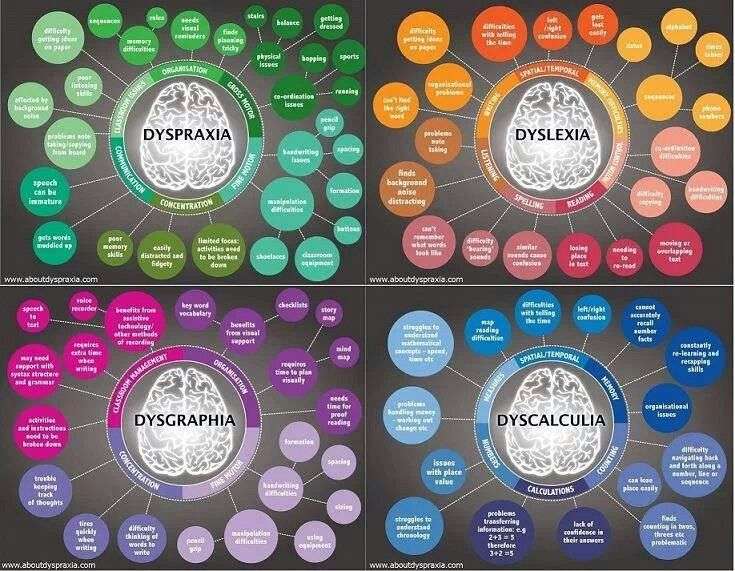
Why Does Dysgraphia Occur
Dysgraphia is basically a simple disconnect in the communication channels between the brain and the hands. However, in a system as complex as brain-body communication, there are lots of different points in the channel where these errors may be found. The specific place where the disconnect occurs, therefore, is not the same among all people with dysgraphia, and all cases of dysgraphia are not caused by the same factor. Some cases of dysgraphia are caused by muscle weakness or motor deficiencies, while others may be due to brain damage or other neurological issues.
Can Dysgraphia Appear Suddenly
Agraphia, or the sudden loss of writing ability, shares many symptoms with dysgraphia, such as the inability to properly form letters or correctly space out words. Agraphia is usually caused by a serious brain injury, stroke, or degenerative brain disease like dementia. Rehabilitation strategies may allow affected individuals to regain some of their lost writing ability. Agraphia often appears with other related disorders such as alexia .
Why Is A Dysgraphia Diagnosis Critical
Even in the digital age, handwriting is an important skill necessary for success in the classroom and beyond. With dysgraphia, the mechanics of writing and other foundational writing skills are difficult, making a student more likely to fall behind peers without the learning disorder. Writing problems are also associated with persistent academic struggles and low self-perception, which can persist to adulthood.4
Whats more, the act of writing often helps the brain remember, organize, and process information. When the physical act of writing is incredibly challenging, a child cant effectively show what they knows. A student with dysgraphia may fail an exam simply because they cant translate his thoughts and answers to paper.
Don’t Miss: What Disability Does The Good Doctor Have
Orthographic Dyslexia: Its Not Just About Phonology
by Sarah C. Wayland, Ph.D. | Mar 5, 2019 | Special Needs Care Navigation, Therapy |
I recently had a conversation with my colleague, Donna Henderson, Psy.D., about a form of dyslexia that she has noticed in some of her clients with autism. My curiosity was piqued because I had noted similar patterns of spelling errors in a number of my clients, but couldnt find a description of the phenomenon in books and articles describing more common forms of developmental dyslexia. When I asked Dr. Henderson for details, she sent the following essay, which she has graciously agreed to allow me to post. Sarah Wayland
Poor awareness of the sounds of language or a lack of understanding of the spelling-sound correspondence is the cause of the most common type of dyslexia. People with this type of dyslexia will make spelling errors that do not make phonetic sense . In contrast, I have noticed that some of the children I work with have an unusual pattern of spelling errors. These kids seem to understand which letters go with which sounds, but they actually over-rely on the letter-sound correlation. For example, they might spell the word garbage as garbij or the word wiggle as wigul.
