotions
- Like to have things a certain way, such as always eating the same food
Possible signs of ASD at any age:
Signs Of Autism In Children
The signs of autism can change as children grow babies and toddlers show different signs of autism than children aged 4 and older.;
Babies and toddlers
Signs of autism in babies and toddlers can include a number of things that affect different parts of their life and behaviour.
Autistic babies and toddlers might:
- start talking later than most children
- seem less aware of others around them for example, they might not respond to their name being called
- make repetitive movements when excited or upset – for example flapping their hands, rocking back and forth, or making the same noise repeatedly
Autistic babies and toddlers might not:
- smile back when you smile at them
- point to show when they want something
- point to show you something they find interesting
Autistic babies and toddlers might:
- spend a long time setting up toys in a certain way, and set them up the same way every time
- enjoy lining toys up in order, or watching parts of them move
Autistic babies and toddlers might not:
- seem interested in playing with other children their age
- seem to use their toys to make up stories or pretend they might also start pretend play at a later age than most children
Autistic babies and toddlers might:
- react strongly to sounds, smells, touch, tastes, or things they can see for example, if they like the way a stuffed toy feels, they want to spend a lot of time stroking the toy
- become upset if given something to eat or drink thats new to them
- eat a limited range of foods
Recommended Reading: Do Autistic Toddlers Dance
Autism Spectrum Disorders And Depression
Young people and adolescents with ASDs also are more likely to have depression. Researchers have found that people with autism spectrum disorders are four times more likely to have depression during their lives.
In addition to feelings of hopelessness and physical symptoms such as tiredness, depression in people with ASDs can consist of:
- Obsessive behaviors
- Sleep problems
What Are Autism Spectrum Conditions
The first few weeks in my new job were overwhelming. I dont like surrounding myself with too many people, and there were a lot of rules to get used to. But then I got a workplace mentor who explained some of the rules about using the work kitchen, and they helped me to draw up a timetable of my working day so everything was in small chunks of time.
Autism Spectrum Conditions are the name for a number of different neurological conditions. They include a wide range of symptoms and different levels of ability. People who have previously been diagnosed with Aspergers Syndrome or with Autism all fall under what we now call ASC.
ASC is a developmental difference – it is something you tend to be born with rather than being caused by head injury or stroke or other neurological condition. People with ASC may not receive an official diagnosis until adulthood if they are what we call high functioning.
Also Check: Life Expectancy Of Autism Spectrum Disorder
Human Rights And Legal Status
The law treats person with intellectual disabilities differently than those without intellectual disabilities. Their human rights and freedoms, including the right to vote, the right to conduct business, enter into a contract, enter into marriage, right to education, are often limited. The courts have upheld some of these limitations and found discrimination in others. The , which sets minimum standards for the rights of persons with disabilities, has been ratified by more than 180 countries. In , and several states, persons with intellectual disabilities are disenfranchised. The ruled in Alajos Kiss v. Hungary that Hungary violated the applicant’s rights by a blank disenfranchisement of persons with intellectual disabilities who did not hold legal capacity.
Treatment Considerations: Asha’s Position

Several treatment options and approaches lack scientific evidence of validity and are not endorsed by ASHA. They are Auditory Integration Training , Facilitated Communication , and Rapid Prompting Method . Below are brief descriptions of these treatments, along with ASHA’s position on each. Click on the hyperlinks provided to read ASHA’s full position statements.
Auditory Integration Training
Auditory Integration Training is a type of sensory integration treatment that involves exercising the middle ear muscles and auditory nervous system to treat a variety of auditory and nonauditory disorders, including auditory processing problems, dyslexia, learning disabilities, attention-deficit disorders, and ASD. The treatment typically involves listening to specially filtered and modulated music for two 30-minute sessions per day for 10 consecutive days. The objective is to reduce distortions in hearing and hypersensitivity to specific frequencies so that the individual will be able to perceive soundsâincluding speechâin a normal fashion.
According to ASHA’s position statement titled, Auditory Integration Training, “The 2002 ASHA Work Group on AIT, after reviewing empirical research in the area to date, concludes that AIT has not met scientific standards for efficacy that would justify its practice by audiologists and speech-language pathologists” .
