Getting Evaluated For Autism Spectrum Disorder
Parent interview In the first phase of the diagnostic evaluation, you will give your doctor background information about your childs medical, developmental, and behavioral history. If you have been keeping a journal or taking notes on anything thats concerned you, share that information. The doctor will also want to know about your familys medical and mental health history.
Medical exam The medical evaluation includes a general physical, a neurological exam, lab tests, and genetic testing. Your child will undergo this full screening to determine the cause of their developmental problems and to identify any co-existing conditions.
Hearing test Since hearing problems can result in social and language delays, they need to be excluded before an Autism Spectrum Disorder can be diagnosed. Your child will undergo a formal audiological assessment where they are tested for any hearing impairments, as well as any other hearing issues or sound sensitivities that sometimes co-occur with autism.
Observation Developmental specialists will observe your child in a variety of settings to look for unusual behavior associated with the Autism Spectrum Disorder. They may watch your child playing or interacting with other people.
Lead screening Because lead poisoning can cause autistic-like symptoms, the National Center for Environmental Health recommends that all children with developmental delays be screened for lead poisoning.
Autism Treatment Network Research On Challenging Behavior
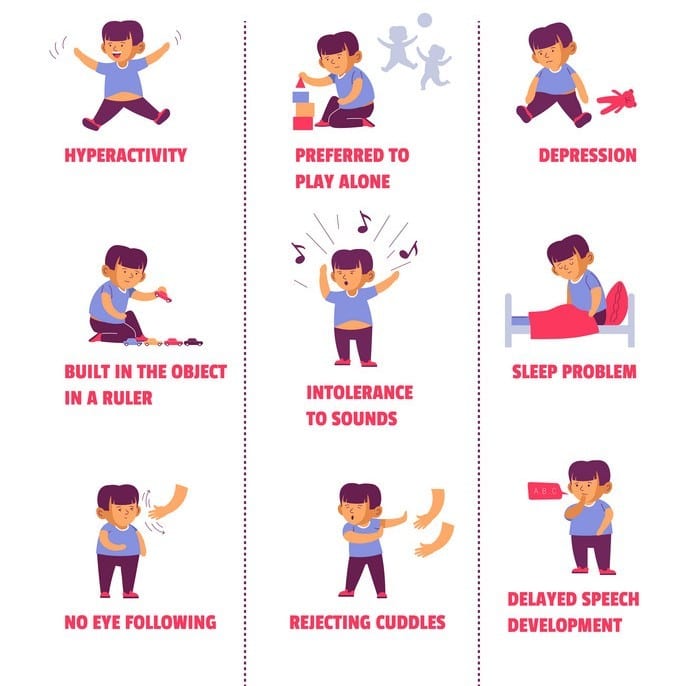
Researchers with the Autism Speaks Autism Treatment Network study challenging behavior in kids and teens with autism. Many children with autism have behavior problems. These can be hard on both the child and the family and caregivers. More than half of kids and teens with autism may be physically aggressive toward caregivers or other kids and grown-ups. This can include hitting, kicking and biting. Other behavior problems can include:
- being hyperactive, anxious and worried
- hurting themselves by banging or hitting their heads
- biting their hands and fingers
Behavior problems happen more often if the child has trouble sleeping. This is more likely if they wake up in the middle of the night. Younger kids are more likely to hurt other people. But older kids and teens are more likely to hurt themselves, especially if they have trouble talking.
For the full reference list and more Frequently Asked Questions addressed by ATN research on challenging behavior, visit asatn.org.
Why Was The New Edition Needed
The American Psychiatric Association periodically updates the DSM to reflect new understanding of mental health conditions and the best ways to identify them.
The goals for updating the criteria for diagnosing autism included:
- More accurate diagnosis
- Identification of symptoms that may warrant treatment or support services
- Assessment of severity level
Recommended Reading: Aspergers And Stuttering
Diagnosis In Young Children
Diagnosis in young children is often a two-stage process.