To understand these different types of errors, its important to first understand how children learn to read as well as what typical dyslexia looks like. It all starts with the phoneme.
Beginning readers and writers must use the phonological form of the word to determine how say or spell it.
How Can I Help My Child

Here are some things you can try:
- Have your child use wide-ruled paper, graph paper, or paper with raised lines to help with letter and word alignment.
- Try pencil grips or other writing aids for comfort.
- Let them use a computer to type instead of write, and teach typing skills early.
- Don’t criticize sloppy work. Praise their hard work and offer positive reinforcement.
- Acknowledge the condition and talk to your child about it.
- Teach them ways to relieve stress before writing. For example, have them shake or rub their hands together quickly.
- Let them squeeze a stress ball to improve hand-muscle strength and coordination.
Talk to your child’s teacher about their condition and needs at school. They may qualify for special education services and an Individualized Education Program or other special assistance . These documents detail your child’s needs and give the school ways to help them.
Some things you might ask for include:
- Shorter writing assignments or different questions from their classmates
- Use of a computer to type instead of write
- Copies of the class notes to limit writing work
- Use of a voice-to-dictation machine or another electronic note taker
- An option to record the teacher’s lectures
- Video or audio reports instead of written homework assignments
- Oral instead of written exams
Don’t Miss: Nick Eh 30 Social Blade
Dysgraphia In Children: Most Common Questions Answered
What are the signs of dysgraphia?
- Poor Grammarâ children with dysgraphia often have difficulty producing sentences that are grammatically correct. Punctuation can be missed and spelling can be poor.
- Poor handwriting Handwriting is often disorganised and children find it hard to spell and write in a straight line as well as space out text. Some children with dysgraphia struggle to know directional differences, such as left/right and over/under.
- Ambidexterityâ Many children with dysgraphia are ambidextrous .
- Frustration from handwriting children with dysgraphia often feel frustrated when asked to write and complain of it causing them to have a sore hand. Some children with dysgraphia also have dyspraxia which can affect motor skills. This in turn can affect their ability to write and make writing uncomfortable.
- Avoidance of school work and low self-esteem children can often try to avoid schoolwork if they have dysgraphia as they are worried about their poor handwriting. It can lead to them feeling embarrassed and having low self-esteem.
- Saying words out loud while writing can be a coping mechanism for a child with dysgraphia.
Is dysgraphia a form of autism?
Dysgraphia is not a form of autism, however it is a co-morbid condition that typically presents in people with autism. It can also present in people who do not have autism.
Is dysgraphia inherited?
What age can you get dysgraphia?
Is dysgraphia a disability?
What Are The Symptoms Of Autism Spectrum Disorder
ASD is a neurodevelopmental disorder that affects how people process certain types of information. The main symptoms are:
- difficulty with social interactions
- engaging in repetitive or ritualistic behaviors
- obsessions with certain topics of interest
Individuals with ASD may share some symptoms in common, such as difficulty in social interactions and repetitive behaviors. But because it is a spectrum disorder, these symptoms can range from mild to severe. Everyone experiences ASD differently. Some children with autism have speech or intellectual delays some do not. Some may have average or above-average IQs. Some may be high-functioning and others may have a severe disability.
Read Also: Life Expectancy Of People With Autism
Why Is Diagnosis Of Dysgraphia And Related Learning Disabilities Important
Without diagnosis, children may not receive early intervention or specialized instruction in all the relevant skills that are interfering with their learning of written language. Considering that many schools do not have systematic instructional programs in handwriting and spelling, it is important to assess whether children need explicit, systematic instruction in handwriting and spelling in addition to word reading and decoding. Many schools offer accommodations in testing and teaching to students with dysgraphia, but these students also need ongoing, explicit instruction in handwriting, spelling, and composition. It is also important to determine if a child with dysgraphia may also have dyslexia and require special help with reading or oral and written language learning disability and need special help with oral as well as written language.
What Tests Are Used To Diagnose Dysgraphia
Among the tests often included in an evaluation for dysgraphia are:
- An IQ test.
