Signs And Symptoms Of Autism Spectrum Disorders
Autism spectrum disorder is a developmental disability caused by differences in the brain. Some people with ASD have a known difference, such as a genetic condition. Other causes are not yet known. Scientists believe there are multiple causes of ASD that act together to change the most common ways people develop. We still have much to learn about these causes and how they impact people with ASD.
There is often nothing about how people with ASD look that sets them apart from other people. They may behave, communicate, interact, and learn in ways that are different from most other people. The abilities of people with ASD can vary significantly. For example, some people with ASD may have advanced conversation skills whereas others may be nonverbal. Some people with ASD need a lot of help in their daily lives others can work and live with little to no support.
ASD begins before the age of 3 years and can last throughout a persons life, although symptoms may improve over time. Some children show ASD symptoms within the first 12 months of life. In others, symptoms may not show up until 24 months or later. Some children with ASD gain new skills and meet developmental milestones, until around 18 to 24 months of age and then they stop gaining new skills, or they lose the skills they once had.
What Is Autism In Simple Terms
In this post, let me address a common question among parents What is autism in simple terms? When I try to explain to them that their child may be suspected of having autistic disorder, they are often confused on what Autism Spectrum Disorder actually is.
What this page contains
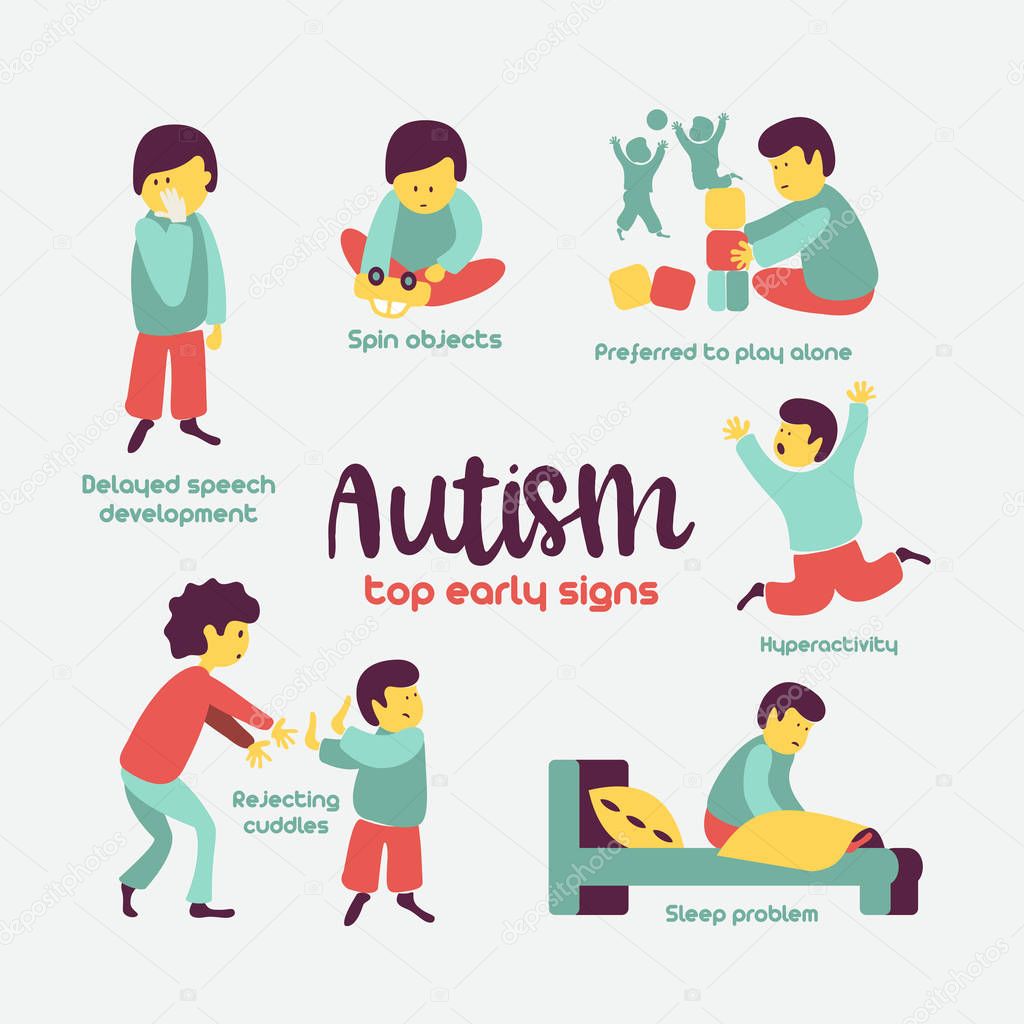
Fig 1
We are not specialists in health. We do not understand jargons like neurobehavioral impairments or spectrum disabilities. Can you please explain what is autism in simple terms? All, we want, is a simple explanation of Autism so that we understand what exactly is wrong with my child, comments Goerge Summers, Father of 3-year-old Sam, diagnosed with ASD
Find Resources That May Help Explain Autism
If you find yourself needing some guidance when talking to your child about autism, consider reaching for a book. There are many picture books that take on the topic in a way thats easy to understand for kids . Just make sure to pick a story that mirrors your childs experience for example, reading a book about a child on the spectrum who doesnt talk and does a lot of hand flapping may not hit home if the child with autism in your kids class is very verbal and social.
