What Are Some Common Signs Of Asd
Even as infants, children with ASD may seem different, especially when compared to other children their own age. They may become overly focused on certain objects, rarely make eye contact, and fail to engage in typical babbling with their parents. In other cases, children may develop normally until the second or even third year of life, but then start to withdraw and become indifferent to social engagement.
The severity of ASD can vary greatly and is based on the degree to which social communication, insistence of sameness of activities and surroundings, and repetitive patterns of behavior affect the daily functioning of the individual.
Social impairment and communication difficultiesMany people with ASD find social interactions difficult. The mutual give-and-take nature of typical communication and interaction is often particularly challenging. Children with ASD may fail to respond to their names, avoid eye contact with other people, and only interact with others to achieve specific goals. Often children with ASD do not understand how to play or engage with other children and may prefer to be alone. People with ASD may find it difficult to understand other peoples feelings or talk about their own feelings.
Asd Risk Genes Overlap With Other Diseases
Large-scale sequencing studies of major psychiatric diseases have revealed extensive overlap in risk loci, challenging the classification of these conditions as distinctive disorders. In 2013, the Cross-Disorder Group of the Psychiatric Genomics Consortium conducted a massive study with 33,332 cases and 27,888 controls in order to identify pathogenic variants shared between ASD, schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, ADHD, and major depressive disorder . In addition to establishing varying degrees of pair-wise crossover, they found loci that reached genome-wide significance for all five disorders near the following genes: inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor heavy chain 3 , arsenite methyltransferase , calcium voltage-gated channel subunit alpha1 C , and CACNB2. Glessner et al. have also conducted a large-scale meta-analysis of structural variants across the same diseases and correlated structural variants in the loci of dedicator of cytokinesis 8 and KN motif and ankyrin repeat domains 1 with all five conditions. Schork et al. recently hypothesized that abnormal gene regulation in radial glia and interneurons during mid-gestation is a mechanism of shared risk, after using GWAS to identify susceptibility loci in genes including phosphodiesterase 1A , protein phosphatase 1 regulatory inhibitor subunit 1C , RHOA, immunoglobulin superfamily member 11 , and sortilin related VPS10 domain containing receptor 3 .
Congenital Heart Disease And Autism: A Possible Link
- , Contributor
Children born with congenital heart disease are now surviving at extraordinarily high rates for most, their life expectancy may be comparable to that of the general population. However, despite the great advances in medical and surgical care, many people with CHD experience long-lasting neurodevelopmental difficulties. These include problems with attention and executive function skills, learning challenges, and in some cases, lower-than-normal IQs.
Also Check: Is The Good Doctor A Good Representation Of Autism
Where Can I Get More Information
For more information on neurological disorders or research programs funded by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, contact the Institute’s Brain Resources and Information Network at:
Office of Communications and Public LiaisonNational Institute of Neurological Disorders and StrokeNational Institutes of HealthBethesda, MD 20892
NINDS health-related material is provided for information purposes only and does not necessarily represent endorsement by or an official position of the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke or any other Federal agency. Advice on the treatment or care of an individual patient should be obtained through consultation with a physician who has examined that patient or is familiar with that patient’s medical history.
All NINDS-prepared information is in the public domain and may be freely copied. Credit to the NINDS or the NIH is appreciated.