Stage 1: General Developmental Screening During Well-Child Checkups
Every child should receive well-child check-ups with a pediatrician or an early childhood health care provider. The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends that all children be screened for developmental delays at their 9-, 18-, and 24- or 30-month well-child visits and specifically for autism at their 18- and 24-month well-child visits. Additional screening might be needed if a child is at high risk for ASD or developmental problems. Those at high risk include children who have a family member with ASD, have some ASD behaviors, have older parents, have certain genetic conditions, or who were born at a very low birth weight.
Parents experiences and concerns are very important in the screening process for young children. Sometimes the doctor will ask parents questions about the childs behaviors and combine those answers with information from ASD screening tools, and with his or her observations of the child. Read more about screening instruments on the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website.
Children who show developmental problems during this screening process will be referred for a second stage of evaluation.
Stage 2: Additional Evaluation
This second evaluation is with a team of doctors and other health professionals who are experienced in diagnosing ASD.
This team may include:
The evaluation may assess:
- Blood tests
How Does The Dsm
Six major changes include:
1. Four previously separate categories of autism consolidated into one umbrella diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder.
Previous categories:
- Pervasive developmental disorder-not otherwise specified
2. Consolidation of three previous categories of autism symptoms into two categories of symptoms.
Previous categories:
- Persistent deficits in social communication/interaction and
- Restricted, repetitive patterns of behavior
3. The addition of sensory issues as a symptom under the restricted/repetitive behavior category. This includes hyper- or hypo-reactivity to stimuli or unusual interests in stimuli
4. A severity assessment scale based on level of support needed for daily function.
5. Additional assessment for:
- Any known genetic causes of autism
- Language level
- Intellectual disability and
- The presence of autism-associated medical conditions
6. Creation of a new diagnosis of social communication disorder for disabilities in social communication without repetitive, restricted behaviors.
You May Like: Dyslexia And Adhd Comorbidity
Terminology And Distinction From Schizophrenia
As late as the mid-1970s there was little evidence of a genetic role in autism while in 2007 it was believed to be one of the most heritable psychiatric conditions. Although the rise of parent organizations and the destigmatization of childhood ASD have affected how ASD is viewed, parents continue to feel social stigma in situations where their child’s autistic behavior is perceived negatively, and many primary care physicians and medical specialists express some beliefs consistent with outdated autism research.
It took until 1980 for the DSM-III to differentiate autism from childhood schizophrenia. In 1987, the DSM-III-R provided a checklist for diagnosing autism. In May 2013, the DSM-5 was released, updating the classification for pervasive developmental disorders. The grouping of disorders, including PDD-NOS, autism, Asperger syndrome, Rett syndrome, and CDD, has been removed and replaced with the general term of Autism Spectrum Disorders. The two categories that exist are impaired social communication and/or interaction, and restricted and/or repetitive behaviors.
The Internet has helped autistic individuals bypass nonverbal cues and emotional sharing that they find difficult to deal with, and has given them a way to form online communities and work remotely.Societal and cultural aspects of autism have developed: some in the community seek a cure, while others believe that autism is simply another way of being.