Related Article: Talking with Your Child About an Autism Diagnosis
When it comes to talking about autism with kids, parents should keep it simple, encourage discussion and focus on their familys values. Paula Butler, a Fishers mom of three, including an 8-year-old son with autism, sums it up nicely: I hope parents of neurotypical kids explain autism with grace so that when the children of today come across someone who is different from them, they treat them with kindness and the respect they deserve. I also hope kids take the opportunity to get to know someone with autism because our kids are amazing!
Don’t Miss: Schedule For Autism
How Common Is Autism Spectrum Disorder
Based on most recent CDC report, ASD is estimated to affect about 1 in 54 children, with boys being more likely to have ASD than girls. There were more than 5 million adults in the US, or 2.21% of the population, with ASD as of 2017. Government statistics suggest that the prevalence of ASD has risen 10% to 17% in recent years.
Autism Spectrum Disorder Diagnostic Criteria 29900
A. Persistent deficits in social communication and social interaction across multiple contexts, as manifested by all of the following, currently or by history :
1. Deficits in social-emotional reciprocity, ranging, for example, from abnormal social approach and failure of normal back-and-forth conversation to reduced sharing of interests, emotions, or affect to failure to initiate or respond to social interactions.
2. Deficits in nonverbal communicative behaviors used for social interaction, ranging, for example, from poorly integrated verbal and nonverbal communication to abnormalities in eye contact and body language or deficits in understanding and use of gestures to a total lack of facial expressions and nonverbal communication.
3. Deficits in developing, maintaining, and understanding relationships, ranging, for example, from difficulties adjusting behavior to suit various social contexts to difficulties in sharing imaginative play or in making friends to absence of interest in peers.
Specify current severity: Severity is based on social communication impairments and restricted, repetitive patterns of behavior .
B. Restricted, repetitive patterns of behavior, interests, or activities, as manifested by at least two of the following, currently or by history :
1. Stereotyped or repetitive motor movements, use of objects, or speech .
2. Insistence on sameness, inflexible adherence to routines, or ritualized patterns of verbal or nonverbal behavior .
Specify if:
Also Check: Stage 3 Autism
What Is The Difference Between Autism And Adhd
Autism and ADHD are sometimes confused with one another.
Children with an ADHD diagnosis consistently have issues with fidgeting, concentrating, and maintaining eye contact with others. These symptoms are also seen in some autistic people.
Despite some similarities, ADHD is not considered a spectrum disorder. One major difference between the two is that people with ADHD do not tend to lack socio-communicative skills.
If you think your child may be hyperactive, talk with their doctor about possible ADHD testing. Getting a clear diagnosis is essential to ensure that your child is receiving the right support.
How Is Autism Diagnosed
Doctors check babies and little kids for signs of autism at every checkup. A parent may think that something is wrong and tell the doctor. Maybe the child is old enough to speak but doesn’t. Or a kid doesn’t seem interested in people or plays in unusual ways.
When a doctor thinks a kid might have autism, he or she will work with a team of experts to see if it is autism or something else.
You May Like: Symmetra Comic Autism
How Is Asd Diagnosed
ASD symptoms can vary greatly from person to person depending on the severity of the disorder. Symptoms may even go unrecognized for young children who have mild ASD or less debilitating handicaps.
Autism spectrum disorder is diagnosed by clinicians based on symptoms, signs, and testing according to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders-V, a guide created by the American Psychiatric Association used to diagnose mental disorders. Children should be screened for developmental delays during periodic checkups and specifically for autism at 18- and 24-month well-child visits.