- Academic assessment that includes reading, arithmetic, writing, and language tests.
- Measures of fine motor skills related to writing.
- Writing samples evaluated for spelling, grammar, and punctuation as well as the quality of ideas presented.
how is dysgraphia diagnosed?
A licensed psychologist trained in learning disorders can diagnose dysgraphia. This could be your childs school psychologist. The specialist will give your child academic and writing tests that measure his ability to put thoughts into words and his fine motor skills. Writing process.
what age can dysgraphia be diagnosed?six yearsnine years
Contents
Recommended Reading: How To Make A Visual Schedule For Autism
Also Check: Did Forrest Gump Have Autism
What They Have In Common
Both dyspraxia and autism can lead to kids feeling awkward in social situations. At school these students may be treated differently by their peers and can become the target of bullying and ridicule. Some dyspraxic and autistic people have distinct speech patterns. When this occurs in dyspraxia it is referred to as apraxia of speech. They can have difficulty controlling the volume and pitch of their speech and using complex and long strings of language. Some people are hypersensitive to temperatures, light and noise and many prefer to stick to a familiar routine to help them complete day-to-day tasks. Attention issues can also be a problem and theres the possibility of co-occurrence with other learning difficulties, such as dyslexia.
dysgraphiadiagnosis
. Similarly, it is asked, who can diagnose dysgraphia?
A. Dysgraphia is typically diagnosed by a professional, such as a physician or licensed psychologist, who specializes in the as-sessment and diagnosis of learning disabilities. Other professionals, such as an occupational therapist, school psychologist, or special educator, may also be involved.
Furthermore, what are the symptoms of dysgraphia? Symptoms
- Cramped grip, which may lead to a sore hand.
- Difficulty spacing things out on paper or within margins
- Frequent erasing.
- Inconsistency in letter and word spacing.
- Poor spelling, including unfinished words or missing words or letters.
- Unusual wrist, body, or paper position while writing.
Is dysgraphia a disability?
Dysgraphia And The Us Public School System
Dysgraphia is often very misunderstood in public schools across the US as to the potential severity of its educational impact. Even when Dysgraphia has been diagnosed by an appropriate professional such as Neuropsychologist or Neurologist, the area of handwriting problems and their effective solutions are often not appropriately addressed for special needs kids in both inclusive and self-contained classrooms. It is often thought that continued handwriting practice will improve a Dysgraphic students ability to use paper and pencil alone as a useful tool to complete all their written schoolwork. This is rarely the case.
While Occupational Therapy and Vision Therapy can sometimes help to improve a Dysgraphic students letter and number formation in isolation and/or in short writing samples, this improvement is not always able to be sustained when kids are actually using their handwriting to complete their written schoolwork. The same thing is true of making kids re-do written assignments to make them more legible. In cases of Dysgraphia, practice does not make perfect.
Recommended Reading: Aspergers Life Span
A Closer Look Into Dysgraphia In Relation To Autism
This conditionare often seen in people who have autism.recent studywas publisheddysgraphia amongst 1,034 students of all ages with ADHD or autismThe results indicated that 59% had this conditionitis common at all ages in children and adolescents with ADHD and autism affecting handwriting.the process of writing much slowerand affects the movement of musclesusually detected around the time a child learns how to writestruggle with other fine motor skillsbuttoning, tying, using scissorssymptoms includetrouble with letter spacingorganizing wordswrites lettershard time writing on a linetrouble holding a pencil correctlyunable to use scissors wellissues with spellingavoids writing altogether types of dysgraphiadyslexic, motor and spatialwritinghandwritingTesting for this condition can help determine the cause of your childâs difficultieswriting If a child is diagnosed with this condition, the next step is to meet with the school to request additional services and supportworking with occupational therapistswritingTechnology may also be helpful such as keyboarding, word processing and/or speech recognition software.
Can Dyspraxia Cause Speech Problems
Dyspraxia can be so mild that a person has trouble with very few speech sounds or only has occasional problems pronouncing words with many syllables. In the most severe cases, a person may not be able to communicate effectively with speech, and may need the help of alternative or additional communication methods.