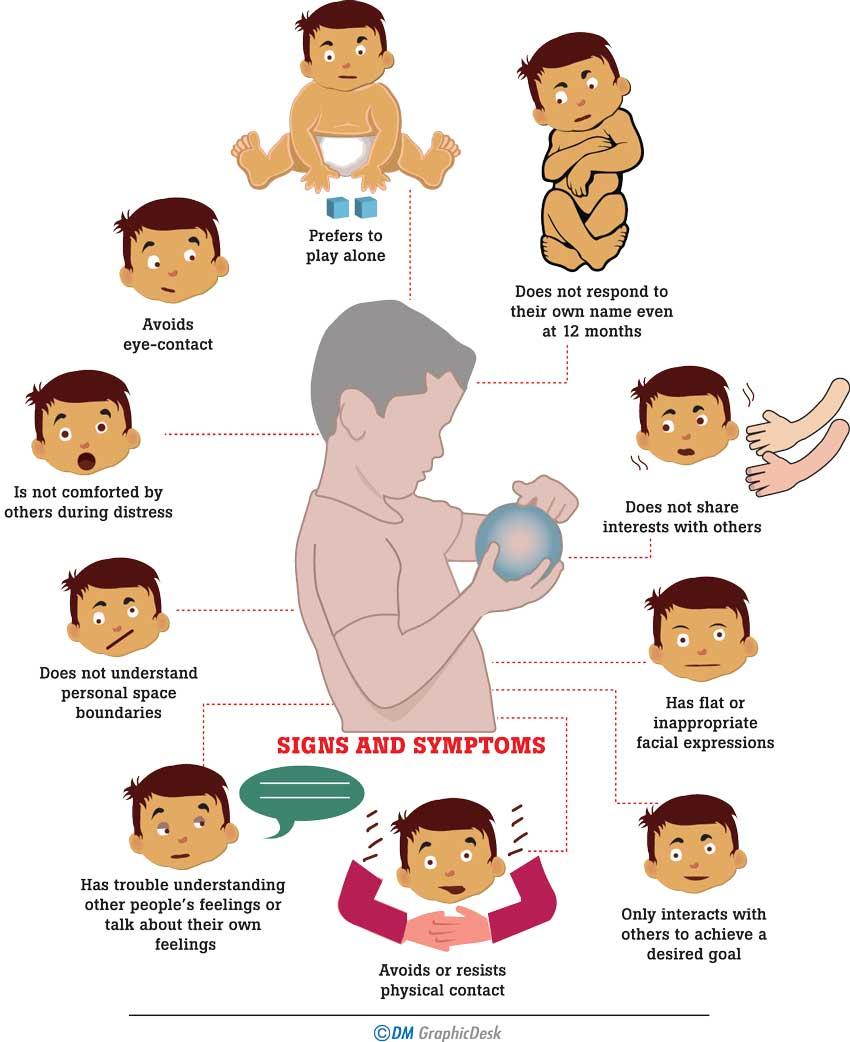
Restrictive / Repetitive Behaviors May Include:
- Repeating certain behaviors or having unusual behaviors. For example, repeating words or phrases, a behavior called echolalia
- Having a lasting intense interest in certain topics, such as numbers, details, or facts
- Having overly focused interests, such as with moving objects or parts of objects
- Getting upset by slight changes in a routine
- Being more or less sensitive than other people to sensory input, such as light, noise, clothing, or temperature
People with ASD may also experience sleep problems and irritability. Although people with ASD experience many challenges, they may also have many strengths, including:
- Being able to learn things in detail and remember information for long periods of time
- Being strong visual and auditory learners
- Excelling in math, science, music, or art
You May Like: What Does The Puzzle Piece Mean
A Landmark Autism Intervention Study Has Shown Dramatically Reduced Diagnosis Rates
We know that for autism, the causes and changes to the brain are happening long before birth. But in a groundbreaking new study, an intervention in infants showing early signs of autism has been able to reduce clinical diagnosis by two-thirds.
Autism spectrum disorder describes a wide-ranging set of conditions affecting a person’s social, communication, and motor skills. Diagnosis is based on criteria outlined in the American Psychiatric Association’s DSM-5 such as persistent deficits in social interactions and reciprocating emotions, an absence of interest in friends, repetitive movements or speech, and extreme or unusual reactions to stimuli.
“These findings are the first evidence that a pre-emptive intervention during infancy could lead to such a significant improvement in children’s social development that they then fell below the threshold for a clinical diagnosis of autism,” says one of the study authors, University of Manchester child psychiatry researcher Jonathan Green.
“Many therapies for autism have tried previously to replace developmental differences with more ‘typical’ behaviors. In contrast, iBASIS-VIPP works with each child’s unique differences and creates a social environment around the child that helps them learn in a way that was best for them.”
The researchers tracked 103 infants who had these early signs of ASD, aged as young as nine months all the way through to three years, in a randomized, blinded experiment.