Very early indicators that require evaluation by an expert include:
- no babbling or pointing by age 1
- no single words by age 16 months or two-word phrases by age 2
- no response to name
- excessive lining up of toys or objects
- no smiling or social responsiveness
Later indicators include:
- impaired ability to make friends with peers
- impaired ability to initiate or sustain a conversation with others
- absence or impairment of imaginative and social play
- repetitive or unusual use of language
- abnormally intense or focused interest
- preoccupation with certain objects or subjects
- inflexible adherence to specific routines or rituals
My School And Neighborhood
Look around your school and neighborhood to see how many barriers need to be changed to help kids with autism to have the same opportunities to be friends and participate in activities just like kids without disabilities.
Don’t Miss: Schedule Boards For Autism
What Does Autism Look Like
This section describes autism spectrum disorder in greater detail. The term spectrum can be dened as a continuous sequence or range . As such, parents, caregivers, and educators will recognize the wide range of strengths and challenges children with ASD exhibit.
Social Communication Impairments may include the following:
Restricted, repetitive patterns of behavior, interests, or activities include:
Many parents, caregivers, and educators report that children with ASD exhibit behavioral challenges such as tantrum behavior, aggressive behavior, self-injurious behavior, property destruction, and noncompliance. Challenging behaviors should be addressed promptly at home and at school.
How Autism Spectrum Disorders Are Described
Psychiatrists and other clinicians rely on the fifth edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders to define autism and its symptoms. The DSM-5 definition recognizes two main symptom areas:
- Deficits in social communication and interaction
- Restricted, repetitive behaviors, interests, or activities
These symptoms appear early in a childs developmentalthough diagnosis may occur later. Autism is diagnosed when symptoms cause developmental challenges that are not better explained by other conditions.
The definition of autism has been refined over the years. Between 1995 and 2011, the DSM-IV grouped Aspergers Syndrome and Pervasive Developmental Disorder Not Otherwise Specified with autism. Aspergers syndrome was an autism spectrum disorder marked by strong verbal language skills and, often, high intellectual ability. PDD-NOS was a more general diagnosis for people who did not fit clearly into the other two categories.
However, the DSM-5 no longer recognizes Aspergers syndrome or PDD-NOS as separate diagnoses. Individuals who would previously have received either of these diagnoses may now receive a diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder instead.
Read Also: Autism Hypnosis
Screening By Age Group
Children Younger Than Age 18 Months
Earlier diagnosis of ASD may lead to earlier treatment. The M-CHAT is the most studied and widely used tool for screening toddlers for ASD. Additional tools are under investigation and are listed in as promising autism screening tests. Language delay can be identified by using the Infant and Toddler Checklist in low-risk infants and toddlers between 12 and 18 months of age., This questionnaire might be useful in identifying infant siblings of children with ASD who are at increased risk for ASD. Additional research may allow for screening of toddlers as young as 12 months by using parent-administered questionnaires such the Communication and Symbolic Behavior Scales Development Profile and the Infant and Toddler Checklist.
Primary care providers are tasked with identifying all children who would benefit from early intervention, not just children at risk for ASD . It is important to identify all clinically significant delays in children with referral for appropriate diagnostic evaluation and intervention. Problems with sleep, eating, constipation, and state regulation are common in the general population but may be particularly challenging in young children with ASD. Pediatricians can help families with management of these symptoms.
Children Ages 18 to 30 Months
Children Older Than 30 Months
Also Check: Life Expectancy For Autism
What Treatments Are Available

Treatments for ASD should target the childs challenges and draw on their strengths. This often requires coordination between a number of health professionals, therapists and educators. These interventions might include:
- behavioural interventions. Services vary across the country so available treatments will depend on which province youre in. Autism Speaks Canada has a list of funded programs broken down by province,
- speech-language therapy to improve verbal, non-verbal, and social communication skills,
- occupational therapy to address challenges in daily living and to help acquire play and self-care skills, and/or
- physiotherapy to help improve endurance, strength, balance and coordination.
When behavioural strategies have already been implemented and appropriate changes to a childs environment have been made, medications may be used in combination with other strategies to address behavioural symptoms and mental health disorders in children with ASD. Medications require careful monitoring with your childs physician.
