How Does Ritalin Help With Adhd
Ritalin may make it easier for you to concentrate, be less fidgety, and gain control of your actions. You may also find it easier to listen and focus at your job or in school, but If youre already prone to anxiety or agitation, or have an existing psychotic disorder, Ritalin may worsen these symptoms. If you have a history of seizures, this medication may cause more seizures, Also if you dont have ADHD you will feel the stimulant working, it will get you high.
What Can I Expect If I Or My Child Has Adhd
ADHD is a complicated condition with various symptom expressions. If you or your child have ADHD, educate yourself as much as possible about the behaviors that make life difficult. Consider medicines and behavioral treatments. Your healthcare provider will help you with these. He or she will sum up the results of the ADHD evaluation and will recommend appropriate treatment. A combination of pharmacotherapy and behavioral treatment, is generally recommended. A trained behavioral health clinician can give general guidelines for managing your own or your childs ADHD and these can be tailored to your familys needs and your childs strengths and weaknesses.
Also, it is always useful to have appropriate expectations for yourself and your child. Dont expect your child to get out of bed the first time you wake them up, and dont be too hard on yourself if making progress is difficult. It is always best to have your partner and friends help with tasks like organizing and time management. Stay in contact with your healthcare provider, especially if there is a change in you or your childs behaviors, or there is a reaction to prescribed medications.
Two important questions to ask yourself are: 1) “Am I moving forward in the world of action or am I living in my head? 2) “Am I moving closer to my values or am I moving away from what I value?”
Three Subtypes Of Adhd
There are three subtypes of ADHD: predominantly inattentive, predominantly hyperactive-impulsive, and a combination of the two.
Predominantly Inattentive Subtype is typically easier to overlook than other forms of ADHD because people who have it often appear shy, day-dreamy, or spacey instead of disruptive.
They may sit quietly, but they are distracted by their own thoughts and have a hard time staying focused on any one thing.
Predominantly Hyperactive-Impulsive Subtype is the most common type of ADHD in children and adults .
People with this subtype tend to fidget or talk excessively. They are impulsive, which can mean they have trouble waiting for things they want or interrupt conversations.
Combination Subtype has features of both the combined hyperactive/impulsive and inattentive subtypes of ADHD .
This type is often how ADHD presents itself clinically. People with this subtype generally experience both of the main features of ADHDinattention and hyperactivity/impulsivity.
Recommended Reading: How To Solve Autism Problem
In The Amygdala The Cerebellum And Elsewhere
There are few things more infuriating to mental health professionals than hearing “ADHD is not real.” Yes, we are headed into the year 2022, and there are still critics, cynics, criticizers, and non-believers vying for the opportunity to disprove the diagnosis.
Do I personally believe that the DSM-5 does a great job at outlining the criteria for the diagnosis? Not by a long shot. Do we need more research to help rule out other disorders that overlap with ADHD symptoms? 100 percent. Does the disorder perhaps even need a different name entirely? Absolutely.