Minor Physical Anomalies In Adults With Autism Spectrum Disorder And Healthy Controls
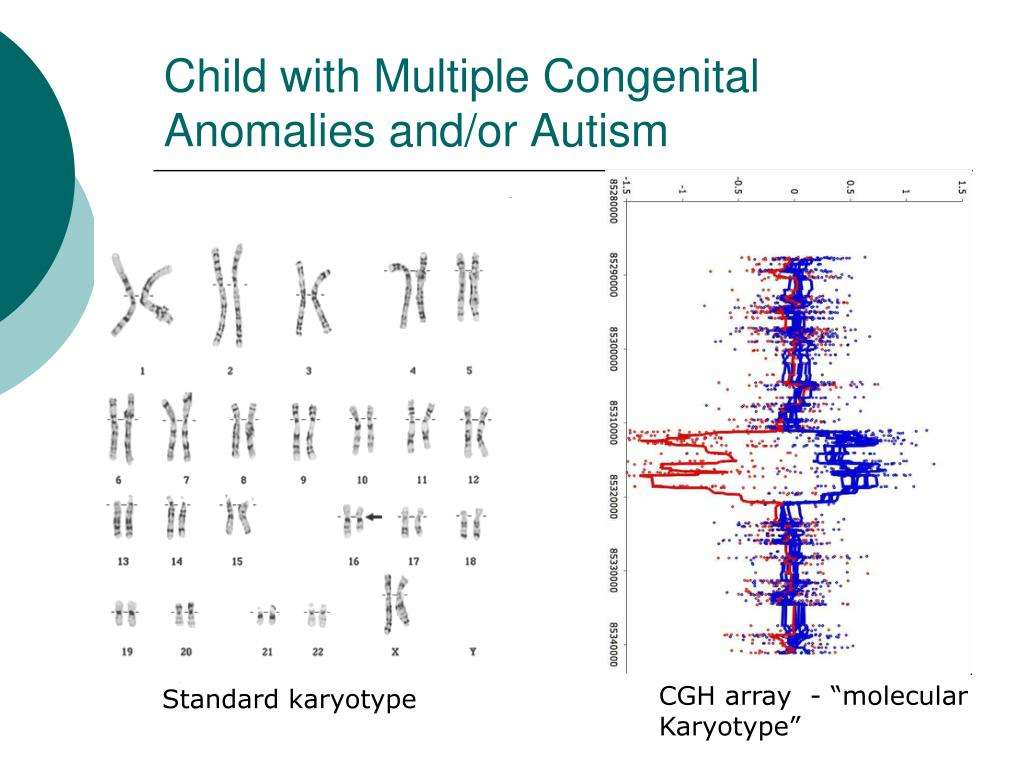
Irina Manouilenko
1Department of Clinical Neuroscience, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden
2Järva Psychiatric Outpatient Clinic, Rinkebysvängen 70A, 4tr, 163 74 Spånga, Sweden
3School of Health and Medical Sciences, Psychiatric Research Center, Örebro University, Örebro, Sweden
Abstract
1. Introduction
Autism spectrum disorder is a group of neurodevelopmental disorders, characterized by atypical development, impairment in reciprocal social interaction and communication, and restricted repetitive and stereotyped patterns of behavior, interests, and activities. ASD includes autistic disorder, Asperger disorder, and pervasive developmental disorders not otherwise specified and occurs in nearly 2% of the population . Males are more affected than females with a sex ratio at about 4:1 . ASD is remarkably heterogeneous and includes people with intelligence levels ranging from severe intellectual disability to very high IQ. Since no specific biological markers for ASD have been identified, the diagnosis of ASD is based on expert evaluation of cognitive, language, social, and emotional functioning along with developmental progress. In twin studies a strong evidence of genetic etiology of ASD has been shown . Several prenatal and perinatal risk factors have also been suggested . Furthermore, autistic traits can be measured at subthreshold level in the normal population, suggesting that the autism phenotype lies along a continuum of quantitative traits .
2. Methods
Don’t Miss: Autism Visual Aid
Clinical Implications And Future Perspectives
When autism was first described, it was hypothesized to be an environmentally caused disease. Decades of research have since revealed that autism is a highly heterogeneous and extremely complex genetic condition. Even though great progress had been made in identifying hundreds of risk genes, very little is known about the different types of modifiers that may exacerbate or ameliorate disease severity. Such modifiers could include epigenetics, sex-linked modifiers, CNVs, double-hit mutations, or environmental factors .
Figure 1. Genetic modifiers in autism spectrum disorder. Autism is estimated to be 4080% heritable. However, both genetic and non-genetic factors modulate the penetrance of risk genes, resulting in a highly heterogeneous disease phenotype for similar pathogenic variants. Examples of genetic modulators include CNV, epigenetics, and double-hit mutations. Examples of non-genetic modifiers include environmental exposures and sex-linked modifiers.
What Disorders Are Related To Asd
Certain known genetic disorders are associated with an increased risk for autism, including Fragile X syndrome and tuberous sclerosis each of which results from a mutation in a single, but different, gene. Recently, researchers have discovered other genetic mutations in children diagnosed with autism, including some that have not yet been designated as named syndromes. While each of these disorders is rare, in aggregate, they may account for 20 percent or more of all autism cases.
People with ASD also have a higher than average risk of having epilepsy. Children whose language skills regress early in life before age 3 appear to have a risk of developing epilepsy or seizure-like brain activity. About 20 to 30 percent of children with ASD develop epilepsy by the time they reach adulthood. Additionally, people with both ASD and intellectual disability have the greatest risk of developing seizure disorder.
Also Check: Autism Symbol Meaning
Terminology And Distinction From Schizophrenia
As late as the mid-1970s there was little evidence of a genetic role in autism while in 2007 it was believed to be one of the most heritable psychiatric conditions. Although the rise of parent organizations and the destigmatization of childhood ASD have affected how ASD is viewed, parents continue to feel social stigma in situations where their child’s autistic behavior is perceived negatively, and many primary care physicians and medical specialists express some beliefs consistent with outdated autism research.