Getting An Autism Spectrum Disorder Diagnosis
The road to an ASD diagnosis can be difficult and time-consuming. In fact, it is often two to three years after the first symptoms of ASD are noticed before an official diagnosis is made. This is due in large part to concerns about labeling or incorrectly diagnosing the child. However, an ASD diagnosis can also be delayed if the doctor doesnt take a parents concerns seriously or if the family isnt referred to health care professionals who specialize in developmental disorders.
If youre worried that your child has ASD, its important to seek out a clinical diagnosis. But dont wait for that diagnosis to get your child into treatment. Early intervention during the preschool years will improve your childs chances for overcoming their developmental delays. So look into treatment options and try not to worry if youre still waiting on a definitive diagnosis. Putting a potential label on your kids problem is far less important than treating the symptoms.
Read Also: Can A Child Outgrow Autism
The Baggage Of Recovery
But Dr. Fein avoids the word recovery to describe her lost-diagnosis group. “‘Recovery’ carries so much baggage,” Dr. Fein said in an interview. “When you say recovery, it conjures up a period of normal development, then they got a disease, and now they’ve recovered,” she said. Instead, this group reached an “optimal outcome,” or OO for short.
She’s not alone in shying away from the word recovery. In a different study, other autism researchers used the phrase “very positive outcome” to describe a group of teenagers who had shed their diagnosis and become full participants in the “social world.”10
Recovery is often associated with a groundbreaking 1987 research report by psychologist O. Ivar Lovaas. Dr. Lovaas said that nine of the 19 children who underwent his form of Applied Behavior Analysis therapy essentially “recovered” from autism. The children had received treatment during “most of their waking hours.” They had “normal intellectual and educational functioning,” and were “indistinguishable from their normal friends” by first grade, according to his research report.11 But he acknowledged that “certain residual deficits” could remain, perhaps faint whispers of autism hidden from parents and teachers.
Epidemiological Understanding Of Pdd
ASD is characterized by impairments in social interactions and communication, as well as repetitive behaviors and restricted interests . A number of social and environmental factors are known to be involved in ASD. For example, inappropriate child rearing by parents with psychiatric problems are suggested to be involved in ASD . Viral infection , environmental chemicals, and drugs are also known to be associated with ASD . In fact, inflammation via microglia, potentially induced by various environmental factors including infection, has been demonstrated in the postmortem brains and by neuroimaging in ASD patients .
Gokul Ramaswami, Daniel H. Geschwind, in, 2018
Also Check: Best Dog Breed For Autistic Child
Autism Therapy For Infants May Reduce Likelihood Of Later Diagnosis
An Australian team has developed the worlds first behavior therapy shown to reduce autism spectrum disorder-like behavior enough in infants to avoid, through improvement, a clinical ASD diagnosis.
The therapy reduced the likelihood of ASD-diagnoses at the three follow-up dates of 18, 24, and 36 months of age by two-thirds in 105 Australian children, and shows that early interventionwhen autism is only suspectedcan jumpstart the childs social skills and produce positive knock-on effects later in life.
The therapy is known as the VIPPP method, because thats how important our children are. In reality it stands for Video Interaction for Promoting Positive Parenting, and acts as a sort of translation app and play-by-play review, whereby following a period of interaction with a child displaying one of the four signs of early ASD, a doctor and parent can review footage of the interaction to help the them understand exactly how the child is trying to communicate.
Instances of avoiding eye-contact or not responding to their name can be signs a child might go on to develop ASD, and working around those barriers to help the child develop social skills when theyre so young was the key to the success of the trial.
MORE: Now Children With Autism or Sensory Issues Can Buy Vans Shoes Designed Exclusively For Them
RELATED: Inspired By Brother With Autism, New App Helps Adults With Special Needs Make Friends
- TAGS
Level : Requiring Substantial Support
People who meet the level 2 criteria need more support than those with level 1 autism. Social challenges can make holding a conversation very difficult.
