Restricted Behavior And Play
Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder are often restricted, rigid, and even obsessive in their behaviors, activities, and interests. Symptoms may include:
- Repetitive body movements moving constantly.
- Obsessive attachment to unusual objects .
- Preoccupation with a narrow topic of interest, sometimes involving numbers or symbols .
- A strong need for sameness, order, and routines . Gets upset by change in their routine or environment.
- Clumsiness, atypical posture, or odd ways of moving.
- Fascinated by spinning objects, moving pieces, or parts of toys .
- Hyper- or hypo-reactive to sensory input .
Distinction From Other Disabilities
, intellectual disability is a subtype of or , which is a broader concept and includes intellectual deficits that are too mild to properly qualify as intellectual disability, or too specific , or acquired later in life through or like . Cognitive deficits may appear at any age. is any disability that is due to problems with . This term encompasses many that have no mental or intellectual components, although it, too, is sometimes used as a euphemism for intellectual disability.
Autism Is Not An Illness
Being autistic does not mean you have an illness or disease. It means your brain works in a different way from other people.
It’s something you’re born with or first appears when you’re very young.
If you’re autistic, you’re autistic your whole life.
Autism is not a medical condition with treatments or a “cure”. But some people need support to help them with certain things.
Also Check: Autism Life Expectancy
How Does It Work Differently
The connections within a brain bring it to life. And its the brain cells or neurons that act as the messengers. When a brain cell is active, it creates an electrical impulse and that gets propagated to other cells in the brain. We think that electrical activity holds the basis of thought and behavior and how the brain functions, Dr. Anderson says.
Researchers indirectly measure these electrical impulses by looking at how synchronized regions of the brain are. When regions are working together, they tend to have brain activity at the same time. Functional connectivity is the measurement of how much two regions of the brain seem to be synchronized or talking together.
What Is The Difference Between Autism And Adhd
Autism and ADHD are sometimes confused with one another.
Children with an ADHD diagnosis consistently have issues with fidgeting, concentrating, and maintaining eye contact with others. These symptoms are also seen in some autistic people.
Despite some similarities, ADHD isnt considered a spectrum disorder. One major difference between the two is that people with ADHD dont tend to lack socio-communicative skills.
If you think your child may be hyperactive, talk with their doctor about possible ADHD testing. Getting a clear diagnosis is essential to ensure that your child is receiving the right treatment.
You May Like: What Is The Life Expectancy Of People With Autism
What Challenges Are Associated With Autism
Autism is often linked with physical, developmental or mental health conditions such as intellectual disability, epilepsy, gastro-intestinal issues, ADHD, dyspraxia, anxiety or depression.
However, many of the disabling challenges associated with autism come about when individuals dont have the respect, understanding and supports that allow them to be comfortable in a non-autistic world.
Diagnosis In Older Children And Adolescents
ASD symptoms in older children and adolescents who attend school are often first recognized by parents and teachers and then evaluated by the schools special education team. The schools team may perform an initial evaluation and then recommend these children visit their primary health care doctor or doctors who specialize in ASD for additional testing.
Parents may talk with these specialists about their childs social difficulties including problems with subtle communication. These subtle communication issues may include problems understanding tone of voice, facial expressions, or body language. Older children and adolescents may have trouble understanding figures of speech, humor, or sarcasm. Parents may also find that their child has trouble forming friendships with peers.
