Autistic People May Act In A Different Way To Other People
Autistic people may:
- find it hard to communicate and interact with other people
- find it hard to understand how other people think or feel
- find things like bright lights or loud noises overwhelming, stressful or uncomfortable
- get anxious or upset about unfamiliar situations and social events
- take longer to understand information
- do or think the same things over and over
If you think you or your child may be autistic, get advice about the signs of autism.
What Are Some Common Signs Of Asd
Even as infants, children with ASD may seem different, especially when compared to other children their own age. They may become overly focused on certain objects, rarely make eye contact, and fail to engage in typical babbling with their parents. In other cases, children may develop normally until the second or even third year of life, but then start to withdraw and become indifferent to social engagement.
The severity of ASD can vary greatly and is based on the degree to which social communication, insistence of sameness of activities and surroundings, and repetitive patterns of behavior affect the daily functioning of the individual.
Social impairment and communication difficultiesMany people with ASD find social interactions difficult. The mutual give-and-take nature of typical communication and interaction is often particularly challenging. Children with ASD may fail to respond to their names, avoid eye contact with other people, and only interact with others to achieve specific goals. Often children with ASD do not understand how to play or engage with other children and may prefer to be alone. People with ASD may find it difficult to understand other peoples feelings or talk about their own feelings.
Terminology And Distinction From Schizophrenia
As late as the mid-1970s there was little evidence of a genetic role in autism while in 2007 it was believed to be one of the most heritable psychiatric conditions. Although the rise of parent organizations and the destigmatization of childhood ASD have affected how ASD is viewed, parents continue to feel social stigma in situations where their child’s autistic behavior is perceived negatively, and many primary care physicians and medical specialists express some beliefs consistent with outdated autism research.
It took until 1980 for the DSM-III to differentiate autism from childhood schizophrenia. In 1987, the DSM-III-R provided a checklist for diagnosing autism. In May 2013, the DSM-5 was released, updating the classification for pervasive developmental disorders. The grouping of disorders, including PDD-NOS, autism, Asperger syndrome, Rett syndrome, and CDD, has been removed and replaced with the general term of Autism Spectrum Disorders. The two categories that exist are impaired social communication and/or interaction, and restricted and/or repetitive behaviors.
The Internet has helped autistic individuals bypass nonverbal cues and emotional sharing that they find difficult to deal with, and has given them a way to form online communities and work remotely.Societal and cultural aspects of autism have developed: some in the community seek a cure, while others believe that autism is simply another way of being.
Don’t Miss: Does Nick Eh 30 Have Autism
Why Children Are Misdiagnosed
Autism is not always a child’s first diagnosis, particularly if he or she is verbal and of average intelligence. Not infrequently, children who wind up with an autism diagnosis receive a range of other diagnoses firstincluding, in some cases, other types of mental disorders.
There is a simple reason for these misdiagnoses: a child who is bright and verbal may not be evaluated for autism. As a result, the child’s symptoms are viewed not as a set of related challenges, but as individual issues that could potentially be signs of another mental illness. There are a number of behaviors in autism and other mental illnesses that may share characteristics and lead to an erroneous diagnosis.
How You Get A Diagnosis

If you notice signs in your child, see your pediatrician. They can refer you to a mental health expert who specializes in ASDs, like one of these:
Psychologist. They diagnose and treat problems with emotions and behavior.
Pediatric neurologist. They treat conditions of the brain.
Developmental pediatrician. They specialize in speech and language issues and other developmental problems.
Psychiatrist. They have expertise in mental health conditions and can prescribe medicine to treat them.
The condition is often treated with a team approach. That means you might see more than one doctor for your child’s care.
The doctor will ask questions about your child’s behavior, including:
- What symptoms do they have, and when did you first notice them?
- When did your child first learn to speak, and how do they communicate?
- Are they focused on any subjects or activities?
- Do they have friends, and how do they interact with others?
Then they’ll observe your child in different situations to see firsthand how they communicate and behave.