Read Also: What Is The Life Expectancy Of People With Autism
What Are The 3 Main Symptoms Of Autism
Teach Kids About Autism
Our Kit for Kids program is designed to teach elementary and middle school students about their peers with autism. The kit is centered around an illustrated booklet entitled Whats Up with Nick?. This colorful, kid-friendly booklet tells the story about a new student, a boy with autism named Nick, through the eyes of a typical peer. The story teaches children that students with autism may think differently or need some accommodations, but all students are of equal worth and should be treated as such.
You can use this program to increase awareness of autism among students from grades K-8. With greater knowledge of autism, our youth will learn to see the person first rather than focus on a classmates disability. By increasing students acceptance of differences, the Kit for Kids creates a more inclusive classroom and overall sense of community.
Read Also: What Is The Life Expectancy Of People With Autism
Social Communication And Interaction Skills
Social communication and interaction skills can be challenging for people with ASD.
Examples of social communication and social interaction characteristics related to ASD can include:
- Avoids or does not keep eye contact
- Does not respond to name by 9 months of age
- Does not show facial expressions like happy, sad, angry, and surprised by 9 months of age
- Does not play simple interactive games like pat-a-cake by 12 months of age
- Uses few or no gestures by 12 months of age
- Does not share interests with others
- Does not point or look at what you point to by 18 months of age
- Does not notice when others are hurt or sad by 24 months of age
- Does not pretend in play
- Shows little interest in peers
- Has trouble understanding other peoples feelings or talking about own feelings at 36 months of age or older
- Does not play games with turn taking by 60 months of age
What Research Is Being Done
The mission of the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke is to seek fundamental knowledge about the brain and nervous system and to use that knowledge to reduce the burden of neurological disease. The NINDS is a component of the National Institutes of Health , the leading supporter of biomedical research in the world. NINDS and several other NIH Institutes and Centers support research on autism spectrum disorder.
Nearly 20 years ago the NIH formed the Autism Coordinating Committee to enhance the quality, pace, and coordination of efforts at the NIH to find a cure for autism. The NIH/ACC has been instrumental in promoting research to understand and advance ASD. The NIH/ACC also participates in the broader Federal Interagency Autism Coordinating Committee , composed of representatives from various U.S. Department of Health and Human Services agencies, the Department of Education, and other governmental organizations, as well as public members, including individuals with ASD and representatives of patient advocacy organizations. One responsibility of the IACC is to develop a strategic plan for ASD research, which guides research programs supported by NIH and other participating organizations.
Also Check: Mildly Autistic Adults
Making Friends Isnt Always Easy And Can Be Especially Challenging For Kids With Autism
An important part of making friends comes from having age-appropriate social skills, which many kids who have autism struggle with. Imagine trying to make friends when you have trouble reading social cues, like body language, facial expressions and tones of voice. Thats part of the reason approximately 52 percent of kids with autism spectrum disorder dont have many friends at school.
But kids who have autism, just like all kids, benefit from having friends in their peer groups. Dont worry, there are steps you can take to support your child in making a new friend.
1. Help your child understand what a friend is
This may seem basic, but you child needs to know what a friend is. She cant be a friend unless she can explain what one is. Keep things simple. Ask questions like, Do you like being around people who call you names? and Do you like being around people who say nice things to you? Understanding abstract concepts can be challenging for young kids, especially those with autism. Be literal when you can. Use clear, plain language like, friends are nice to you and say things that make you feel better when you have a bad day.
2. Visual models like social stories
Children with autism often learn better when they can see or read what theyre supposed to do. Social stories guide a child through a specific situation using pictures and words. Writing a script or drawing out the flow of a conversation can help your child understand the basics of how to talk to a friend.
What Is The Difference Between Autism And Autism Spectrum Disorder
The term autism was changed to autism spectrum disorder in 2013 by the American Psychiatric Association. ASD is now an umbrella term that covers the following conditions:
- Autistic disorder.
- Pervasive developmental disorder not otherwise specified .
- Asperger syndrome.
People with ASD have trouble with social interactions and with interpreting and using non-verbal and verbal communication in social contexts. Individuals with ASD may also have the following difficulties:
- Inflexible interests.
- Insistence on sameness in environment or routine.
- Repetitive motor and sensory behaviors, like flapping arms or rocking.
- Increased or decreased reactions to sensory stimuli.
How well someone with ASD can function in day-to-day life depends on the severity of their symptoms. Given that autism varies widely in severity and everyday impairment, the symptoms of some people arent always easily recognized.
You May Like: Is The Good Doctor Good Representation