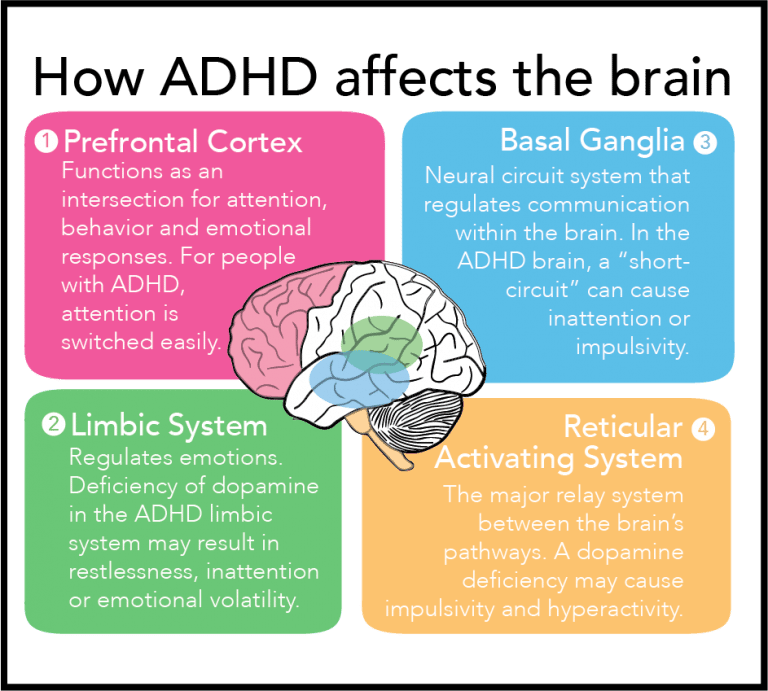
ADHD is not a disorder of attention deficit instead, it is a disorder of regulating attention and emotions due to structural and functional differences in the brain and neural networks. I suspect that the doubt and suspicion of the disorder stem from the belief that ADHD is categorized by a single deficit rather than categorized dimensionally. ADHD is not a disorder of ability but performance due to neuroanatomical differences.
Regardless, it’s time that ADHD be recognized for what it is: a neurodevelopmental disorder, not a myth, nor a result of poor parenting. Below I will outline structures of the brain that are different in volume and shape and how those differences are thought to be linked to behaviors associated with ADHD. The ADHD brain is structurally and functionally distinct, and hopefully, the evidence below will keep the naysayers quiet… for now.
What Happens If Adhd Is Left Untreated
Symptoms will continue if ADHD is left untreated and people are left to manage them on their own. Children may struggle at school, home and in social situations, and adults may struggle with work, education, interactions with friends and family and more. Untreated ADHD makes life harder than it has to be.
You May Like: Is Tip Toeing A Sign Of Autism
How Is Pharmacotherapy Used To Treat Adhd
A group of drugs called psychostimulants are an effective treatment for ADHD. The two most commonly used medicines in this class are methylphenidates and dextroamphetamines . These medicines help people with ADHD focus their thoughts and ignore distractions. Stimulant medicines are effective in 70% to 90% of patients with ADHD. New medicines are also being developed.
Examples of short-acting , intermediate-acting and long-acting forms of these medications include:
Methylphenidates
- Short-acting: Ritalin®, Focalin®, Methylin Chewable®, Methylin Solution®.
- Long-acting intermediate release: Ritalin SR®, Methylin®, Metadate ER®.
- Long-acting extended-release: Concerta®, Aptensio® XR, Metadate CD®, Metadate ER®, Ritalin LA®, Focalin XR®, Daytrana®, Quillivant XR® Jornay.
D-Amphetamines
- Short-acting: Dextrostat®, Dexedrine Tabs®, Evekeo®, Zenzedi®, Adderall®, ProCentra®.
- Long-acting intermediate release: Adderall®, Dexedrine Spansule®.
- Long-acting extended-release: Vyvanse®, Adderall XR®, Dyanavel® XR, Adzenys® XR-ODT.
Non-stimulant medicines include atomoxetine guanfacine , and clonidine . They are often used as additional treatment, or can be used on their own if the healthcare provider approves. New nonstimulant formulations are in the pipeline of several pharmaceutical companies.
What Are Some Additional Strategies For Managing My Childs Adhd At Home
You may find the following strategies helpful for managing ADHD in the home:
Behavior:
- Give clear and specific directions and limits: Children with ADHD need to know exactly what others expect from them.
- Catch your child being good: Punishing a child only teaches them what not to do. Recognizing and acknowledging positive behaviors is an effective way to teach your child what to do. This increases the expression of appropriate behavior.