Facilitated Communication
Rapid Prompting Method
Don’t Miss: Is Dr Shaun Murphy Really Autistic
Problems With Communication And Social Interaction
These can include:
- issues with communication, including difficulties sharing emotions, sharing interests, or maintaining a back-and-forth conversation
- issues with nonspeaking communication, such as trouble maintaining eye contact or reading body language
- difficulties developing and maintaining relationships
Autism Spectrum Disorders And Bipolar Disorder
Bipolar disorder, a mental illness that is marked by periods of mania and periods of depression, is another condition sometimes associated with autism spectrum disorders.
One study evaluated people who were then diagnosed with Asperger syndrome and would now be diagnosed with ASDs. It found that prescribing mood stabilizerssuch as lithium and valproic acidor second-generation antipsychotics could help treat both the symptoms of ASDs and bipolar disorder.
Read Also: Overwatch Symmetra Autistic
Social Communication And Interaction Skills
Social communication and interaction skills can be challenging for people with ASD.
Examples of social communication and social interaction characteristics related to ASD can include:
- Avoids or does not keep eye contact
- Does not respond to name by 9 months of age
- Does not show facial expressions like happy, sad, angry, and surprised by 9 months of age
- Does not play simple interactive games like pat-a-cake by 12 months of age
- Uses few or no gestures by 12 months of age
- Does not share interests with others
- Does not point or look at what you point to by 18 months of age
- Does not notice when others are hurt or sad by 24 months of age
- Does not pretend in play
- Shows little interest in peers
- Has trouble understanding other peoples feelings or talking about own feelings at 36 months of age or older
- Does not play games with turn taking by 60 months of age
What Are The Signs Of Autism Spectrum Disorder
Signs of ASD range from mild to severely disabling, and every person is different. The following signs are considered to be red flags that indicate your young child may be at risk for autism. If your child shows any of the following signs, please get in touch with your childs healthcare provider to discuss a referral for an autism evaluation.
The signs include the following:
- Your child doesnt respond to their name being called at all or responds inconsistently.
- Your child doesnt smile widely or make warm, joyful expressions by the age of 6 months.
- Your child doesnt engage in smiling, making sounds and making faces with you or other people by the age of 9 months.
- Your child doesnt babble by 12 months.
- No back-and-forth gestures such as showing, pointing, reaching or waving by 12 months.
- No words by 16 months.
- No meaningful, two-word phrases by 24 months.
- Any loss of speech, babbling or social skills at any age.
Read Also: Life Expectancy With Autism
Autistic Traits And Diagnosis
Autistic traits meaning things that autistic people often do, think, and feel are often shared by people who dont have autism too. This doesnt mean that everyone is a little bit autistic, or that autistic people dont need support.
To be diagnosed with autism, a person has to have a lot of autistic traits from birth, and those traits need to have a big effect on their life. In order to be diagnosed with autism, those traits must cause what a healthcare professional would call clinically significant difficulties in their day-to-day life. This means that they have difficulties with day-to-day life due to their autistic traits and need to use their own ways of overcoming those difficulties, or the people in their life need to help them to overcome them, or both.
Being in a supportive environment makes a big difference to an autistic persons wellbeing and quality of life.
Psychological therapies like cognitive behavioural therapy are often used to treat depression, anxiety, and sleep problems, both in people who have autism and people who dont.
Psychological therapies can help to manage conditions linked with autism, like anxiety, but psychological therapies arent a treatment for autism itself. Therapy techniques might need to be adapted to work for an autistic person.
Challenges in daily living
Possible therapies include:
Finding the right therapies
Language Delay Speech Disorder And Developmental Language Disorder
Language delay is when young children have difficulties understanding and/or using spoken language. If a child has a language delay that doesnt go away, this might be a sign of a developmental language disorder. Children with developmental language disorders have language difficulties that affect their everyday lives and make it harder for them to learn to read.
A speech disorder is when children have difficulty pronouncing the sounds in words. Children with speech disorders dont necessarily have language delay or developmental language disorder.
Not all children who have language delay have problems with speech.
How common are language delays and disorders in autistic children? Autistic children have trouble communicating with others, which means their social communication development can be delayed or disordered. They might also have difficulties with other aspects of language, but their speech development is the least likely to be affected. About 25-50% of autistic children cant communicate verbally.
How are language delays and language disorders treated?Speech pathologists help children with speech and language problems. They might recommend individual or group programs that build language skills. They might also help children develop other ways to communicate, like pictures or picture boards, key word signing or speech generating devices.
Find out more
Also Check: Creating A Visual Schedule Autism