Also Check: Mild Asd Symptoms
Constructs Antibodies And Reagents
Plasmids of human Dock4 cDNA and its mutants, Dock4 945VS , SH3 , C , SH3-F , Dock shRNA, and ELMO2 were described previously . cDNA of Dock4 R853H was generated by mutagenesis using the following primers, CATGTGTGCACATATCCTTAGCAACGTATT and TGCTAAGGATATGTGCACACATGATCAGGT . cDNA of Dock4 AAA mutant, which is deficient of GEF activity, was constructed by mutagenesis. All cDNAs with a C-terminal Flag tag were subcloned into the pCAGIG vector, which contains a GFP coding sequence separated by an internal ribosome entry site .
The following primary antibodies were used: Dock4, ELMO2 and GAPDH were purchased from Abcam -tubulin and -tubulin III were from Sigma Tau1 and Rap1 were from Millipore Rac1 was from BD Biosciences Flag was from Sigma. Retinoic acid was purchased from Sigma, and Rhodamine-phalloidin was from Invitrogen.
Read Also: Camels Milk Autism
What If I Think My Child Has Dysgraphia
Dysgraphia is no longer an official diagnosis. Instead there is a diagnosis of Specific learning disorder with impairment in written expression which refers to a person experiencing trouble expressing their thoughts in writing rather than the transcription challenges experienced by someone with dysgraphia.
If you think your child may have dysgraphia, there are certain tests for writing and fine motor skills which may help to clarify the situation, even if no formal diagnosis can be given. Occupational therapists and physical therapists can help with testing motor skills.
It is possible that your child does not have dysgraphia, but a different condition. For example, trouble with handwriting could actually be caused by dysgraphia and trouble with spelling could be caused by dyslexia.
You May Like: Is Nonny From Bubble Guppies Autistic
Does Dysgraphia Occur Alone Or With Other Specific Learning Disabilities
Children with impaired handwriting may also have attention-deficit disorder inattentive, hyperactive, or combined inattentive and hyperactive subtypes. Children with this kind of dysgraphia may respond to a combination of explicit handwriting instruction plus stimulant medication, but appropriate diagnosis of ADHD by a qualified professional and monitoring of response to both instruction and medication are needed.
Dysgraphia may occur alone or with dyslexia or with oral and written language learning disability .
Dyslexia is a disorder that includes poor word reading, word decoding, oral reading fluency, and spelling. Children with dyslexia may have impaired orthographic and phonological coding, rapid automatic naming and focused, switching, and/or sustained attention.
Oral and written language learning disability is impaired language . These disorders affect spoken as well as written language. Children with these language disorders may also exhibit the same writing and reading and related disorders as children with dysgraphia or dyslexia.
What Is Dysgraphia The Handwriting Disorder Explained
Dr. William Chen | December 15, 2020
Do you have difficulty writing legibly or remembering how to spell common words, no matter how much you practice? You arent alone: Frequently struggling to form letters by hand or express your ideas in writing may mean youre one of the 4% of adults who have dysgraphia. This little-known learning disability can affect multiple aspects of written coherence, even in individuals with above-average intelligence. Fortunately, supportive technology and treatments can help people with this condition overcome writing-related challenges and reach their full potential in the workplace.
Also Check: Autism Puzzle Colors
About Dr Arielle Schwartz
Meet Dr. Arielle Schwartz
As a psychologist and mother of two, my passion is to teach parents how to integrate the tools of play therapy into your home and through clinical supervision, teach other clinicians how to support families with highly sensitive children. I understand the unique challenges parents can face in raising sensitive children and specialize in working with children with sensory processing disorders, speech/language delays, anxiety, challenging behaviors, trauma exposure, and emotional problems.