- Set up an effective behavior system: Create a consistent system to reward appropriate behavior and respond to misbehavior with alternatives such as a “time out” or loss of privileges. Corporal punishment is not effective. A common practice is to use “marbles-in-a-jar” wherein the child earns one marble for a specified appropriate behavior in the household. When a certain number of marbles are earned, they can be exchanged for a privilege.
Organization:
- Stick to a schedule: Follow the same routine every day, from wake-up time to bedtime. The schedule should include time for homework and play.
- Use a calendar or planner the child can see: Create a place to write down important reminders, responsibilities and events. These tools may be especially helpful for adolescents and young adults who struggle with time management.
- Organize items that are needed every day: Have a place for everything and keep everything in its place. This includes clothing, backpacks and school supplies. An organization checklist may be helpful.
Homework time:
Also Check: What Age Can They Diagnose Autism
Why Does The Adhd Brain Lose Interest In Tasks
PET imaging studies of brains in people diagnosed with ADHD demonstrate that chemicals that activate reward-recognizing circuits in the brain tend to bind on significantly fewer receptor sites in people with ADHD than do those in a healthy comparison group. These and other imaging studies may help explain why people with ADHD tend to be less able than their peers to anticipate pleasure or register satisfaction with tasks for which the payoff is delayed. An important effect is that they have great difficulty in activating themselves to get started on tasks that are not especially interesting to them and in sustaining motivation to complete tasks for which the rewards are not imminently available. Thomas E. Brown, Ph.D., from his book Smart But Stuck
What Makes Adhd Symptoms Worse
Certain behaviors are expected depending on the age of a person. Because the brain doesnt develop at the same rate in everyone, cognitive functions may be poor in some people and not in others. A child 10 years old, for example, might only have the abilities of a younger child 8 years old rather than his or her same age peers. Therefore, as you or your child get older, the problem is not that ADHD gets worse, its that the childs abilities are not developing synchronized with age.
Although ADHD doesnt get worse, the tasks expected of the person become more complicated with age and circumstances, such as increased demands in school, therefore, the problematic behaviors become more problematic. For example, as the child may get a lower grade for turning in late work. Examples of other complications include:
Also Check: What Causes Autism In Pregnancy
Adhds Impact On Productivity:
In numerous studies and articles, the link between work productivity and untreated ADHD has shown to be great.
Symptoms displayed in the workplace can have a large influence on how productive the employee is at their job. Employees are easily distracted and may struggle to stay focused, especially in todays workplace. As a result, they may have a tendency to make mistakes. Their challenges with organizing, prioritizing, and planning also affect their productivity. Effective treatment and ADHD-friendly strategies can help reduce symptoms and allow a person with ADHD to perform their job at an optimum level. Furthermore, factors such as work environment, job tasks, coping skills and workplace accommodations may influence an employees ability to succeed. However, some common factors that must be overcome are poor planning skills, memory issues, self-discipline, behavior awareness, lack of motivation and concentration.
An employee with ADHD will likely find they are better able to manage the effect of their ADHD on productivity as they learn about how their brain works and its impact on their efforts. With awareness, comes better-informed strategies. Coaching and training can also greatly help the employee with ADHD.
ADHD and Burnout:
The following articles provide strategies for preventing and managing burnout in ADHD employees.
How Do Stimulants Work In The Adhd Brain
Stimulation is an easily measured feature of the first-line stimulant medications, but it is not clear that stimulation is how and why they work for attention deficit disorder . There are 43 medications currently available that stimulate in the same way that amphetamine and methylphenidate do, but only three of those medications make ADHD better. The rest make it worse. Just being a stimulant is not enough to make a medication work in an ADHD brain.
A PET scan study was done monitoring a specially prepared solution of methylphenidate to see where it wound up in the human brain. Everyone expected that it would go to somewhere in the fronto-parietal cortex, or to some area that was rich in adrenaline or dopamine nerves. It didnt. Instead it was actively pulled out of the blood and concentrated in only one area at the exact center of the brain called the corpus striatum.