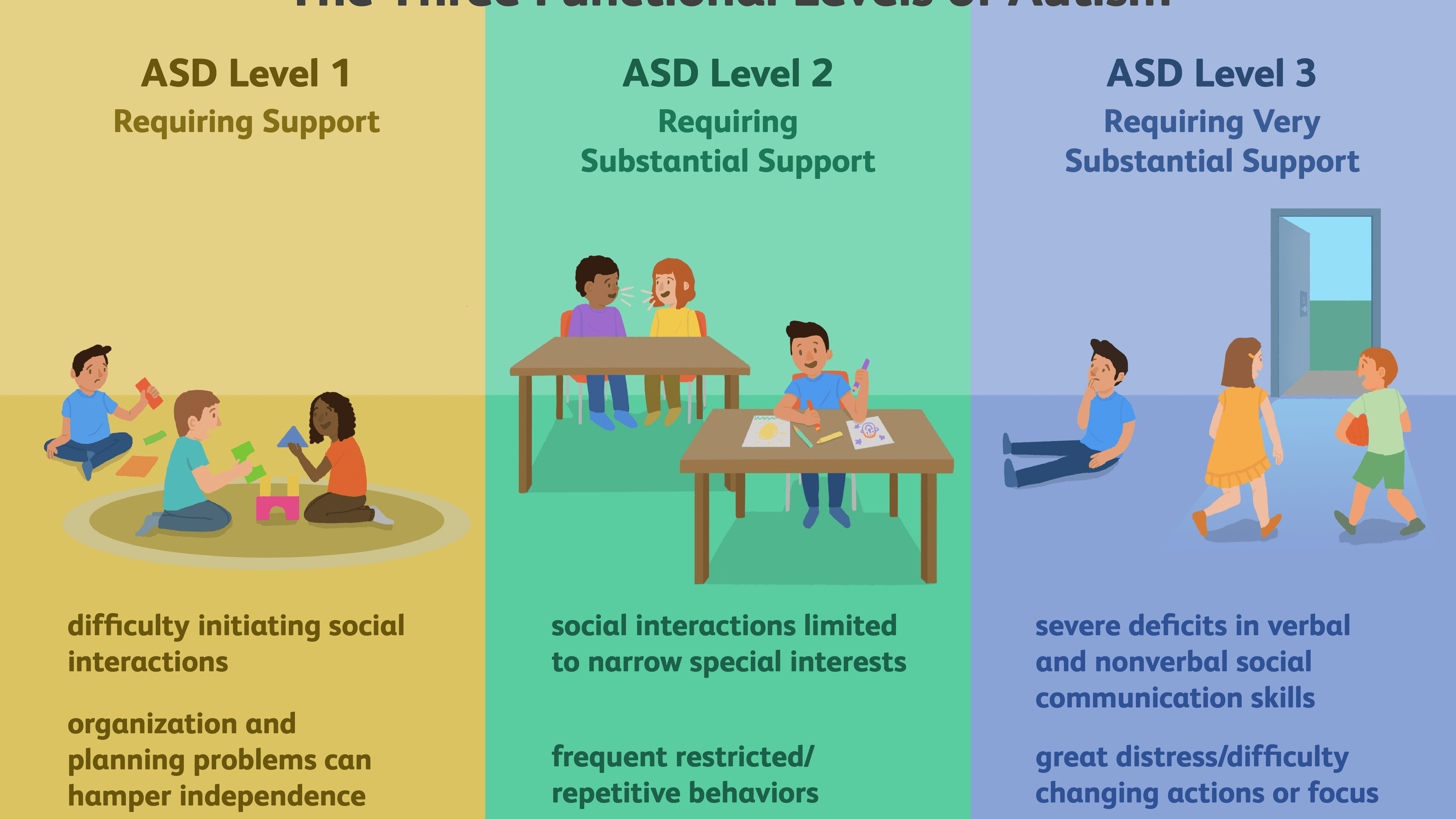
You May Like: Is Level 2 Autism High Functioning
Highly Focused Interests Or Hobbies
Many autistic people have intense and highly focused interests, often from a fairly young age. These can change over time or be lifelong. Autistic people can become experts in their special interests and often like to share their knowledge. A stereotypical example is trains but that is one of many. Greta Thunberg’s intense interest, for example, is protecting the environment.
Like all people, autistic people gain huge amounts of pleasure from pursuing their interests and see them as fundamental to their wellbeing and happiness.
Being highly focused helps many autistic people do well academically and in the workplace but they can also become so engrossed in particular topics or activities that they neglect other aspects of their lives.
Take a look at the Spectrum magazine, written for and by autistic people
Understanding Autism Spectrum Disorders
Autism is not a single disorder, but a spectrum of closely related disorders with a shared core of symptoms. Every individual on the autism spectrum has problems to some degree with social interaction, empathy, communication, and flexible behavior. But the level of disability and the combination of symptoms varies tremendously from person to person. In fact, two kids with the same diagnosis may look very different when it comes to their behaviors and abilities.
If youre a parent dealing with a child on the autism spectrum, you may hear many different terms including high-functioning autism, atypical autism, autism spectrum disorder, and pervasive developmental disorder. These terms can be confusing, not only because there are so many, but because doctors, therapists, and other parents may use them in dissimilar ways.
But no matter what doctors, teachers, and other specialists call the autism spectrum disorder, its your childs unique needs that are truly important. No diagnostic label can tell you exactly what challenges your child will have. Finding treatment that addresses your childs needs, rather than focusing on what to call the problem, is the most helpful thing you can do. You dont need a diagnosis to start getting help for your childs symptoms.
Whats in a name?
You May Like: Is Level 2 Autism High Functioning
What Is Executive Functioning
“If you think of your brain as an orchestra, executive functioning is the conductor, making sure all the parts are working together and working properly,” explained neuropsychologist Michael Rosenthal of the Child Mind Institute. Dr. Rosenthal is an author of a new study on executive function problems in teens with ASD and intelligence quotient scores of 70 or above.
People use executive skills when they make plans, keep track of time, remember past experiences and relate them to the present, change course if they hit a roadblock, ask for help, maintain self-control and work successfully in a group.11
Something as mundane as food shopping requires multiple executive skills, Dr. Rosenthal said.