Dr. Arielle Schwartz is a licensed clinical psychologist, wife, and mother in Boulder, CO. She offers trainings for therapists, maintains a private practice, and has passions for the outdoors, yoga, and writing. Dr. Schwartz is the author of The Complex PTSD Workbook: A Mind-Body Approach to Regaining Emotional Control and Becoming Whole. She is the developer of Resilience-Informed Therapy which applies research on trauma recovery to form a strength-based, trauma treatment model that includes Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing , somatic psychology and time-tested relational psychotherapy. Like , and sign up for email updates to stay up to date with all her posts.
You May Like: Is Freddie Highmore Actually Autistic
Is Dysgraphia A Form Of Autism
In childhood, the disorder generally emerges when children are first introduced to writing. Dysgraphia can occur after neurological trauma or it might be diagnosed in a person with physical impairments, Tourette Syndrome, ADHD, Learning Disabilities, or an Autism Spectrum Disorder such as Aspergers Syndrome.
Don’t Miss: Is The Good Doctor Actor Autistic
Types Of Dysgraphia Symptoms And How To Help
Do you work with children who have trouble with the ability to write, regardless of their ability to read?
Perhaps you have students without cognitive impairment, who continue to struggle with written expression.
If you work with students who have ADHD or Autism Spectrum Disorder, you may encounter difficulties with written expression as well considering that a recent study indicated that 59% had dysgraphia, and 92% had a weakness in graphomotor ability relative to other abilities .
Sue Ramin-Hutchison and Merri Domer , have compiled helpful information on the types of dysgraphia, symptoms and how to help.
What Are The General Symptoms Of Dysgraphia
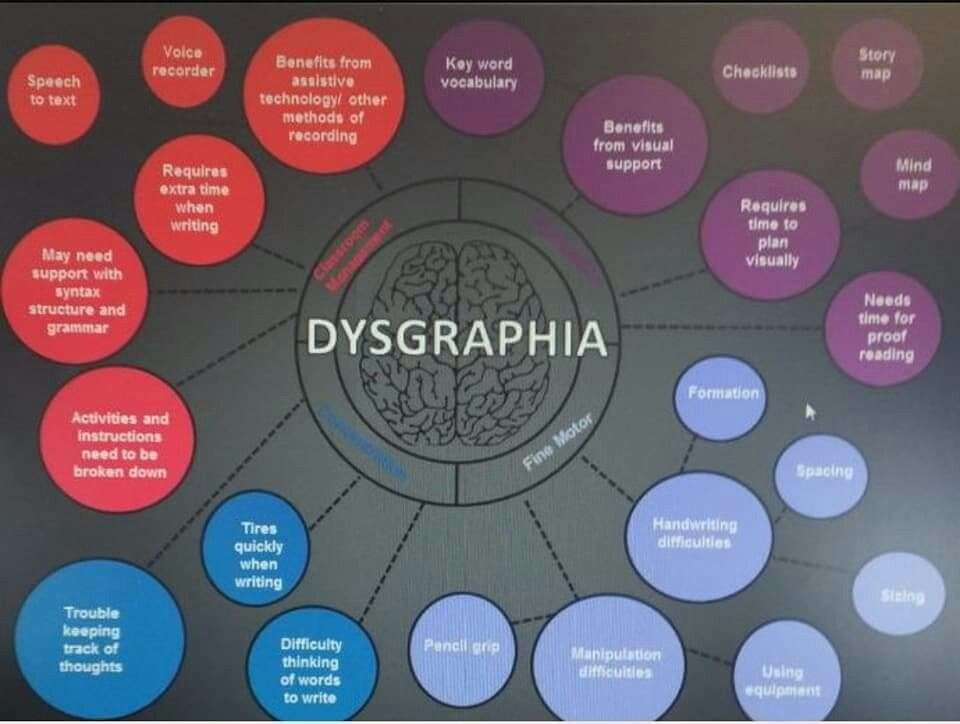
- A mixture of upper case/lower case letters
- Irregular letter sizes and shapes
- Unfinished letters
- Talks to self while writing
- General illegibility
- Reluctance or refusal to complete writing tasks
- Crying and stress .
- Experiencing physical pain in the hand and/or arm when writing
- Poor use of lines and spaces
Don’t Miss: Do People With Autism Die Early