It took until 1980 for the DSM-III to differentiate autism from childhood schizophrenia. In 1987, the DSM-III-R provided a checklist for diagnosing autism. In May 2013, the DSM-5 was released, updating the classification for pervasive developmental disorders. The grouping of disorders, including PDD-NOS, autism, Asperger syndrome, Rett syndrome, and CDD, has been removed and replaced with the general term of Autism Spectrum Disorders. The two categories that exist are impaired social communication and/or interaction, and restricted and/or repetitive behaviors.
The Internet has helped autistic individuals bypass nonverbal cues and emotional sharing that they find difficult to deal with, and has given them a way to form online communities and work remotely.Societal and cultural aspects of autism have developed: some in the community seek a cure, while others believe that autism is simply another way of being.
Genetic Causes And Modifiers Of Autism Spectrum Disorder
- Department of Physiology, Feinberg School of Medicine, Northwestern University, Chicago, IL, United States
Autism Spectrum Disorder is one of the most prevalent neurodevelopmental disorders, affecting an estimated 1 in 59 children. ASD is highly genetically heterogeneous and may be caused by both inheritable and de novo gene variations. In the past decade, hundreds of genes have been identified that contribute to the serious deficits in communication, social cognition, and behavior that patients often experience. However, these only account for 1020% of ASD cases, and patients with similar pathogenic variants may be diagnosed on very different levels of the spectrum. In this review, we will describe the genetic landscape of ASD and discuss how genetic modifiers such as copy number variation, single nucleotide polymorphisms, and epigenetic alterations likely play a key role in modulating the phenotypic spectrum of ASD patients. We also consider how genetic modifiers can alter convergent signaling pathways and lead to impaired neural circuitry formation. Lastly, we review sex-linked modifiers and clinical implications. Further understanding of these mechanisms is crucial for both comprehending ASD and for developing novel therapies.
Recommended Reading: Social Blade Tfue
Congenital Abnormality Of Ocular Movements May Be Due To Defects Of The Nuclei Of Cranial Nerves Or Of The Peripheral Nerve
These are defined as structural changes that have significant medical. Congenital anomalies may have a genetic, infectious or environmental origin Many of studies show that congenital anomalies in newborns have increased due to this kind of treatment. For milder autism spectrum disorders, the symptoms can hide for quite a while. An estimated 6% of babies worldwide are born with a congenital anomaly, resulting in hundreds of thousands of associated deaths.
Is Autism A Congenital Anomaly
Is Autism A Congenital Anomaly. Congenital uterine anomalies may lead to symptoms such as pelvic pain, prolonged or otherwise abnormal bleeding at the time of menarche, recurrent pregnancy loss, or preterm delivery, and thus may be identified in patients, including adolescents, who present with these disorders. Congenital anomalies of the kidney and ureter are a significant cause of morbidity in foetus, neonate, infancy and adulthood.
Learn vocabulary, terms and more with flashcards, games and other study tools. Autism is a developmental disorder characterized by difficulties with social interaction and communication, and by restricted and repetitive behavior. These are also termed as the birth defects. Congenital anomalies comprise a wide range of abnormalities of body structure or function that are present at birth and are of prenatal origin. 341 males, 76 females) than in comparison children (n=2,067
Recommended Reading: Death Note Autism
Sanger Dideoxy Terminator Sequencing
Selected variants were confirmed by Sanger dideoxy terminator sequencing. Primers were designed with Primer3 software. PCR was carried out with HotStarTaq PCR kit and GC-Rich PCR kit was used for GC rich regions. Sequencing products were resolved on an ABI3730 capillary sequencing instrument and chromatograms were analysed with Mutation Surveyor version 3.3 .
The Association Between Congenital Anomalies And Autism Spectrum Disorders In A Finnish National Birth Cohort
Laura Timonen-Soivio
Department of Child Psychiatry, Turku University and Turku University Central Hospital, Turku, Finland
Alan S Brown
Department of Psychiatry, College of Physicians and Surgeons of Columbia University, New York State Psychiatric Institute, New York, NY, USA
Laura Timonen-Soivio
Department of Child Psychiatry, Turku University and Turku University Central Hospital, Turku, Finland
Alan S Brown
Department of Psychiatry, College of Physicians and Surgeons of Columbia University, New York State Psychiatric Institute, New York, NY, USA
Recommended Reading: Articles On Autism In Children
Do Symptoms Of Autism Change Over Time
For many children, symptoms improve with age and behavioral treatment. During adolescence, some children with ASD may become depressed or experience behavioral problems, and their treatment may need some modification as they transition to adulthood. People with ASD usually continue to need services and supports as they get older, but depending on severity of the disorder, people with ASD may be able to work successfully and live independently or within a supportive environment.