Also Check: Can A Child With Autism Have Dyslexia
Correcting Misdiagnosis And Allowing Multiple Diagnoses Increase Cases
Policy changes in regards to correcting ASD misdiagnosis and allowing for multiple diagnoses has increased ASD prevalence. Historically, ASD has been grossly misdiagnosed, generally as an intellectual disability or attention deficit hyperactivity disorder . Compounding the misdiagnosis factor, medical professionals were restricted to single diagnoses, most opting for an alternative to ASD given the lack of support and services. Both of these policies changed in 2013 with the updated version of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders , after which ASD prevalence continued to spike.
Is Autism Spectrum Disorder A Mental Illness
Autism spectrum disorder has, thanks to the hard work of advocates, become much more well known in recent years, and yet, many questions remain. A common question is whether autism is a mental health disorder or whether it falls under a different diagnostic category.
Unfortunately, this debate misunderstands the nature of mental health diagnostics. A better and more important question may be how can we best meet the deep needs of those with autism spectrum disorder and their families.
Also Check: Can A Child Outgrow Autism
Mental Health And Autism
Those of us with autism are more likely to experience mental health problems than the general population. This can be because there are fewer resources and support to help develop coping skills. Also, we can experience more negative life events, face stigma and discrimination from people and services. Its really important that services are able to properly identify mental health problems, so people can get the right support at the right time.
Diagnosis In Older Children And Adolescents
ASD symptoms in older children and adolescents who attend school are often first recognized by parents and teachers and then evaluated by the schools special education team. The schools team may perform an initial evaluation and then recommend these children visit their primary health care doctor or doctors who specialize in ASD for additional testing.
Parents may talk with these specialists about their childs social difficulties including problems with subtle communication. These subtle communication issues may include problems understanding tone of voice, facial expressions, or body language. Older children and adolescents may have trouble understanding figures of speech, humor, or sarcasm. Parents may also find that their child has trouble forming friendships with peers.
Read Also: What Is The Life Expectancy Of People With Autism
Autism And Bipolar Disorder
People with bipolar disorder tend to alternate between a frenzied state known as mania and episodes of depression.
It is important to understand the symptoms of true bipolar disorder from those of autism by looking at when the symptoms appeared and how long they lasted. For example, a child with autism may be consistently high-energy and socially intrusive through childhood. As such, her tendency to talk to strangers and make inappropriate comments are likely part of her autism, and not a symptom of a manic mood swing.
Treatments: Some of the medications used to treat bipolar disorder can be problematic for some with autism who has difficulty recognizing and expressing feelings. A psychiatrist can provide additional medications that may be safer.
How Mental Illness Is Diagnosed And Treated
Diagnosis
Because of the wide range of mental illnesses in the books, along with the fact that many people have one or more co-occurring mental illnesses, diagnosing mental health problems can be challenging. Diagnosis of mental illnesses is made using specific criteria found in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual for Mental Disorders. In general, mental illness can be classified as mild, moderate or severe. If more than one mental illness is present, mental health professionals will try to determine whether one led to or influenced another. For example, someone with social anxiety may also experience depression as a result of feeling isolated.
Treatment
For someone who is on the autism spectrum and also has a mental illness, treating the mental illness in the context of the developmental disorder is essential for success. People with autism should find a mental health provider who is experienced in treating people who are on the spectrum.
Treating mental illness, like treating autism, requires a highly individualized treatment plan. Ideally, treatment will include both medication and therapy, along with lifestyle changes that support good mental health.
Medication
Therapy
Some of the therapies used to treat mental illness include:
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
Helps individuals identify and change dysfunctional thought patterns and develop skills for coping with negative thoughts and emotions
Interpersonal Therapy
Acceptance and Commitment Therapy
Recommended Reading: Does Jerry Seinfeld Have Autism
Myth: People With Autism Can’t Feel Or Express Emotion Or Understand The Emotions Of Others
Truth: People on the spectrum enjoy a wide range of emotions like neurotypical people, but they often express their emotions in different ways. Although some people with autism may have trouble deciphering unspoken communication or tones of voice, the majority can feel empathy when someone clearly expresses their emotions.
How Is Autism Treated
There is no cure for ASD. Therapies and behavioral interventions are designed to remedy specific symptoms and can substantially improve those symptoms. The ideal treatment plan coordinates therapies and interventions that meet the specific needs of the individual. Most health care professionals agree that the earlier the intervention, the better.