“First you need ‘initiation’ skills to get yourself off the couch. The next step is to ‘plan and organize’ a list of the items you need to get. You need to think about how many meals you need to make and how much money you have in the bank. Let’s imagine the first thing on your list is pears, but when you go to the produce section, the pears are all bruised. You have to have the ‘cognitive flexibility’ to say, ‘Instead of pears, I will buy apples.’ You need ‘inhibition’ to keep from going to the candy aisle, and your ‘working memory’ will help you keep track of the items you’ve purchased,” he said.
What Is Pervasive Developmental Disorder Not Otherwise Specified
PDD-NOS is another outdated diagnostic term meaning autism that is more severe than Aspergers Syndrome, but less severe than Classic Autism. It is sometimes referred to as atypical autism because a child or adult diagnosed with PDD-NOS may not exhibit all the traits of classic autism.
For instance, someone who had been diagnosed with PDD-NOS might exhibit autistic traits socially, but may not exhibit other common signifiers like sensory issues or repetitive behaviors.
Read Also: Autism Visual Schedule
What Are The Different Types Of Autism
As psychiatrists, psychologists, and therapists seek to understand and categorize autism, their definitions change over time. Pre-2013, autism was defined in 5 categories: Pervasive Developmental Disorders : Autistic Disorder, Aspergers Disorder, Retts Disorder, Childhood Disintegrative Disorder and Pervasive Developmental Disorder Not Otherwise Specified .
Post 2013, for simplification, autism is now defined as Autism Spectrum Disorder and no longer categorizes individuals the same way.
Below will outline how autism is defined today, but will also include former categorization since these terms are still sometimes used.
Clinical Development And Diagnoses

Leo Kannerearly infantile autism
The word autism first took its modern sense in 1938 when Hans Asperger of the Vienna University Hospital adopted Bleuler’s terminology autistic psychopaths in a lecture in German about child psychology. Asperger was investigating an ASD now known as Asperger syndrome, though for various reasons it was not widely recognized as a separate diagnosis until 1981.Leo Kanner of the Johns Hopkins Hospital first used autism in its modern sense in English when he introduced the label early infantile autism in a 1943 report of 11 children with striking behavioral similarities. Almost all the characteristics described in Kanner’s first paper on the subject, notably “autistic aloneness” and “insistence on sameness”, are still regarded as typical of the autistic spectrum of disorders. It is not known whether Kanner derived the term independently of Asperger.
Kanner’s reuse of autism led to decades of confused terminology like infantile schizophrenia, and child psychiatry’s focus on maternal deprivation led to misconceptions of autism as an infant’s response to “refrigerator mothers“. Starting in the late 1960s autism was established as a separate syndrome.
You May Like: Can Autism Be Passed Down
Domain A: Social Communication And Social Interaction
Differences or challenges relating to language and social communication and social interaction across multiple contexts, both currently or historically. These include difficulty or differences in:
- Social-emotional communication and personal exchanges.
- Non-verbal communicative behaviours used for social interaction.
- Developing, maintaining and understanding relationships.
Forms Of Relation And Interaction
According to , forms of relation and interaction in sociology and may be described as follows: first and most basic are animal-like , i.e. various physical movements of the body. Then there are movements with a meaning and purpose. Then there are , or social actions, which address other people, which solicit a response from another agent.
Next are , a pair of social actions, which form the beginning of social interactions. Social interactions in turn form the basis of social relations. Symbols define social relationships. Without symbols, our social life would be no more sophisticated than that of animals. For example, without symbols people would have no aunts or uncles, employers or teachers-or even brothers and sisters. In sum, symbolic integrations analyze how social life depends on the ways people define themselves and others. They study , examining how people make sense out of life, how they determine their relationships.
Read Also: Can Autism Be Passed Down
So What Exactly Is Autism Anyway
by Steph Brontman |
As I was sitting at my kitchen table thinking about what to write, it occurred to me that not everyone really understands what autism is. I mean, to be totally honest, I didnt, or at least not fully, until I heard some friends talking about it. So, I figured since you have somehow found your way to my blog and are reading this post, you might want to know too.
One disclaimer before I get started, and its one of my favorite sayings, is if you met one person with autism, then youve met one person with autism. In other words, while myself and fellow autistics do have a lot of traits in common, we are all individuals and what is a struggle for one person with autism may be quite easy for someone else, just like neurotypicals .
Anyway, since my definition of autism is limited to my personal experience, I looked online to see what I could find as a formal definition, and this one from the CDC really resonated with me.