What Role Do Genes Play
Twin and family studies strongly suggest that some people have a genetic predisposition to autism. Identical twin studies show that if one twin is affected, then the other will be affected between 36 to 95 percent of the time. There are a number of studies in progress to determine the specific genetic factors associated with the development of ASD. In families with one child with ASD, the risk of having a second child with the disorder also increases. Many of the genes found to be associated with autism are involved in the function of the chemical connections between brain neurons . Researchers are looking for clues about which genes contribute to increased susceptibility. In some cases, parents and other relatives of a child with ASD show mild impairments in social communication skills or engage in repetitive behaviors. Evidence also suggests that emotional disorders such as bipolar disorder and schizophrenia occur more frequently than average in the families of people with ASD.
Recommended Reading: Can A Child Outgrow Autism
Clinical Development And Diagnoses
Leo Kannerearly infantile autism
The word autism first took its modern sense in 1938 when Hans Asperger of the Vienna University Hospital adopted Bleuler’s terminology autistic psychopaths in a lecture in German about child psychology. Asperger was investigating an ASD now known as Asperger syndrome, though for various reasons it was not widely recognized as a separate diagnosis until 1981.Leo Kanner of the Johns Hopkins Hospital first used autism in its modern sense in English when he introduced the label early infantile autism in a 1943 report of 11 children with striking behavioral similarities. Almost all the characteristics described in Kanner’s first paper on the subject, notably “autistic aloneness” and “insistence on sameness”, are still regarded as typical of the autistic spectrum of disorders. It is not known whether Kanner derived the term independently of Asperger.
Kanner’s reuse of autism led to decades of confused terminology like infantile schizophrenia, and child psychiatry’s focus on maternal deprivation led to misconceptions of autism as an infant’s response to “refrigerator mothers“. Starting in the late 1960s autism was established as a separate syndrome.
What Is Autism Spectrum Disorder
Autism spectrum disorder refers to a group of complex neurodevelopment disorders characterized by repetitive and characteristic patterns of behavior and difficulties with social communication and interaction. The symptoms are present from early childhood and affect daily functioning.
The term spectrum refers to the wide range of symptoms, skills, and levels of disability in functioning that can occur in people with ASD. Some children and adults with ASD are fully able to perform all activities of daily living while others require substantial support to perform basic activities. The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders includes Asperger syndrome, childhood disintegrative disorder, and pervasive developmental disorders not otherwise specified as part of ASD rather than as separate disorders. A diagnosis of ASD includes an assessment of intellectual disability and language impairment.
ASD occurs in every racial and ethnic group, and across all socioeconomic levels. However, boys are significantly more likely to develop ASD than girls. The latest analysis from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimates that 1 in 68 children has ASD.
Recommended Reading: Low Functioning Autism Definition
Case And Control Selection
Information was extracted from the Western Australian Maternal and Child Health Research Data Base, which is a register of statutory information that has collected data from the Western Australian Midwives Notification System, birth notifications, and death registrations for all of Western Australia since 1980 . Two control groups were selected from the Western Australian Maternal and Child Health Research Data Base: all known unaffected siblings of cases and a randomly selected population control group of 3 controls per case, frequency-matched by sex to the case group. In total, there were 465 cases, 481 siblings of cases, and 1,313 population controls. Births occurring in 1996 and 1997 were originally in the data set but were excluded because of incomplete case ascertainment for those years. This resulted in there being slightly fewer than 3 controls per case. Further information on case ascertainment, sampling procedures, and study population characteristics can be obtained elsewhere .
Guidelines Recommend Early Evaluation And Treatment
This and other research is raising awareness about the critical need to screen for ASD features in children with CHD, as early as possible. The American Heart Association and the American Academy of Pediatrics have provided guidelines for routine neurodevelopmental evaluation and treatment of children, adolescents, and adults with CHD. Identification of early symptoms related to autism should be done as early as 18 months or whenever there is a concern, with periodic checkups at critical junctures, including school entry and preadolescence. This may be done at a multidisciplinary clinic that provides developmental care for young children with CHD and their families , or by a child psychologist, pediatric neurologist, or neuropsychologist in the community setting.
Once atypical behaviors are identified, prompt interventions to foster social communication, positive parent-child interaction, and social behaviors can be initiated through Early Intervention or other in-home or community-based agencies. Given the amount of variability in the behavioral profiles of children with ASD, these programs must be tailored to each individuals needs, and may include interventions such as applied behavior analysis , occupational therapy, or speech and language therapy. We believe that a proactive approach will lead to improved developmental trajectories and better quality of life for those with CHD and their families.
Don’t Miss: Autism Life Span