Even with support, the person may find it hard to communicate coherently, and they are more likely to respond in ways that neurotypical people consider surprising or inappropriate.
The person may:
- only discuss very specific topics
- have difficulty understanding or using nonverbal communication, including facial expression
For example, they may face away from the person with whom they are communicating.
People with level 2 autism may also find daily functioning difficult due to the challenges of coping with change. Facing change might cause them to experience significant distress.
Recommended Reading: Life Expectancy Of Autism
Why Children Are Misdiagnosed
Autism is not always a child’s first diagnosis, particularly if he or she is verbal and of average intelligence. Not infrequently, children who wind up with an autism diagnosis receive a range of other diagnoses firstincluding, in some cases, other types of mental disorders.
There is a simple reason for these misdiagnoses: a child who is bright and verbal may not be evaluated for autism. As a result, the child’s symptoms are viewed not as a set of related challenges, but as individual issues that could potentially be signs of another mental illness. There are a number of behaviors in autism and other mental illnesses that may share characteristics and lead to an erroneous diagnosis.
Another Perspective Of Outcome Research
Outcome research can determine which therapies work and underscore the importance of early diagnosis and intervention. But some say it carries a downside. “Autism is a natural part of the human condition and not something to recover from or eliminate,” according to a statement by the Autistic Self Advocacy Network , a disability rights group run by autistic people.
“Words like recovery and optimal outcome do reinforce a really damaging idea, as the obvious corollary is a suboptimal outcome, which is a terrible thing to call a person,” explained Julia Bascom, deputy executive director of ASAN. “There’s this idea that being non-autistic, non-disabled is better than being autistic and being disabled, which isn’t true. We connect that mindset with a lack of research on what services and supports work best for autistic people across their lifespan, and on how to diagnose adults,” she said.
“People think that if you can cure autism, if it’s a sickness that people can recover from, then money would be better spent on research into how to prevent autism, rather than on supporting people across their lifespans,” said Ms. Bascom, who is autistic.
Ms. Bascom says ASAN hears from adults who may not meet criteria for a current autism diagnosis but who “have clinical depression, social skills issues, and sensory integration problems. That doesn’t sound like a recovery,” she said.
Image credits: Photo of Deborah Fein from Dr. Fein chart adapted from NeuroImage: Clinical12
Recommended Reading: Is James Holzhauer Autistic
Use Of Artificial Intelligence To Shorten The Behavioral Diagnosis Of Autism
-
* E-mail:
Affiliations Center for Biomedical Informatics, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts, United States of America, Department of Pathology, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, Massachusetts, United States of America
-
Affiliation Center for Biomedical Informatics, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts, United States of America
-
Affiliation Laboratories of Cognitive Neuroscience, Boston Childrens Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts, United States of America
-
Affiliation Center for Biomedical Informatics, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts, United States of America
-
Affiliation Center for Biomedical Informatics, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts, United States of America
Tell The Child Specifically What You Expect And Allow Him To Earn Privileges For Complying With Your Expectations
For instance, if your child often has a tantrum in a store when he cant go to the toy aisle, tell him exactly what you expect of him before you go to the store and reward him with a privilege for following that expectation. For instance, you can say something like We are going to Target. We are going to the school supply aisle to buy paper and pens, and then we will pay and go home. Once in the store you can give reminders .
Let the child know that he can earn a privilege for following the rules. Privilege ideas include getting a sticker of a favorite character, playing a favorite game once at home, watching a favorite show, going on the computer, staying up ten minutes past bed time, etc. Try to think of a privilege that your child might like or ask him what he would like to work towards.
When the child earns the privilege, praise him with specific language. In the example above you could say, You followed the rules at the Target. We got the paper and pens, paid, and came home. Nice work! Now you can enjoy some computer time. Make sure the privilege is something the child wants. You can let the child choose what he would like to work for ahead of time. Children also benefit from nonverbal praise such as high fives, smiles, thumbs up, etc.
Don’t Miss: Are Stuttering And Autism Related