Educational/behavioral interventions: Early behavioral/educational interventions have been very successful in many children with ASD. In these interventions therapists use highly structured and intensive skill-oriented training sessions to help children develop social and language skills, such as applied behavioral analysis, which encourages positive behaviors and discourages negative ones. In addition, family counseling for the parents and siblings of children with ASD often helps families cope with the particular challenges of living with a child with ASD.
You May Like: Best Dogs For Autistic Child
How Doctors Define Autism
Autism spectrum disorder is indeed categorized as a mental disorderalso called a mental illnessin the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders . The DSM-5 also classifies autism as a neurodevelopmental disorder . In other words, although autism is classified as a general mental disorder, it may be better conceptualized by its subcategory: a developmental disorder.
There are many characteristics of autism that overlap with other mental illnesses, so autism is often misdiagnosed as another mental illness. While there can be people who have more than one type of mental illnessincluding developmental disordersthe two may be defined, treated, and managed very differently.
What Are The Symptoms Of Autism
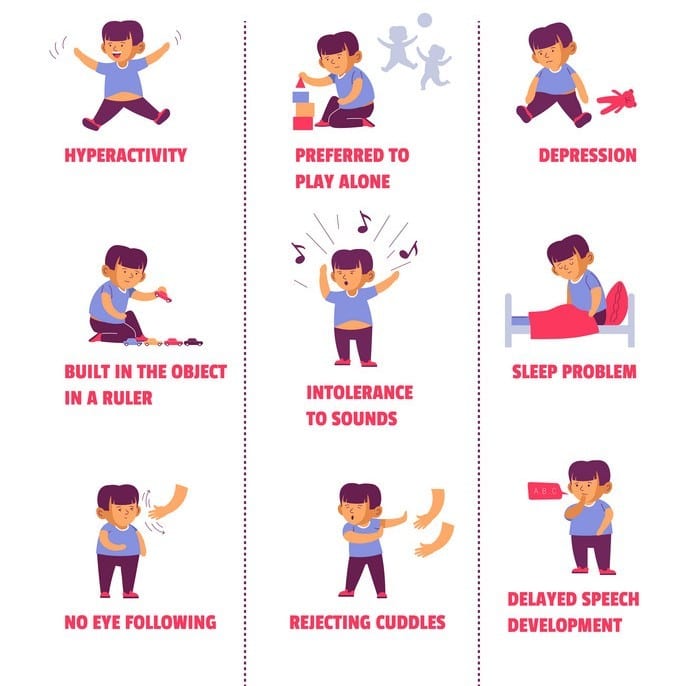
The behaviours associated with autism fall into two broad areas: impaired social interaction and communication, and restricted and repetitive behaviours and interests.
The common signs and symptoms of autism are:
- lack of social or emotional exchanges like pointing, smiling, showing you things
- lack of non-verbal communication such as nodding and shaking head, using hand gestures
- difficulty developing and maintaining relationships appropriate to the age, such as peer play, lack of close friends
- delayed expressed speech and understanding of speech
- lack of eye contact when speaking
- loss of language skills at any age
- excessively following routines, patterns or behaviour, and becoming distressed at changes
- stereotyped or repetitive speech, movements or use of objects, such as rolling wheels before eyes, flapping hands, toe walking
- strongly reacting to sensory input such as sound, pain or textures
- restricted or fixated interests such as only playing with certain toys or discussing certain topics
- being aggressive toward other people or toward self
You May Like: Does Stephen Hawking Have Autism
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Asd
People with ASD have difficulty with social communication and interaction and have restricted interests and repetitive behaviors. The list below gives some examples of the types of behaviors that are common in people diagnosed with ASD. Not all people with ASD will have all behaviors, but most will have several of the behaviors listed below.