The striatum has no adrenaline or dopamine activity. The striatum is your executive assistant. It scans all of your thoughts, feelings, and experiences and sends the one most important thing up to your cortex for you to think about. Everything else is handled behind the scenes.
Recommended Reading: Can A Child Get Autism Later In Life
The Link Between Ahdh And Risky Behavior
Because people with ADHD have lower levels of dopamine, the chemical that gives you a sense of excitement and arousal, they may be more likely to engage in risky behaviors like drugs, alcohol, having sex at an earlier age, or even adrenaline-seeking activities like bungee jumping or car racing. This is because the thrill of the behavior increases dopamine in the brain. Its especially difficult for those with ADHD to do mundane, boring tasks because of their need for stimulating activities. Rossillo says.
But this doesnt mean that all people with ADHD should become stuntmen to be fulfilled a 9-to-5 desk job just might not be their thing. Many individuals with ADHD may ultimately look for jobs that include constant movement, high intensity, or a fast-paced environment, Rossillo says. Emergency room doctor, anyone?
How Does Adhd Affect The Nervous System
The nervous system includes how your brain and body communicate with each other.
People who have ADHD might be more sensitive to touch, taste, or smell .
That means how ADHD affects the nervous system is actually a symptom of how it affects how you feel about something.
And how ADHD affects the nervous system can also make it harder for people to control how they react.
People with ADHD are more likely to have problems managing their emotions .
That means that how you feel about something or how well you can focus on something is ultimately why ADHD affects the brain and how we communicate with our body in how ADHD affects how the body works.
You May Like: Is Max From Max And Ruby Autistic
Cardiovascular And Other Health Risks For Adults With Adhd
5. Cerebellum. The cerebellum is associated with the coordination of motor movements balance control, gait, posture, muscle tone, and voluntary muscle activity. Damage to this area in humans results in a loss in the ability to control fine movements, maintain posture, and motor learning. A 2017 study found that children with ADHD had significantly smaller cerebellar volumes. This structural difference could help account for the fine motor delays often seen in ADHD, i.e., using a pencil or grasping a spoon. It could also be responsible for dyspraxia, a developmental coordination disorder, which can co-occur with ADHD.
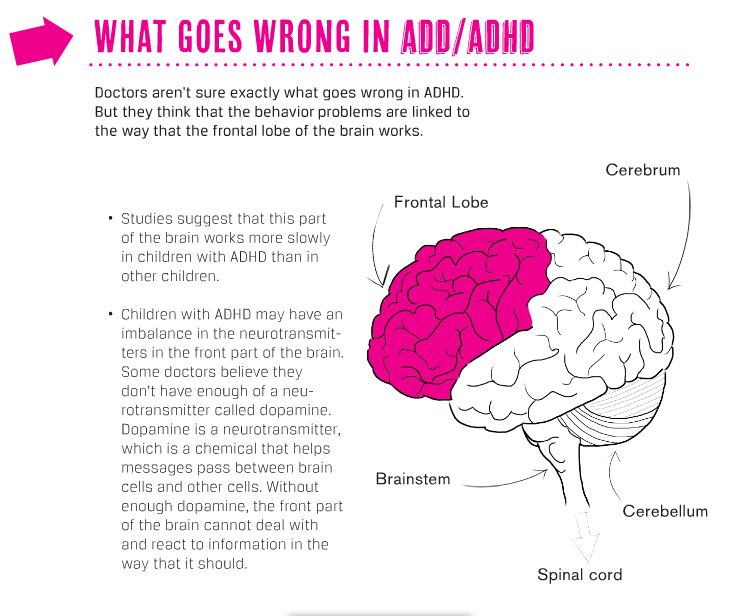
6. Prefrontal cortex. The prefrontal cortex is related to self-awareness, , judgment, insight, empathy, and the ability to self-regulate emotion and behavior. Studies have found that ADHD is associated with weaker function in the PFC, thinner PFC, and different structure of the prefrontal cortex. This may help us account for the ADHD shortfalls in advantageous , planning for the future, time management, procrastination, poor social skills, difficulty in maintaining relationships, externalization behaviors such as disruptive, aggressive, and defiant behaviors, lack of impulse control, and disorganization.