Autism spectrum disorder is a developmental disability that can cause significant social, communication and behavioral challenges. There is often nothing about how people with ASD look that sets them apart from other people, but people with ASD may communicate, interact, behave, and learn in ways that are different from most other people. The learning, thinking, and problem-solving abilities of people with ASD can range from gifted to severely challenged. Some people with ASD need a lot of help in their daily lives others need less.
Social Communication / Interaction Behaviors May Include:
- Making little or inconsistent eye contact
- Tending not to look at or listen to people
- Rarely sharing enjoyment of objects or activities by pointing or showing things to others
- Failing to, or being slow to, respond to someone calling their name or to other verbal attempts to gain attention
- Having difficulties with the back and forth of conversation
- Often talking at length about a favorite subject without noticing that others are not interested or without giving others a chance to respond
- Having facial expressions, movements, and gestures that do not match what is being said
- Having an unusual tone of voice that may sound sing-song or flat and robot-like
- Having trouble understanding another persons point of view or being unable to predict or understand other peoples actions
Read Also: Can Autism Be Passed Down
What Is The Prevalence Of Autism
The exact prevalence of autism in Australia and internationally is unknown.
The Australian Bureau of Statistics reports that there were 205,200 Australians with autism in 2018, which is around 1% of the population or 1 in 100.
Internationally this rate varies significantly, from 1 person in every 59 people in the USA, to the average prevalence across Asia, Europe, and North America is between one and two percent.
Statistics also show that:
- the number of Australians diagnosed with autism increased by 42% between 2012 and 2015
- three out of four people diagnosed with autism are young people, aged between 5 and 24 years and
- 1-2 out of 4 Australians diagnosed with autism are female.
While the reported prevalence of autism varies around the world, there has been a clear increase in the number of people diagnosed on the autism spectrum in recent years, but this doesnt necessarily suggest that there are more autistic people in the world than there were ten or twenty years ago.
Evidence suggests that the increase is the result of a number of cultural and clinical factors, including social influences driving greater awareness of autism, and improved diagnostic procedures and changes in diagnostic criteria allowing more people to access a diagnosis.
According to Professor Whitehouse, from Australias Autism CRC, research shows the majority of the increase in autism prevalence over this period was due to an increase in diagnosing children with less severe behaviours.
What Are The Major Symptoms Of Autism
Its important to point out that no two people who are on the spectrum exhibit autistic traits in exactly the same way. While there are often commonalities between ASD people, it would be in error to say that ALL autistic people have all the same symptoms or attributes. However, below is a list of symptoms that are often associated with ASD.
Read Also: What Is The Life Expectancy Of People With Autism
Grooming And Personal Hygiene
Some teens may need reminders to shower and shave. They may not understand the importance of grooming to social acceptance, or they may have less social motivation to smell and look clean. “They may be rejected because of poor personal hygiene but may not connect one to the other, or they may not have the skills to address the issue,” Dr. Keefer said.
Ms. Sicile-Kira recommends doing detective work to determine why your teen is shower-averse. Does he understand the importance and mechanics of good hygiene? Is the problem sensory? Suppose he hates the sensation of water pounding on his body from a shower head. If that’s the case, she said, “Give him a plastic cup to pour water on his head, so he has control over the flow of water.”
Even with good hygiene, adolescence can be a time of frustration or uncertainty for almost anyone. The social world with its cliques and pecking order becomes decidedly more complex during high school. Factor in dating, with its own set of unwritten rules, and students with ASD may feel adrift.
Problems with social and communication skills can leave them particularly vulnerable to bullying. IAN research shows that children with ASD are bullied at a much higher rate than their unaffected siblings, and that bullying spikes from fifth to eighth grades for them.13
What’s It Like To Have Autism Spectrum Disorder

A kid with autism might have trouble:
- talking and learning the meaning of words
- making friends or fitting in
- dealing with changes
- dealing with loud noises, bright lights, or crowds
Kids also might move in an unusual way or do the same thing over and over .
A kid with autism may have a little trouble with these things, or a lot. Some kids need only a little bit of help, and others might need a lot of help with learning and doing everyday stuff.
Don’t Miss: Do People Outgrow Autism
A Note Re Terminology
In New Zealand, the term used in diagnosis is Autism Spectrum Disorder .
This is the term used in the NZ Autism Spectrum Disorder Guideline and in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual for Mental Disorders Fifth Edition criteria which is the guide clinicians use when making a diagnosis.
Some autistic people prefer to use the term autism as they dislike the negative meaning implied by the word Disorder in Autism Spectrum Disorder.
Altogether Autism uses the term autism except when talking about diagnosis, where the term Autism Spectrum Disorder is used.
Other commonly used terms are Autism Spectrum, Autism Spectrum Condition, Aspergers Syndrome, Aspie, High Functioning Autism, Pervasive Developmental Disorder not otherwise specified .