Social communication/interaction behaviors may include:
- Making little or inconsistent eye contact
- Having a tendency not to look at or listen to people
- Rarely sharing enjoyment of objects or activities by pointing at or showing things to others
- Failing to, or being slow to, respond to someone calling their name or to other verbal attempts to gain attention
- Having difficulties with the back and forth of conversation
- Often talking at length about a favorite subject without noticing that others are not interested or without giving others a chance to respond
- Having facial expressions, movements, and gestures that do not match what is being said
- Having an unusual tone of voice that may sound sing-song or flat and robot-like
- Having trouble understanding another persons point of view or being unable to predict or understand other peoples actions
Restrictive/repetitive behaviors may include:
People with ASD may also experience sleep problems and irritability. Although people with ASD experience many challenges, they may also have many strengths, including:
Deficits In Social Communication
Children with autism may hyper-focus on their areas of particular interest, essentially ignoring the interests and concerns of others. In autism, this behavior is the result of deficits in social communication in essence, children with autism may be unaware that others have thoughts and feelings different from their own.
This could be another potential area of misdiagnoses, however, since the behavior itself can very much resemble some of the self-obsession that may be present in narcissistic personality disorder.
Also Check: Aspergers Hereditary From Mother Or Father
Social Communication / Interaction Behaviors May Include:
- Making little or inconsistent eye contact
- Tending not to look at or listen to people
- Rarely sharing enjoyment of objects or activities by pointing or showing things to others
- Failing to, or being slow to, respond to someone calling their name or to other verbal attempts to gain attention
- Having difficulties with the back and forth of conversation
- Often talking at length about a favorite subject without noticing that others are not interested or without giving others a chance to respond
- Having facial expressions, movements, and gestures that do not match what is being said
- Having an unusual tone of voice that may sound sing-song or flat and robot-like
- Having trouble understanding another persons point of view or being unable to predict or understand other peoples actions
Mental Illness Vs Developmental Disorder
Mental illnesses are health conditions that involve changes in mood, emotion, thinking, and behaving. They are associated with mental distress and problems with social functioning. Around one in five adults in the United States has some form of mental illness at any given time, according to the American Psychiatric Association.1 The most common mental illnesses are anxiety and depression. Mental illness can occur at any age and is treatable with medication, therapy, or a combination of medication and therapy.
One in Five Adults Have a Form of Mental Disorder
Developmental disorders like autism differ from mental illness in several important ways. Developmental disorders generally appear at birth or during childhood and are diagnosed by the age of 18. While mental illness doesnt typically interfere with cognitive abilities, a developmental disorder may impact a persons ability to learn or to understand certain thoughts. Unlike mental illness, which can be successfully treated, developmental disorders are lifelong disabilities.
Autism is 4 Times More Common in Boys Than Girls
Read Also: Autism Cognitive Development
What Help And Resources Are Available For People Who Need Support Or Further Advice
Get advice by seeing:
- A health visitor
- Any other health professional your child sees e.g. doctor or therapist
- Special Educational Needs staff at your childs school
For more information:
It is important to gain a better understanding of autism to provide the best support you or your loved ones need. They provide diagnosis, more information on treatments available and help you connect to the right support.
- Speacial Needs and Parents
Mental Health And Comorbidity In Asd

The research findings regarding any relationship between ASD severity and comorbidity remain ambiguous. Reinvall et al. reported that some studies have identified higher rates of comorbid depression and anxiety in those with higher functioning ASD, noting that this finding is often attributed to the fact that individuals who are higher functioning are more aware of their social differences than those with more severe ASD symptoms. However, the authors note that studies conducted via interview as opposed to questionnaire tend to show no difference in comorbidity among those with varying IQ or varying levels of ASD severity. Mannion et al. also note that people with more severe ASD, particularly those who have difficulty communicating, tend to receive diagnoses of comorbid psychopathology less often as differential diagnosis can be harder to assess. Even without communication barriers they note that differential diagnosis of comorbidity in ASD can be challenging as core symptoms of ASD such as rigidity, rumination and social withdrawal can also be symptoms of various mental health disorders including anxiety and depression .
Recommended Reading: Autism Symbol Meaning
Myth: People With Autism Don’t Want Friends
Truth: Surely, there are some people with autism who choose to stay away from other people, but the vast majority enjoy socializing and want to have friends. But some dont know how to interact with others, and they may make social mistakes that leave them feeling anxious about interacting with people in the future.