LinkedIn and Facebook image: Riderfoot/Shutterstock
What Does Adhd Do To The Brain
How does ADHD affect the brain? Research shows how it affects the three regions of your brain: the prefrontal cortex, striatum, and cerebellum.
The Prefrontal Cortex is the front part of your brain that regulates behavior, personality expression, judgment, motivationbasically everything you do with emotions .
On the other hand, the striatum controls how you plan, how you act on those plans, and how you adapt to changing situations.
And the cerebellum is the part of your brain that helps control how quickly or slowly things happen .
People with ADHD have trouble filtering out unnecessary or irrelevant stimuli, which can make it harder to focus on what they want to focus on.
They also tend to be more impulsive and impatient, making them less able to inhibit responses .
Also Check: Can Smoking While Pregnant Cause Autism
Why Is The Adhd Brain Often Swamped By Emotion
There are two primary ways in which emotions play a critical role in the chronic difficulties of people with ADHD. Both are related to working memory impairmentsthe persons limited capacity to keep in mind and use multiple bits of emotion-laden information at the same time. Sometimes the working memory impairments of the ADHD brain allow a momentary emotion to become too strong the person is flooded with one emotion and unable to attend to other emotions, facts, and memories relevant to that memory.
At other times, the working memory impairments of ADHD leave the person with insufficient sensitivity to the importance of a particular emotion because he or she hasnt kept other relevant information sufficiently in mind, or factored it into his or her assessment of the situation. Thomas. E. Brown, Ph.D., from his book Smart But Stuck
How Does It Work
Have you ever tried patting your head with one hand while rubbing your belly with the other?
While it may feel impossible at first, over time you may find you are able to do so without putting much thought into it. This simple activity exercises your brain, pushing it to perform a complex task.
ADHD brain exercises follow that same logic.
Developing science suggests the brain is pliable and that our experiences can continue to rewire and change our brains throughout our lives.
This idea, called neuroplasticity, is the basis for brain training.
Brain training programs work to harness neuroplasticity, says Cara Koscinski, a doctor of occupational therapy. This means our brains can form new connections over time.
These new connections can allow the brain to:
- adapt to learning new things
- recover from traumatic injury, like stroke
- build connections for smoother function
- enhance impulse control and decision-making
Based on the science of neuroplasticity, its thought that practicing certain tasks and skills can rewire the brain to improve memory or attention.
Those with ADHD may be able to improve ADHD characteristics through brain training, but its still best to support with other treatments.
Brain training is a non-pharmaceutical intervention that uses technology tools to help people with ADHD improve executive functioning, explains counselor Joshua McKivigan.
Executive functioning is a skill set that includes:
- paying attention
- making decisions
Brain exercises include:
Don’t Miss: How To Know If My Baby Has Autism
Adhd Slows Brain Development
The brain develops the same way in the ADHD brain. However, brain development is slower, especially in the front parts that help control attention and impulsivity. Thus, ADHD is considered a neurodevelopmental disorder.
Over time, the ADHD brain does mature. However, depending on severity of symptoms, the brain might not reach the same level of maturity as the non-ADHD brain. Indeed, neuroscientists found that adults who were diagnosed with ADHD as children had a lower total brain volume than adults who were not diagnosed with ADHD. The cortical thickness of the outer layer of their brain was lower and they had more cortical thinning in the parts of the brain affected by ADHD.
Essentially, this means that these adults had fewer brain cells in these areas. A reason why may be because the non-ADHD brain develops brain cells faster than the ADHD brain. Thus, those individuals have more grey matter to start with in the first place before cortical thinning starts to happen.